压测利器Webbench(附源码)
程序员行者孙 2024-06-14 08:33:03 阅读 79
web压力测试工具webbench介绍
webbench最多可以模拟3万个并发连接去测试网站的负载能力,并发能力比较高,可以测试https及动态静态页面。
核心原理
父进程fork若干个子进程,每个子进程在用户要求时间或默认的时间内对目标web循环发出实际访问请求,父子进程通过管道进行通信,子进程通过管道写端向父进程传递在若干次请求访问完毕后记录到的总信息,父进程通过管道读端读取子进程发来的相关信息,子进程在时间到后结束,父进程在所有子进程退出后统计并给用户显示最后的测试结果,然后退出。
编译安装
1.wget https://www.ha97.com/code/webbench-1.5.tar.gz2.tar zxvf webbench-1.5.tar.gz3.cd webbench-1.54.make5.make install
使用
1.webbench -c 1000 -t 30 baidu.com
参数说明:-c表示并发数,-t表示时间(s)
webbench [option]... URL -f|--force Don't wait for reply from server. -r|--reload Send reload request - Pragma: no-cache. -t|--time <sec> Run benchmark for <sec> seconds. Default 30. -p|--proxy <server:port> Use proxy server for request. -c|--clients <n> Run <n> HTTP clients at once. Default one. -9|--http09 Use HTTP/0.9 style requests. -1|--http10 Use HTTP/1.0 protocol. -2|--http11 Use HTTP/1.1 protocol. --get Use GET request method. --head Use HEAD request method. --options Use OPTIONS request method. --trace Use TRACE request method. -?|-h|--help This information. -V|--version Display program version.
主要原理图
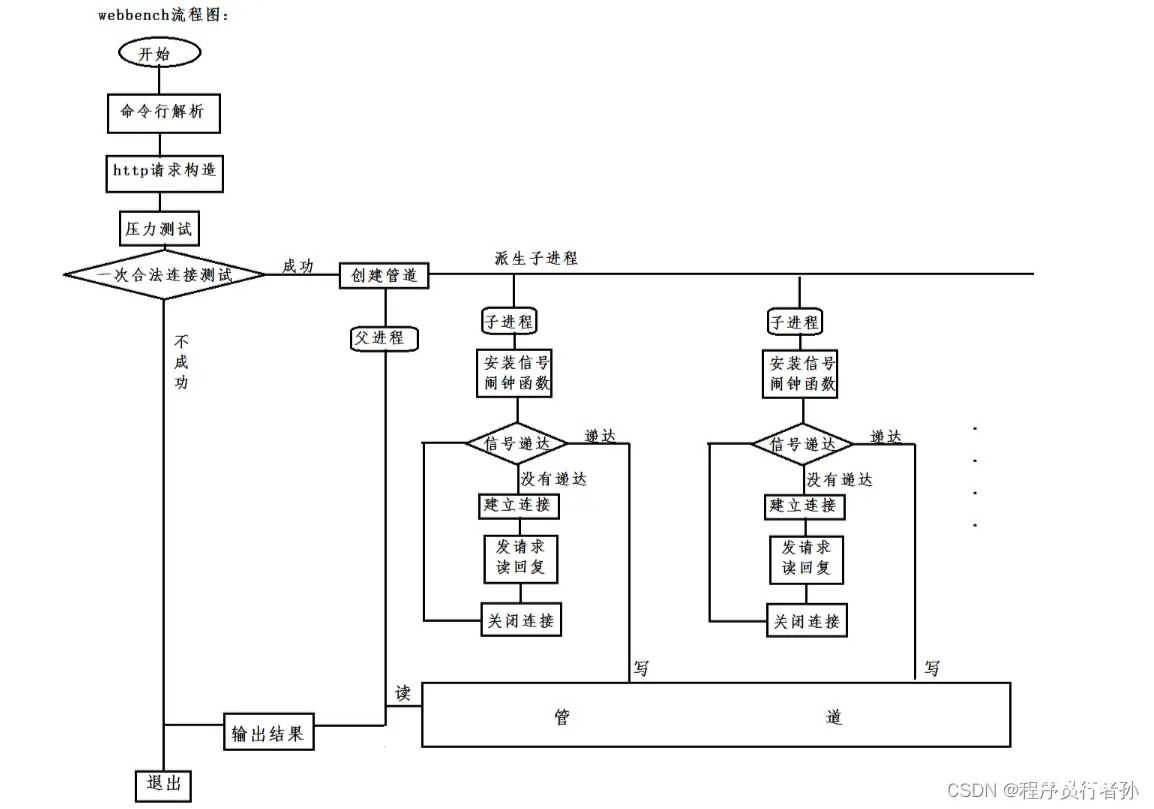
webbench 的主要压测流程:
1.解析参数:用户通过命令行参数指定目标网址、并发连接数、测试时长等参数。webbench 首先会解析这些参数,确定压测的目标和条件。
2.创建并发连接:webbench 根据用户指定的并发连接数,在测试开始时创建相应数量的并发连接。这些连接将模拟多个客户端同时访问目标网站。
3.建立连接:对于每个并发连接,webbench 发起一个 HTTP 请求并尝试与目标服务器建立连接。这些连接可能是非阻塞的,允许同时处理多个连接。
4.发送请求:一旦连接建立成功,webbench 就会向目标服务器发送 HTTP 请求。这些请求可以是简单的 GET 请求,也可以包含其他 HTTP 方法和自定义的请求头信息。
5.接收响应:webbench 在发送请求后会等待目标服务器的响应。它可以根据用户指定的超时时间来确定是否需要等待响应,或者在超时后放弃等待并关闭连接。
6.记录结果:在测试过程中,webbench 会记录每个请求的响应时间、状态码等信息。这些信息将用于后续的性能分析和结果报告。
7.重复测试:根据用户指定的测试时长,webbench 会在一定时间内不断重复发送请求和接收响应,以模拟持续的并发访问情况。
8.汇总结果:在测试结束后,webbench 会汇总所有请求的结果,并计算出一些统计信息,如平均响应时间、成功率等。这些信息将作为压测结果向用户展示。
9.生成报告:最后,webbench 会根据测试结果生成一份报告,包括压测的详细信息、性能指标和可能的改进建议。用户可以根据这份报告来评估服务器的性能表现和优化方向。
源码:
webbench.c
#include "socket.c" #include <unistd.h> #include <sys/param.h> #include <rpc/types.h> #include <getopt.h> #include <strings.h> #include <time.h> #include <signal.h> //统计的压力测试最终结果表示volatile int timerexpired = 0; int speed = 0; int failed = 0; int bytes = 0;//http请求方法#define METHOD_GET 0 #define METHOD_HEAD 1 #define METHOD_OPTIONS 2 #define METHOD_TRACE 3 #define PROGRAM_VERSION "1.5" // 默认设置:一般需用户自己传入命令行参数设置 int method = METHOD_GET; //默认请求方法为GET方式 int clients = 1; //默认只模拟一个客户端 int force = 0; //默认需要等待服务器响应int force_reload = 0; //失败时重新请求 int proxyport = 80; //默认访问服务器端口为80 char *proxyhost = NULL; //默认无代理服务器 int benchtime = 30; //默认模拟请求时间为30s // globals 版本号 int http10 = 1; //0:- http/0.9, 1:- http/1.0, 2:- http/1.1 int mypipe[2]; //管道用于父子进程通信char host[MAXHOSTNAMELEN]; //存储服务器网络地址 #define REQUEST_SIZE 2048 char request[REQUEST_SIZE]; //存放http请求报文信息数组//函数声明 static void benchcore(const char* host,const int port, const char *request); static int bench(void); static void build_request(const char *url); // 用法与各参数详细含义 static void usage(void) { fprintf(stderr, "webbench [option]... URL\n" //用法 " -f|--force Don't wait for reply from server.\n" " -r|--reload Send reload request - Pragma: no-cache.\n" " -t|--time <sec> Run benchmark for <sec> seconds. Default 30.\n" " -p|--proxy <server:port> Use proxy server for request.\n" " -c|--clients <n> Run <n> HTTP clients at once. Default one.\n" " -9|--http09 Use HTTP/0.9 style requests.\n" " -1|--http10 Use HTTP/1.0 protocol.\n" " -2|--http11 Use HTTP/1.1 protocol.\n" " --get Use GET request method.\n" " --head Use HEAD request method.\n" " --options Use OPTIONS request method.\n" " --trace Use TRACE request method.\n" " -?|-h|--help This information.\n" " -V|--version Display program version.\n" ); }; //结构体数组:每一个元素格式为:{长选项,选项后是否带有参数,int*指针(为NULL),对应短选项或static const struct option long_options[]= //不为NULL,将第四个参数值给第三个参数} { {"force",no_argument,&force,1}, {"reload",no_argument,&force_reload,1}, {"time",required_argument,NULL,'t'}, {"help",no_argument,NULL,'?'}, {"http09",no_argument,NULL,'9'}, {"http10",no_argument,NULL,'1'}, {"http11",no_argument,NULL,'2'}, {"get",no_argument,&method,METHOD_GET}, {"head",no_argument,&method,METHOD_HEAD}, {"options",no_argument,&method,METHOD_OPTIONS}, {"trace",no_argument,&method,METHOD_TRACE}, {"version",no_argument,NULL,'V'}, {"proxy",required_argument,NULL,'p'}, {"clients",required_argument,NULL,'c'}, {NULL,0,NULL,0} }; int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { int opt = 0; int options_index = 0; char *tmp = NULL; //一、检验命令行参数 //1.不带选项时直接输出用法help信息 if(argc == 1) { usage(); return 2; } //2.带选项时则解析命令行参数并根据传入选项进行相关设置 // getopt_long 为命令行解析的库函数,根据argc来寻找(argv,"912Vfrt:p:c:?h")这两个字符串匹配的选项, //如果是短选项,则直接返回这个选项给opt, //如果是长选项,则到option long_options[]结构体数组中寻找匹配其长选项,返回其对应的短选项给opt, //若其第三个参数不为NULL,将第四个参数值给第三个参数,并且返回0给opt //此函数自带全局变量: //optarg:指向选项后的参数:-t 100,指向100; //optind: 当前访问到的argv索引值 //opterr: 其值非0时,代表有无效选项,缺少参数,输出错误信息 //optopt: 发现无效选项时,函数返回“? / :”,将其值设为无效选项字符 while((opt = getopt_long(argc,argv,"912Vfrt:p:c:?h",long_options/*结构体数组指针*/,&options_index)) != EOF ) { switch(opt) //根据返回值判断用户传入的参数进行相关设置 { case 0 : break; case 'f': force = 1;break; //force=1代表不等待服务器响应 case 'r': force_reload = 1;break; //发送重新加载请求 case '9': http10 = 0;break; case '1': http10 = 1;break; case '2': http10 = 2;break; case 'V': printf(PROGRAM_VERSION"\n"); exit(0); case 't': benchtime = atoi(optarg); //设置用户传入的运行时间 break; case 'c': clients = atoi(optarg); //设置创建的客户端数 break; case 'p': //使用代理服务器,设置其代理网络号和端口号:格式:-p server:port tmp = strrchr(optarg,':'); //查找“:”在optarg中最后一次出现的位置 proxyhost = optarg; //设置网络号 if(tmp == NULL) //没有:号,没有端口号 { break; } if(tmp == optarg) //端口号在首位置,错误:缺失主机名 { fprintf(stderr,"Error in option --proxy %s: Missing hostname.\n",optarg); return 2; } if(tmp == optarg + strlen(optarg)-1) //:号在末位,缺少端口号 { fprintf(stderr,"Error in option --proxy %s Port number is missing.\n",optarg); return 2; } *tmp = '\0'; //将:号置为“\0” proxyport = atoi(tmp+1); //设置新的端口号 break; case ':': case 'h': case '?': usage();return 2;break; } } //getopt_long函数将选项解析完成后,读到url不会在读取,此时argv[optind]指向url //optind 被 getopt_long设置为命令行参数中未读取的下一个元素下标值 if(optind == argc) //若相等即没有输入URL { fprintf(stderr,"webbench: Missing URL!\n"); usage(); return 2; } //若客户端选项后参数设为0,则更改 if(clients == 0) clients = 1; if(benchtime == 0) benchtime = 60; //输出webbench版本相关信息 fprintf(stderr,"Webbench - Simple Web Benchmark "PROGRAM_VERSION"\n" "Copyright (c) Radim Kolar 1997-2004, GPL Open Source Software.\n" ); //二、构造HTTP请求到request数组 build_request(argv[optind]); //传入URL //http请求构造成功后 //以下输出提示信息 printf("\nBenchmarking: "); //测压开始 switch(method) //用的请求方法 { case METHOD_GET: default: printf("GET");break; case METHOD_OPTIONS: printf("OPTIONS");break; case METHOD_HEAD: printf("HEAD");break; case METHOD_TRACE: printf("TRACE");break; } printf(" %s",argv[optind]); //访问的url switch(http10) //http协议版本号 { case 0: printf(" (using HTTP/0.9)");break; case 2: printf(" (using HTTP/1.1)");break; } printf("\n"); //模拟连接客户端数目 if(clients == 1) printf("1 client"); else printf("%d clients",clients); //连接测试的时间 printf(", running %d sec", benchtime); if(force) printf(", early socket close"); //输出代理服务器的信息 if(proxyhost != NULL) printf(", via proxy server %s:%d",proxyhost,proxyport); if(force_reload) printf(", forcing reload"); printf(".\n"); //开始压力测试,返回 bench 函数执行结果 return bench(); } //二、构造HTTP请求到request数组void build_request(const char *url) { char tmp[10]; int i; //初始化 bzero(host,MAXHOSTNAMELEN); bzero(request,REQUEST_SIZE); //判断应该使用的 HTTP 协议 if(force_reload && proxyhost != NULL && http10 < 1) http10 = 1; if(method == METHOD_HEAD && http10 < 1) http10 = 1; if(method == METHOD_OPTIONS && http10 < 2) http10 = 2; if(method == METHOD_TRACE && http10 < 2) http10 = 2; //1.填写http请求第一行 //填写请求方法method switch(method) { default: case METHOD_GET: strcpy(request,"GET");break; case METHOD_HEAD: strcpy(request,"HEAD");break; case METHOD_OPTIONS: strcpy(request,"OPTIONS");break; case METHOD_TRACE: strcpy(request,"TRACE");break; } strcat(request," "); //URL 合法性判断 //若没有"://"则不合法 if(NULL == strstr(url,"://")) { fprintf(stderr, "\n%s: is not a valid URL.\n",url); exit(2); } //若url过长非法 if(strlen(url)>1500) { fprintf(stderr,"URL is too long.\n"); exit(2); } if(proxyhost == NULL) //若无代理服务器 { if(0 != strncasecmp("http://",url,7)) //忽略大小写比较 { //只支持 HTTP 地址 fprintf(stderr,"\nOnly HTTP protocol is directly supported, set --proxy for others.\n"); exit(2); } } //找到主机名开始的地方:如:http://baidu.com:80/ i = strstr(url,"://")-url+3; //i==7 // 必须以 / 结束 if(strchr(url+i,'/')==NULL) //在字符串中寻找“/” ,找不到则非法URL { fprintf(stderr,"\nInvalid URL syntax - hostname don't ends with '/'.\n"); exit(2); } if(proxyhost == NULL) //若无代理服务器 { // 得到端口号从主机名 if(index(url+i,':') != NULL && index(url+i,':') < index(url+i,'/')) //若带有端口号,index函数与strchr相似 { //设置网络号 strncpy(host,url+i,strchr(url+i,':')-url-i); //如将baidu.com拷贝到host数组里即网络地址 //初始化 bzero(tmp,10); strncpy(tmp,index(url+i,':')+1,strchr(url+i,'/')-index(url+i,':')-1); //将端口号拷贝到tmp数组中 //设置端口 proxyport = atoi(tmp); if(proxyport==0) proxyport=80; } else //没有端口号,直接拷贝域名到host数组中 { strncpy(host,url+i,strcspn(url+i,"/")); //strcspn找url+i到“/”之间的字符个数 } //将资源路径填入请求行里 strcat(request+strlen(request),url+i+strcspn(url+i,"/")); } else //若有代理服务器 { strcat(request,url); //直接填入URL到请求行中 } //填入http版本号到请求行中 if(http10 == 1) strcat(request," HTTP/1.0"); else if (http10==2) strcat(request," HTTP/1.1"); strcat(request,"\r\n"); //2.填请求报头:NAME:VALUE if(http10 > 0) strcat(request,"User-Agent: WebBench "PROGRAM_VERSION"\r\n"); if(proxyhost == NULL && http10 > 0) { strcat(request,"Host: "); strcat(request,host); strcat(request,"\r\n"); } if(force_reload && proxyhost != NULL) { strcat(request,"Pragma: no-cache\r\n"); } if(http10 > 1) strcat(request,"Connection: close\r\n"); //3.填入空行 if(http10>0) strcat(request,"\r\n"); //构造完成} static int bench(void) //父进程做的工作{ int i,j,k; pid_t pid = 0; FILE *f; //建立网络连接 :先测试一次,服务器是否可以正常连接成功 i = Socket(proxyhost == NULL ? host:proxyhost, proxyport); if(i < 0) { fprintf(stderr,"\nConnect to server failed. Aborting benchmark.\n"); return 1; } close(i); //测试成功,一次连接完成关闭 //建立管道通信 if(pipe(mypipe)) { perror("pipe failed."); return 3; } //派生子进程进行压力测试 :传入多少个客户端则建立多少个子进程进行连接 for(i = 0;i < clients;i++) { pid = fork(); if(pid <= (pid_t)0) { sleep(1); break; //使子进程立刻跳出循环,要不就子进程继续 fork 了 } } //子进程创建失败 if( pid < (pid_t)0) { fprintf(stderr,"problems forking worker no. %d\n",i); perror("fork failed."); return 3; } //子进程执行 if(pid == (pid_t)0) { //子进程发出实际请求 if(proxyhost == NULL) benchcore(host,proxyport,request); else benchcore(proxyhost,proxyport,request); // 打开管道写:连接请求状态的信息 f = fdopen(mypipe[1],"w"); //将文件描述符转换为文件指针 if(f == NULL) { perror("open pipe for writing failed."); return 3; } //写入f文件中此进程在一定时间中请求成功的次数,失败的次数,读取服务器回复的总字节数 fprintf(f,"%d %d %d\n",speed,failed,bytes); fclose(f); return 0; } else { //父进程打开管道读 f = fdopen(mypipe[0],"r"); if(f == NULL) { perror("open pipe for reading failed."); return 3; } setvbuf(f,NULL,_IONBF,0); //设置f的缓冲区为无缓冲区 speed = 0; //连接成功总次数 failed = 0; //失败请求数 bytes = 0; //传输字节数 while(1) { pid = fscanf(f,"%d %d %d",&i,&j,&k); if(pid<2) { fprintf(stderr,"Some of our childrens died.\n"); break; } speed += i; //连接成功总次数 failed += j; //连接失败总次数 bytes += k; //传输总字节数 //子进程是否读取完 if(--clients == 0) break; } fclose(f); //统计结果计算 printf("\nSpeed=%d pages/min, %d bytes/sec.\nRequests: %d susceed, %d failed.\n", (int)((speed+failed)/(benchtime/60.0f)), //总连接次数/总时间=每分钟请求连接次数 (int)(bytes/(float)benchtime), //每秒传输字节数 speed, //连接成功次数 failed); //连接失败次数 } return i; } //信号处理函数 static void alarm_handler(int signal) { timerexpired = 1; } //子进程处理发起请求void benchcore(const char *host,const int port,const char *req) { int rlen; char buf[1500]; int s,i; struct sigaction sa; //安装信号 sa.sa_handler = alarm_handler; sa.sa_flags = 0; if(sigaction(SIGALRM,&sa,NULL)) exit(3); //设置闹钟函数 alarm(benchtime); rlen = strlen(req); nexttry: while(1){ //收到信号则使 timerexpired = 1 if(timerexpired) { if(failed > 0) { failed--; } return; } //建立 socket连接, 进行 HTTP 请求 s = Socket(host,port); if(s < 0) { failed++; //连接失败则++ continue; } if(rlen!=write(s,req,rlen)) { failed++; //写失败++ close(s); continue; } //HTTP 0.9 的处理 if(http10==0) // 如果关闭不成功 if(shutdown(s,1)) //关闭连接写一半 { failed++; close(s); continue; } // -f 选项时未设置时等待读取服务器回复 if(force == 0) { while(1) { if(timerexpired) break; i = read(s,buf,1500); if(i<0) { failed++; //读失败++ close(s); goto nexttry; } else if(i == 0) //读完退出 break; else bytes+=i; //统计服务器回复的字节数 } } if(close(s)) { failed++; //关闭失败++ continue; } speed++; //成功连接一次++一次 } }
socket.c
#include <sys/types.h> #include <sys/socket.h> #include <fcntl.h> #include <netinet/in.h> #include <arpa/inet.h> #include <netdb.h> #include <sys/time.h> #include <string.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <stdarg.h> int Socket(const char *host, int clientPort) { int sock; unsigned long inaddr; struct sockaddr_in ad; struct hostent *hp; // 初始化地址 memset(&ad, 0, sizeof(ad)); ad.sin_family = AF_INET; // 尝试把主机名转化为数字 inaddr = inet_addr(host); if (inaddr != INADDR_NONE) memcpy(&ad.sin_addr, &inaddr, sizeof(inaddr)); else { // 取得 ip 地址 hp = gethostbyname(host); //得到主机的二进制Ip给hp->h_addr if (hp == NULL) return -1; memcpy(&ad.sin_addr, hp->h_addr, hp->h_length); } ad.sin_port = htons(clientPort); // 建立 socket sock = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0); if (sock < 0) return sock; // 建立链接 if (connect(sock, (struct sockaddr *)&ad, sizeof(ad)) < 0) return -1; return sock; }
声明
本文内容仅代表作者观点,或转载于其他网站,本站不以此文作为商业用途
如有涉及侵权,请联系本站进行删除
转载本站原创文章,请注明来源及作者。