移情别恋c++ ദ്ദി˶ー̀֊ー́ ) ——8.stack&&queue
码码生的 2024-09-11 08:35:01 阅读 89
1.用栈实现队列
. - 力扣(LeetCode)

思路
1.将一个栈当作输入栈,用于压入 push 传入的数据;另一个栈当作输出栈,用于 pop 和 peek 操作。
2.每次 pop 或 peek 时,若输出栈为空则将输入栈的全部数据依次弹出并压入输出栈,这样输出栈从栈顶往栈底的顺序就是队列从队首往队尾的顺序。
<code>class MyQueue {
private:
stack<int> inStack, outStack;
void in2out() {
while (!inStack.empty()) {
outStack.push(inStack.top());
inStack.pop();
}
}
public:
MyQueue() {}
void push(int x) {
inStack.push(x);
}
int pop() {
if (outStack.empty()) {
in2out();
}
int x = outStack.top();
outStack.pop();
return x;
}
int peek() {
if (outStack.empty()) {
in2out();
}
return outStack.top();
}
bool empty() {
return inStack.empty() && outStack.empty();
}
};
2. 用队列实现栈

<code>class MyStack {
public:
queue<int> queue1;
queue<int> queue2;
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
MyStack() {
}
/** Push element x onto stack. */
void push(int x) {
queue2.push(x);
while (!queue1.empty()) {
queue2.push(queue1.front());
queue1.pop();
}
swap(queue1, queue2);
}
/** Removes the element on top of the stack and returns that element. */
int pop() {
int r = queue1.front();
queue1.pop();
return r;
}
/** Get the top element. */
int top() {
int r = queue1.front();
return r;
}
/** Returns whether the stack is empty. */
bool empty() {
return queue1.empty();
}
};
3.数组中的第k个最大元素

思路:
1.先取数组的前k个元素,使用向上调整算法建立小堆(a[0]为最小值)
2.再遍历剩余数组,如果元素大于a[0],则替代a[0]入堆并使用向下调整算法调整
3.返回a[0];
<code>
typedef struct heap
{
int* a;
int size;
int capacity;
}HP;
void swap(int* p1, int* p2)
{
int t = 0;
t = *p1;
*p1 = *p2;
*p2 = t;
}
void heapinit(HP* php)
{
assert(php);
php->a = NULL;
php->size = 0;
php->capacity = 0;
}
void adjustup(int* a, int child) //向上调整法 //上方必须是堆
{
int parent = (child-1)/2;
while (child>0)
{
if (a[parent]>=a[child]) //小堆为>=,大堆为<=
{
swap(&a[parent],&a[child]);
child = parent;
parent = (child - 1)/2;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
}
void adjustdown(int* a,int n, int parent) //向下调整法,!!!!!!(仅适用于根结点两端都是大堆或小堆)
{
int child = 2 * parent + 1;
while (child<=n) //
{
if (child + 1<=n && a[child + 1] < a[child]) // child+1>n可以推出child==n,所以只有左孩子
{
child++; //选出左右孩子中最大的一个‘>’,最小的为'<'
}
if (a[parent]>=a[child]) //大堆为“<=”,小堆为“>=”
{
swap(&a[parent], &a[child]);
parent = child;
child = 2 * parent + 1; //每次都先找左孩子
}
else
{
break;
}
}
}
void heappush(HP* php, int data)
{
php->a[php->size] = data;
php->size++;
adjustup(php->a, php->size - 1);
}
int findKthLargest(int* nums, int numsSize, int k) {
HP sl;
heapinit(&sl);
sl.a=(int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*k);
int i=0;
for(i=0;i<k;i++)
heappush(&sl, nums[i]);
for(i=k;i<numsSize;i++)
{
if(nums[i]>sl.a[0])
{
sl.a[0]=nums[i];
adjustdown(sl.a,k-1,0); //记得是k-1
}
}
return sl.a[0];
}
4.最小栈

<code>class MinStack {
public:
public:
void push(int x) {
// 只要是压栈,先将元素保存到_elem中
_elem.push(x);
// 如果x小于_min中栈顶的元素,将x再压入_min中!!!!!!!!!!
if (_min.empty() || x <= _min.top())
_min.push(x);
}
void pop() {
// 如果_min栈顶的元素等于出栈的元素,_min顶的元素要移除!!!!!!!!
if (_min.top() == _elem.top())
_min.pop();
_elem.pop();
}
int top()
{
return _elem.top();
}
int getMin()
{
return _min.top();
}
private:
// 保存栈中的元素
std::stack<int> _elem;
// 保存栈的最小值
std::stack<int> _min;
};
5.栈的弹出压入序列

1.设置flag,i,i用来遍历pushv数组;
2.当arr.top()==popV[flag]时,arr.pop(),flag++,
3.当pushV[i]==popV[flag]时,flag++;
4.遍历完成后,
for(;flag<popV.size();flag++)
{
if(popV[flag]!=arr.top())
return false;
else
{
arr.pop();
}
}
5.return true
<code>class Solution {
public:
bool IsPopOrder(vector<int>& pushV, vector<int>& popV) {
int flag=0;
for(int i=0;i<pushV.size();i++)
{
if(pushV[i]!=popV[flag])
{
if(!arr.empty())
{
if(arr.top()==popV[flag])
{
arr.pop();
flag++;
while(!(arr.empty())&&arr.top()==popV[flag])
//如果连续遇到arr.top()==popV[flag],则一直arr.pop();flag++,直至两者不同
{
arr.pop();
flag++;
}
arr.push(pushV[i]);
}
else {
arr.push(pushV[i]);
}
}
else
arr.push(pushV[i]);
}
else
{
flag++;
}
}
for(;flag<popV.size();flag++)
{
if(popV[flag]!=arr.top())
return false;
else
{
arr.pop();
}
}
return true;
}
private:
stack<int> arr;
};
6.逆波兰表达式求值

1.设置两个stack,一个存数字(arr),一个存符号(brr)
2.遍历数组,若为数字则 入栈arr;
3.若为符号,则入栈brr,并取brr.top,arr.top(两次)
进行operation,并把返回值压入arr栈中;
4.返回arr.top;
<code>class Solution {
public:
int operation(int a, int b, string s) {
if (s[0] == '+')
return b + a; //记得是b在前,a在后,因为栈是后进先出
if (s[0] == '-')
return b - a;
if (s[0] == '*')
return b * a;
if (s[0] == '/')
return b / a;
return 1; // 记得写一个return
// 1,因为系统判定如果if都不走,那么就没有返回值
}
int evalRPN(vector<string>& tokens) {
int num = 0;
int result = 0;
string j;
int a;
int b;
int end;
for (int i = 0; i < tokens.size(); i++) {
if (tokens[i] == "+" || tokens[i] == "-" || tokens[i] == "*" ||
tokens[i] == "/") {
brr.push(tokens[i]);
a = arr.top();
arr.pop();
b = arr.top();
arr.pop();
end = operation(a, b, brr.top());
arr.push(end);
brr.pop();
} else {
j = tokens[i];
if (j[0] == '-') {
for (int i = 1; i < j.size(); i++) {
num = num * 10 + (j[i] - '0');
}
arr.push(-num);
num = 0;
} else {
for (int i = 0; i < j.size(); i++) {
num = num * 10 + (j[i] - '0');
}
arr.push(num);
num = 0;
}
}
}
end = arr.top();
return end;
}
private:
stack<int> arr;
stack<string> brr;
};
7.二叉树层序遍历
. - 力扣(LeetCode)
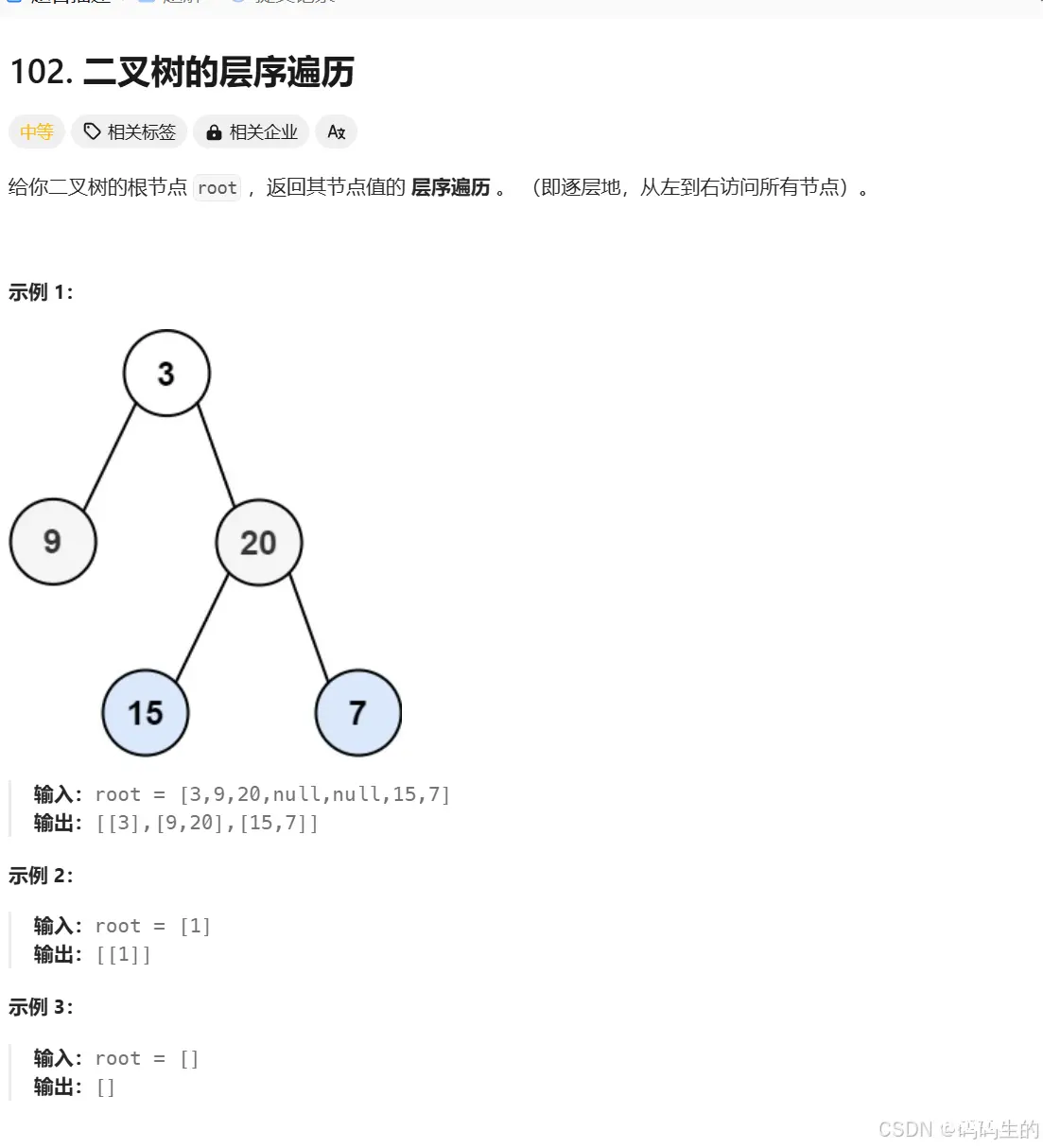
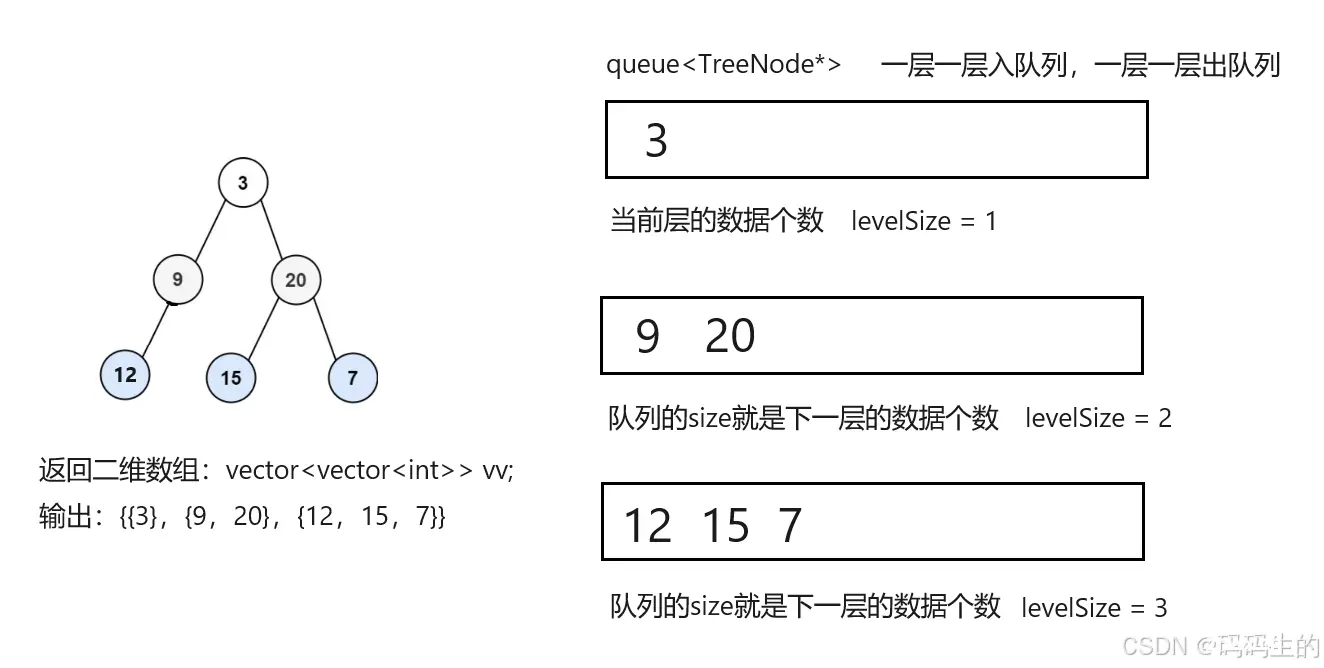
<code>class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> levelOrder(TreeNode* root)
{
vector<vector<int>> vv;
queue<TreeNode*> q;
int levelSize = 0; //记录某一层数据的个数
if(root != nullptr)
{
q.push(root);
levelSize = 1;
}
while(!q.empty())
{
//当前层数据的个数,控制数据一层一层的出
vector<int> v;
while(levelSize--)
{
TreeNode* front = q.front(); //保留队头指针
v.push_back(front->val); //尾差队头指针中的数据
q.pop(); //出队
if(front->left != nullptr) //左孩子不为空,入队
{
q.push(front->left);
}
if(front->right != nullptr) //右孩子不为空,入队
{
q.push(front->right);
}
}
vv.push_back(v);
//当前层出完,下一层都进队列了,队列的size就是下一层的数据个数
levelSize = q.size();
}
return vv;
}
};
声明
本文内容仅代表作者观点,或转载于其他网站,本站不以此文作为商业用途
如有涉及侵权,请联系本站进行删除
转载本站原创文章,请注明来源及作者。