C#(CSharp)入门教程
渴望力量的土狗 2024-08-18 10:35:01 阅读 70
目录
C#的第一个程序
变量
折叠代码
变量类型和声明变量
获取变量类型所占内存空间(sizeof)
常量
转义字符
隐式转换
显示转换
异常捕获
运算符
算术运算符
布尔逻辑运算符
关系运算符
位运算符
其他运算符
字符串拼接
条件分支语句
if...else 语句
switch语句
循环语句
while语句
do while语句 (使用较少)
for循环 (最常用)
补充内容
随机数
C#的第一个程序
因为笔者学习过Java,所以个人感觉C#上手起来很快,很多都是java中学习过的,所以不再赘述。该系列文章主要是分享给有一定编程经验的小伙伴,但是又想要学习C#的来使用,零基础的可能会比较吃力,所以酌情使用。
<code>using System;
namespace CSharp入门_第一个程序
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//使用Console调用方法
Console.WriteLine("Hello World");
//WriteLine方法会自动空一行(换行)
//使用Write则不会换行
Console.WriteLine("我爱敲代码");//输出
Console.Write("你好!");
Console.Write("世界");
//Console.ReadKey();//需要使用该语句,不然控制台会一闪而过,或者只执行不调试也可以
Console.WriteLine("请玩家输入名字:");
//C#的输入
Console.ReadLine();
//玩家输入完毕
Console.Write("玩家输入完毕!请开始游戏吧!");
//这里注意!不使用ReadKey是会直接闪过控制台的,所以我们还是可以使用Ctrl+F5
}
}
}
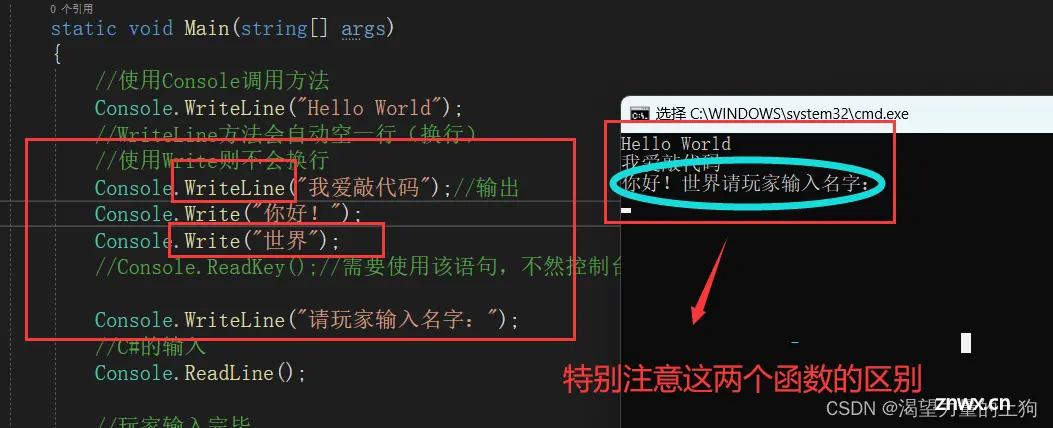
需要特别注意的是向控制台输入内容:
<code>//向控制台输入信息
Console.ReadLine();
//判断是否按键,只有玩家按键了才会结束(可以用来防止跳过控制台显示)
Console.ReadKey();
变量
折叠代码
using System;
namespace CSharp入门_变量
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("变量");
//1、折叠代码(防止代码过于凌乱)输入#region按下tab自动补全
#region 声明变量
#endregion
}
}
}
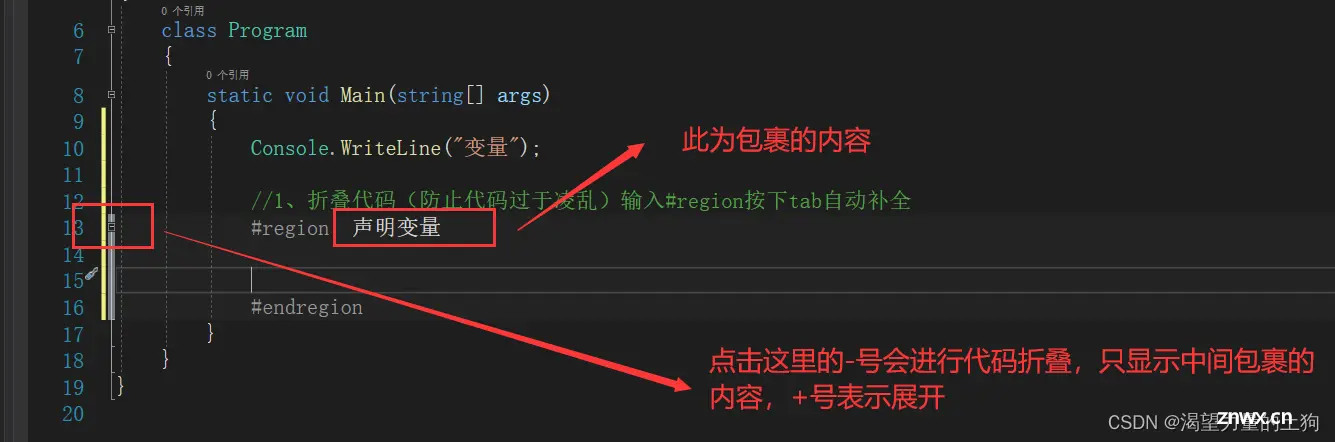
点击-号后我们可以看到中间部分进行了折叠:
变量类型和声明变量
<code>using System;
namespace CSharp入门_变量
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("变量");
//1、折叠代码(防止代码过于凌乱)输入#region按下tab自动补全
#region 声明变量
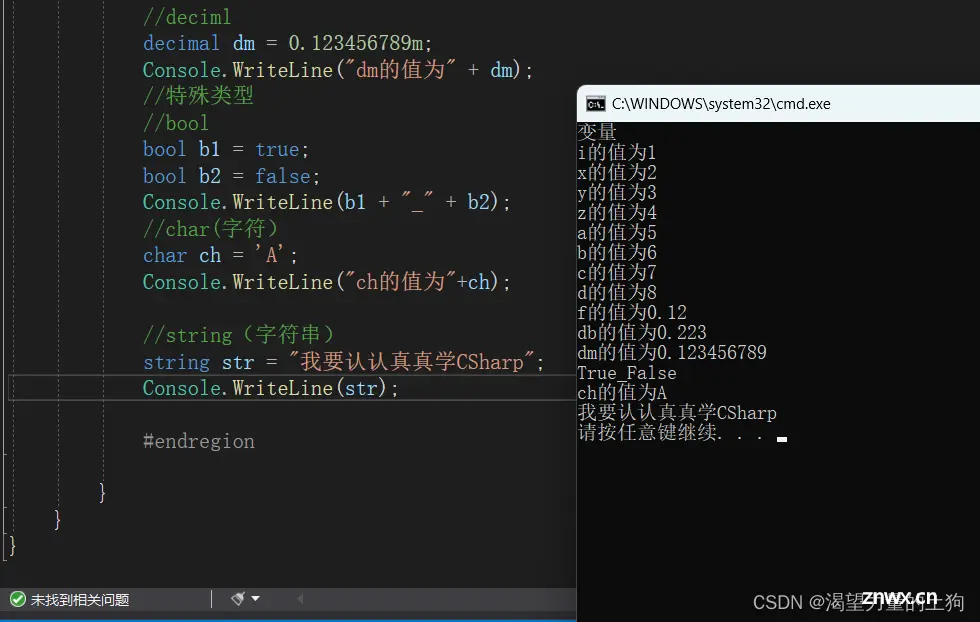
//有符号整型
//sbyte
sbyte i = 1;
Console.WriteLine("i的值为" + i);
//short
short x = 2;
Console.WriteLine("x的值为" + x);
//int
int y = 3;
Console.WriteLine("y的值为" + y);
//long
long z = 4;
Console.WriteLine("z的值为" + z);
//无符号整型
//byte
byte a = 5;
Console.WriteLine("a的值为" + a);
//ushort
ushort b = 6;
Console.WriteLine("b的值为" + b);
//uint
uint c = 7;
Console.WriteLine("c的值为" + c);
//ulong
ulong d = 8;
Console.WriteLine("d的值为" + d);
//浮点数(小数)
//float
float f = 0.12f;
Console.WriteLine("f的值为" + f);
//double
double db = 0.223;
Console.WriteLine("db的值为" + db);
//deciml
decimal dm = 0.123456789m;
Console.WriteLine("dm的值为" + dm);
//特殊类型
//bool
bool b1 = true;
bool b2 = false;
Console.WriteLine(b1 + "_" + b2);
//char(字符)
char ch = 'A';
Console.WriteLine("ch的值为"+ch);
//string(字符串)
string str = "我要认认真真学CSharp";
Console.WriteLine(str);
#endregion
}
}
}
获取变量类型所占内存空间(sizeof)
<code>using System;
namespace CSharp入门_变量
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("变量");
//1、折叠代码(防止代码过于凌乱)输入#region按下tab自动补全
#region 声明变量
//有符号整型
//sbyte
sbyte i = 1;
Console.WriteLine("i的值为" + i);
//short
short x = 2;
Console.WriteLine("x的值为" + x);
//int
int y = 3;
Console.WriteLine("y的值为" + y);
//long
long z = 4;
Console.WriteLine("z的值为" + z);
//无符号整型
//byte
byte a = 5;
Console.WriteLine("a的值为" + a);
//ushort
ushort b = 6;
Console.WriteLine("b的值为" + b);
//uint
uint c = 7;
Console.WriteLine("c的值为" + c);
//ulong
ulong d = 8;
Console.WriteLine("d的值为" + d);
//浮点数(小数)
//float
float f = 0.12f;
Console.WriteLine("f的值为" + f);
//double
double db = 0.223;
Console.WriteLine("db的值为" + db);
//deciml
decimal dm = 0.123456789m;
Console.WriteLine("dm的值为" + dm);
//特殊类型
//bool
bool b1 = true;
bool b2 = false;
Console.WriteLine(b1 + "_" + b2);
//char(字符)
char ch = 'A';
Console.WriteLine("ch的值为"+ch);
//string(字符串)
string str = "我要认认真真学CSharp";
Console.WriteLine(str);
#endregion
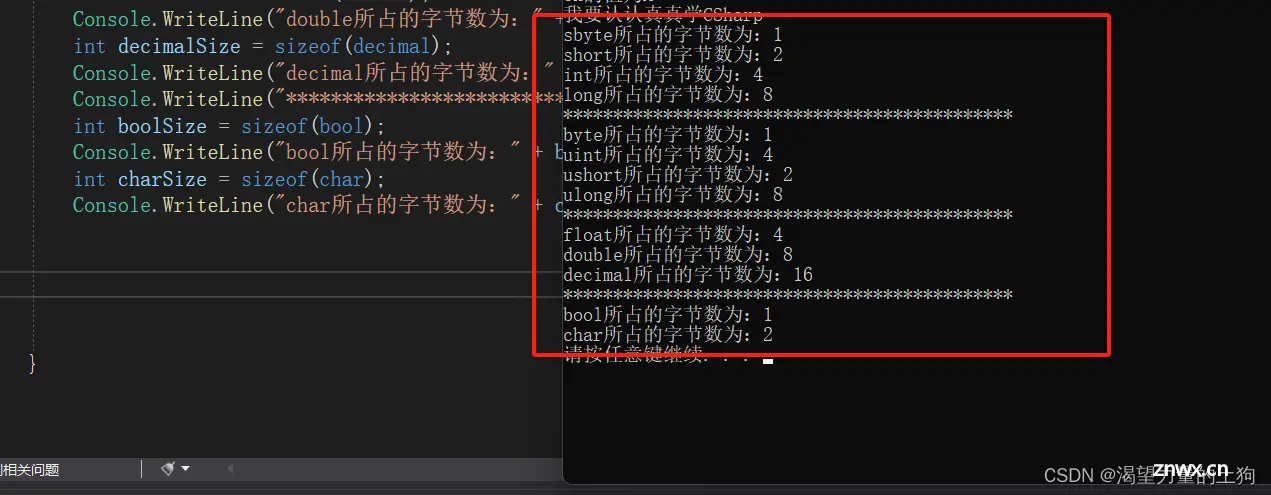
int sbyteSize = sizeof(sbyte);
Console.WriteLine("sbyte所占的字节数为:" + sbyteSize);
int shortSize = sizeof(short);
Console.WriteLine("short所占的字节数为:" + shortSize);
int intSize = sizeof(int);
Console.WriteLine("int所占的字节数为:" + intSize);
int longSize = sizeof(long);
Console.WriteLine("long所占的字节数为:" + longSize);
Console.WriteLine("*********************************************");
int byteSize = sizeof(byte);
Console.WriteLine("byte所占的字节数为:" + byteSize);
int uintSize = sizeof(uint);
Console.WriteLine("uint所占的字节数为:" + uintSize);
int ushortSize = sizeof(ushort);
Console.WriteLine("ushort所占的字节数为:" + ushortSize);
int ulongSize = sizeof(ulong);
Console.WriteLine("ulong所占的字节数为:" + ulongSize);
Console.WriteLine("*********************************************");
int floatSize = sizeof(float);
Console.WriteLine("float所占的字节数为:" + floatSize);
int doubleSize = sizeof(double);
Console.WriteLine("double所占的字节数为:" + doubleSize);
int decimalSize = sizeof(decimal);
Console.WriteLine("decimal所占的字节数为:" + decimalSize);
Console.WriteLine("*********************************************");
int boolSize = sizeof(bool);
Console.WriteLine("bool所占的字节数为:" + boolSize);
int charSize = sizeof(char);
Console.WriteLine("char所占的字节数为:" + charSize);
}
}
}
常量
<code>using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace CSharp入门_常量
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
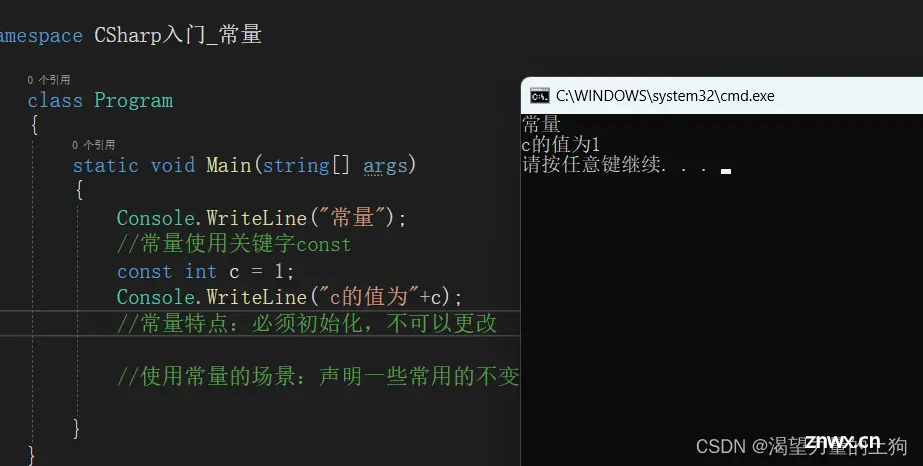
Console.WriteLine("常量");
//常量使用关键字const
const int c = 1;
Console.WriteLine("c的值为"+c);
//常量特点:必须初始化,不可以更改
//使用常量的场景:声明一些常用的不变的量,如π
}
}
}
转义字符
<code>using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace CSharp入门_转义字符
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("转义字符");
/*
* 转义字符的使用
*/
//单引号 \'
string str1 = "\'哈哈哈\'";
Console.WriteLine("str1 = "+str1);
//双引号 \"
string str2 = "\"CSharp太好学啦!\"";
Console.WriteLine("str2 = " + str2);
//换行 \n
string str3 = "\"CSharp\n太好学啦!\"";
Console.WriteLine("str3 = " + str3);
//斜杠 \\
string str4 = "\"CSharp\\太好学啦!\"";
Console.WriteLine("str4 = " + str4);
/*
* 下面的是不太常用的转义字符
*
*/
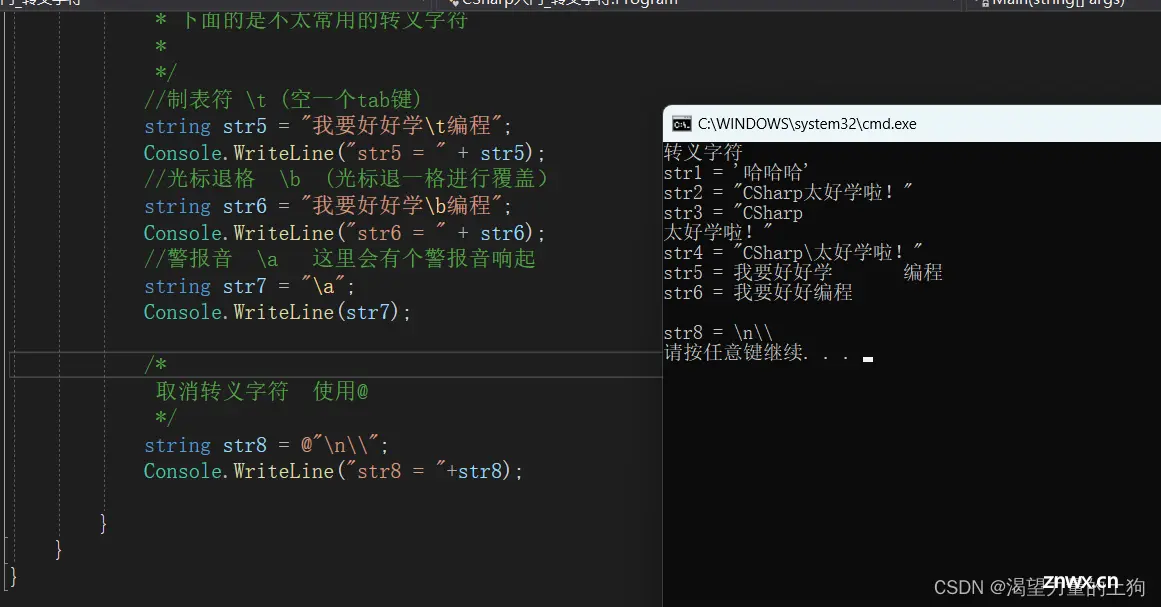
//制表符 \t (空一个tab键)
string str5 = "我要好好学\t编程";
Console.WriteLine("str5 = " + str5);
//光标退格 \b (光标退一格进行覆盖)
string str6 = "我要好好学\b编程";
Console.WriteLine("str6 = " + str6);
//警报音 \a 这里会有个警报音响起
string str7 = "\a";
Console.WriteLine(str7);
/*
取消转义字符 使用@
*/
string str8 = @"\n\\";
Console.WriteLine("str8 = "+str8);
}
}
}
隐式转换
<code>using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace CSharp入门_隐式转换
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("隐式转换");
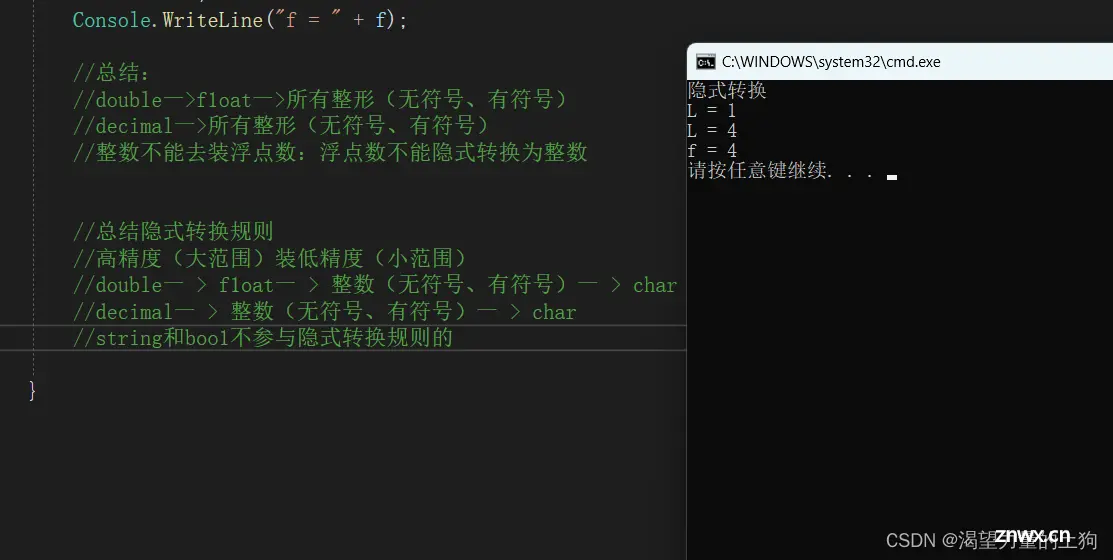
//大范围装小范围,记住这个就可以
long L = 5;
int i = 1;
L = i;
Console.WriteLine("L = "+L);
//一般都是这个规律,但是浮点型中decimal不能隐式转换为float和double
//特殊类型如bool,char,string之间不存在隐式转换,但是char可以隐式转换为整数
//(因为char取值范围是0-65535,其对应的数字 其实是一个ascll码,一个数字就是一个对应关系)
//无符号的不能装有符号的,但是有符号的可以装无符号的,因为无符号数没有负数,而有符号数则有负数
//即有符号数不能隐式转换为无符号数,无符号数可以隐式转换为有符号数(要注意范围是涵盖的,大装小)
uint ui = 4;
L = ui;
Console.WriteLine("L = " +L );
//浮点数可以装任何类型的 整型
float f = L;
Console.WriteLine("f = " + f);
//总结:
//double一>f1oat一>所有整形(无符号、有符号)
//decimal一>所有整形(无符号、有符号)
//整数不能去装浮点数:浮点数不能隐式转换为整数
//总结隐式转换规则
//高精度(大范围)装低精度(小范围)
//double一 > f1oat一 > 整数(无符号、有符号)一 > char
//decimal一 > 整数(无符号、有符号)一 > char
//string和boo1不参与隐式转换规则的
}
}
}
显示转换
<code>using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace CSharp入门_显示转换
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("显示转换");
//1、强制类型转换 将高精度类型强制转换为低精度类型
//语法:变量类型 变量名 = (强转的类型)变量;
//需要注意:精度和范围
short st = 1;
int i = 5;
st = (short)i;
Console.WriteLine("st的值为:" + st);
//如果我们范围超过就会出问题
short so = 2;
int x = 40000;
so = (short)x;
Console.WriteLine("so的值为:" + so);
//注意:在强制类型转换的时候一定要注意范围,在强制转换浮点型的时候会出现精度变低的情况,要注意
//浮点数强转成整形时会直接抛弃掉小数点后面的小数
double b = 1.5999999;
i = (int)b;
Console.WriteLine("i的值为:" + i);
//2、Parse转换 (将字符串类型转换为对应的类型)字符串必须能够转换为对应类型,不然会报错,还有范围
//语法:变量类型.Parse("字符串");
int i2 = int.Parse("123");
Console.WriteLine("i2的值为:" + i2);
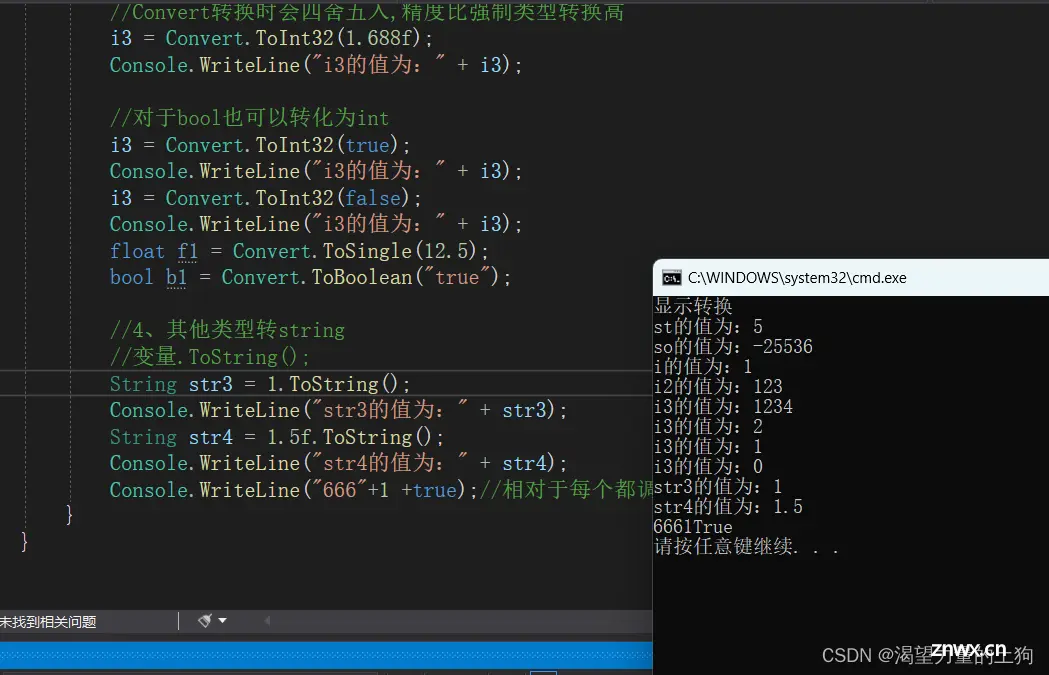
//3、Convert转换
//作用:
//更准确的将各个类型之间进行相互转换
//语法:Convert.To目标类型(变量或常量)
//注意:填写的变量或常量必须正确否则出错
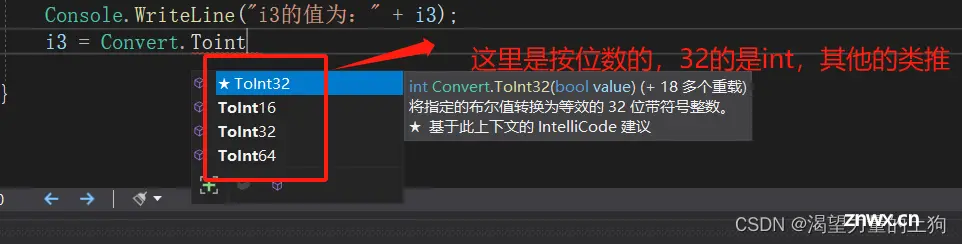
int i3 = Convert.ToInt32("1234");
Console.WriteLine("i3的值为:" + i3);
//Convert转换时会四舍五入,精度比强制类型转换高
i3 = Convert.ToInt32(1.688f);
Console.WriteLine("i3的值为:" + i3);
//对于bool也可以转化为int
i3 = Convert.ToInt32(true);
Console.WriteLine("i3的值为:" + i3);
i3 = Convert.ToInt32(false);
Console.WriteLine("i3的值为:" + i3);
float f1 = Convert.ToSingle(12.5);
bool b1 = Convert.ToBoolean("true");
//4、其他类型转string
//变量.ToString();
String str3 = 1.ToString();
Console.WriteLine("str3的值为:" + str3);
String str4 = 1.5f.ToString();
Console.WriteLine("str4的值为:" + str4);
Console.WriteLine("666"+1 +true);//相对于每个都调用了tostring
}
}
}
异常捕获
<code>using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace CSharp入门_异常捕获
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("异常捕获");
#region 作用
//异常捕获作用:避免代码错误造成程序卡死
//string str = Console.ReadLine();
// int i = int.Parse(str);//比如这里的str如果输入的范围大于int就会卡死
#endregion
#region 语法
try
{
//希望进行异常捕获的代码块
//如果try中的代码块出现异常就进入catch
}
catch(Exception e)//可以通过e得到具体的报错信息(可以不写)
{
//如果异常进行的动作
}
finally//可选
{
//不管有没有出错,都会执行其中的代码
}
#endregion
#region 测试
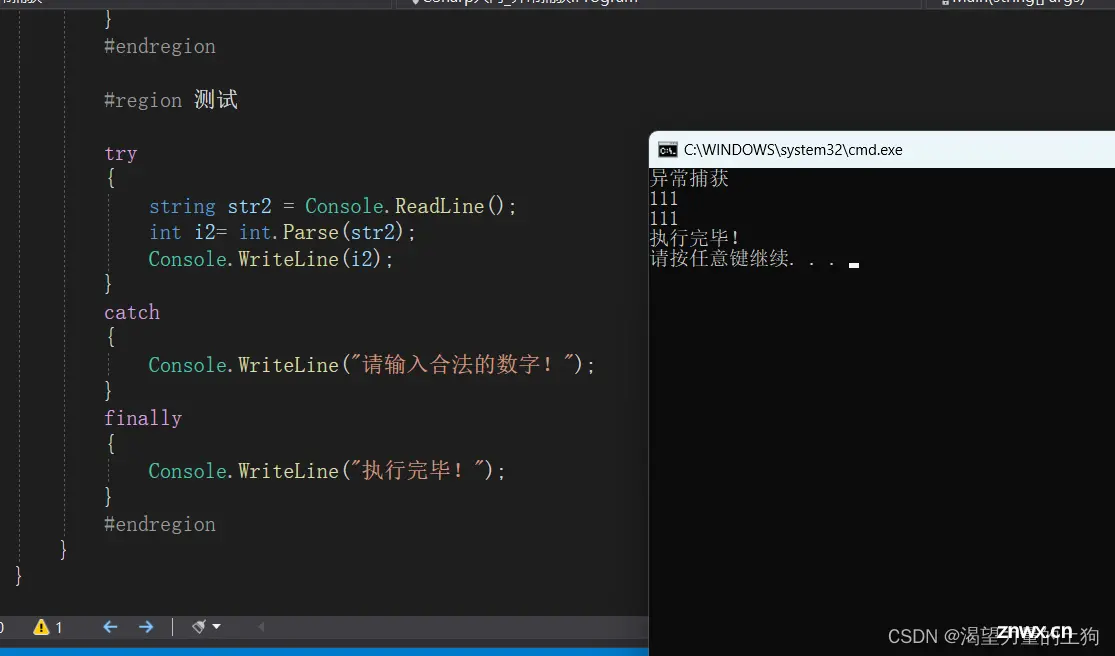
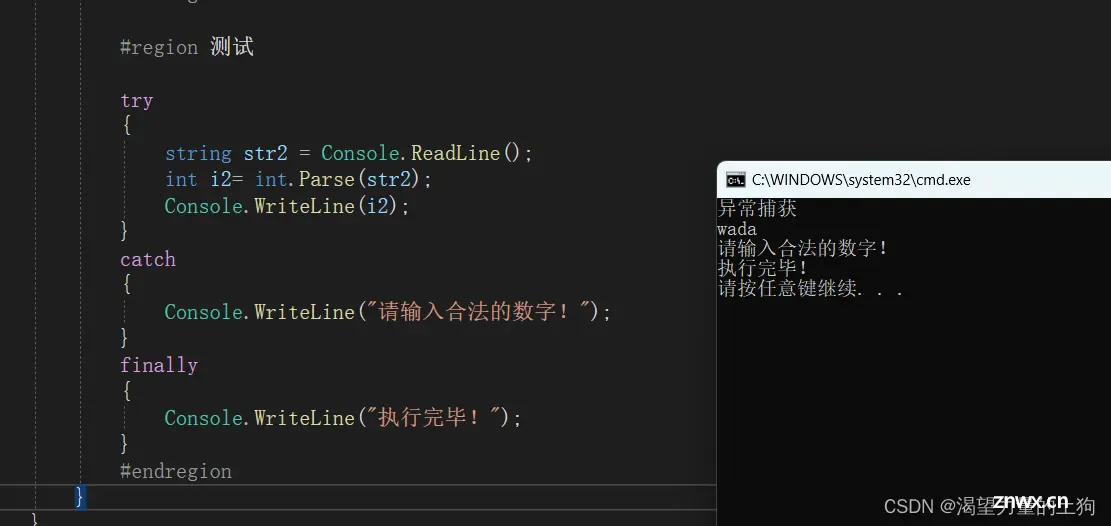
try
{
string str2 = Console.ReadLine();
int i2= int.Parse(str2);
Console.WriteLine(i2);
}
catch
{
Console.WriteLine("请输入合法的数字!");
}
finally
{
Console.WriteLine("执行完毕!");
}
#endregion
}
}
}
如果输入不合法:
运算符
算术运算符
| 一元运算符 | 描述 | 实例 |
|---|---|---|
| ++ | 增量运算符 | ++a 输出 11 |
| -- | 减量运算符 | --a 输出 9 |
| + | 一元加运算符 | +a 输出 10 |
| - | 一元减运算符 | -a 输出 -10 |
| 二元运算符 | 描述 | 实例 |
|---|---|---|
| * | 乘法运算符 | a * b 输出 200 |
| / | 除法运算符 | b / a 输出 2 |
| % | 余数运算符 | b % a 输出 0 |
| + | 加法运算符 | b + a 输出 30 |
| - | 减法运算符 | b - a 输出 10 |
布尔逻辑运算符
| 布尔运算符 | 描述 | 实例 |
|---|---|---|
| ! | 逻辑非运算符 | !a 为 False |
| & | 逻辑与运算符 | a & b 为 False |
| | | 逻辑或运算符 | a | b 为 True |
| ^ | 逻辑异或运算符 | a ^ b 为 True |
| && | 条件逻辑与运算符 | a && b 为 False |
| || | 条件逻辑或运算符 | a || b 为 True |
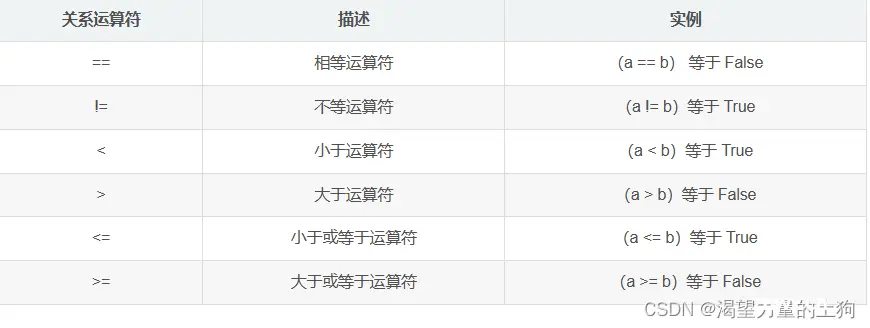
关系运算符
位运算符
| 位运算符 | 描述 | 实例 |
|---|---|---|
| ~ | 按位求补运算符 | ~a 等于 -2 |
| << | 左移位运算符 | a << 2 等于 4 |
| >> | 右移位运算符 | a >> 2 等于 0 |
| >>> | 无符号右移运算符 | a >>> 2 等于 0 |
| & | 逻辑与运算符 | a & b 等于 0 |
| ^ | 逻辑异或运算符 | a ^ b 等于 3 |
| | | 逻辑或运算符 | a | b 等于 3 |
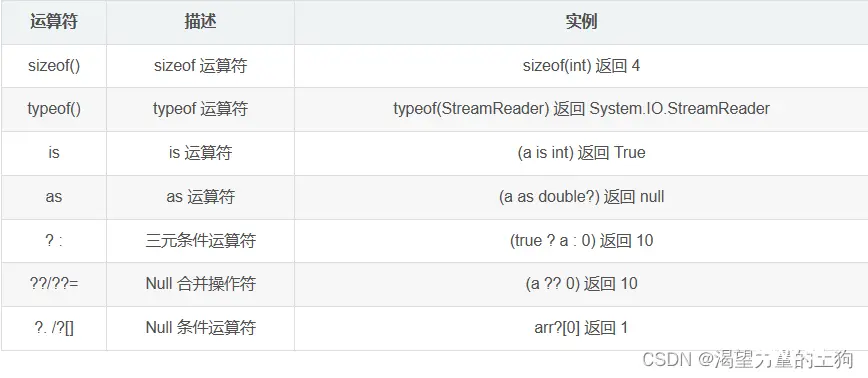
其他运算符
字符串拼接
<code>using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace CSharp入门_字符串拼接
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("字符串拼接");
//1、用+号进行字符串拼接
string str = "123";
Console.WriteLine(str+"456");
str = str + 1;
Console.WriteLine(str);
str = "123";
str += "1" + 4 + true;
Console.WriteLine(str);
str += 1 + 2 + 3 + 4;
Console.WriteLine(str);
str += "" + 1 + 2 + 3;
Console.WriteLine(str);
//2、使用string.Format();
//string.Format("待拼接的内容",内容1,内容2,.....)
//拼接内容中的固定规则
//想要被拼接的内容用占位符替代{数字}数字:n依次往后
string str3;
str3 = string.Format("我爱{0}, 我今年{1}岁, 我想好好学习{2}", "学习",18, "C#");
Console.WriteLine(str3);
str3 = string.Format("{0}{1}{2}", 1, true, false);
Console.WriteLine(str3);
//3、控制台打印
Console.WriteLine("A{0}B{1}C{2}", 1, true, false);
//注意:后面的内容可以比前面多,但是不能比前面少,否则会报错,还有占位符数字要从0开始
}
}
}

条件分支语句
if...else 语句
<code>using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace CSharp入门_条件分支语句
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("条件分支语句");
//if语句
int i = 0;
int flag = 0;
if (flag == 0)
{
i = 100;
flag = 1;
}
Console.WriteLine(i);
//if...else
if (flag == 1)
{
i = 200;
}
else
{
i = 1;
}
Console.WriteLine(i);
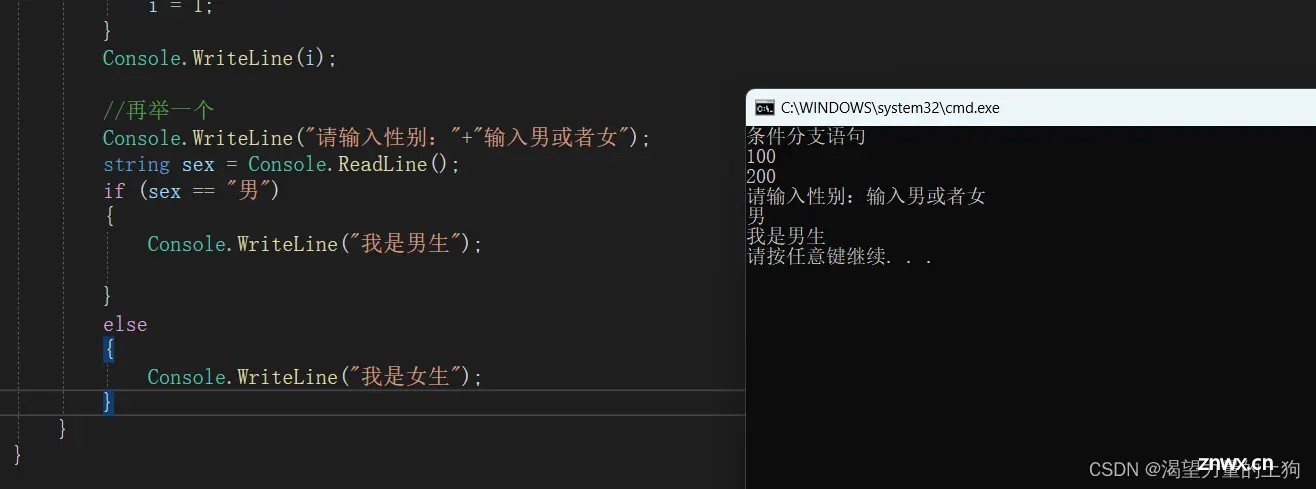
//再举一个
Console.WriteLine("请输入性别:"+"输入男或者女");
string sex = Console.ReadLine();
if (sex == "男")
{
Console.WriteLine("我是男生");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("我是女生");
}
}
}
}
switch语句
<code> //switch语句
int a = 3;
switch (a)
{
case 1: //条件只能是常量
Console.WriteLine("a = 1");
break;
case 2:
Console.WriteLine("a = 2");
break;
case 3:
Console.WriteLine("a = 3");
break;
default:
Console.WriteLine("什么条件都不满足,执行default语句");
break;
}
//switch也支持自定义常量
int b = 2;
const int x = 2;
switch (b)
{
case 1: //条件只能是常量
Console.WriteLine("b = 1");
break;
case x:
Console.WriteLine("b = 2");
break;
case 3:
Console.WriteLine("b = 3");
break;
default:
Console.WriteLine("什么条件都不满足,执行default语句");
break;
}
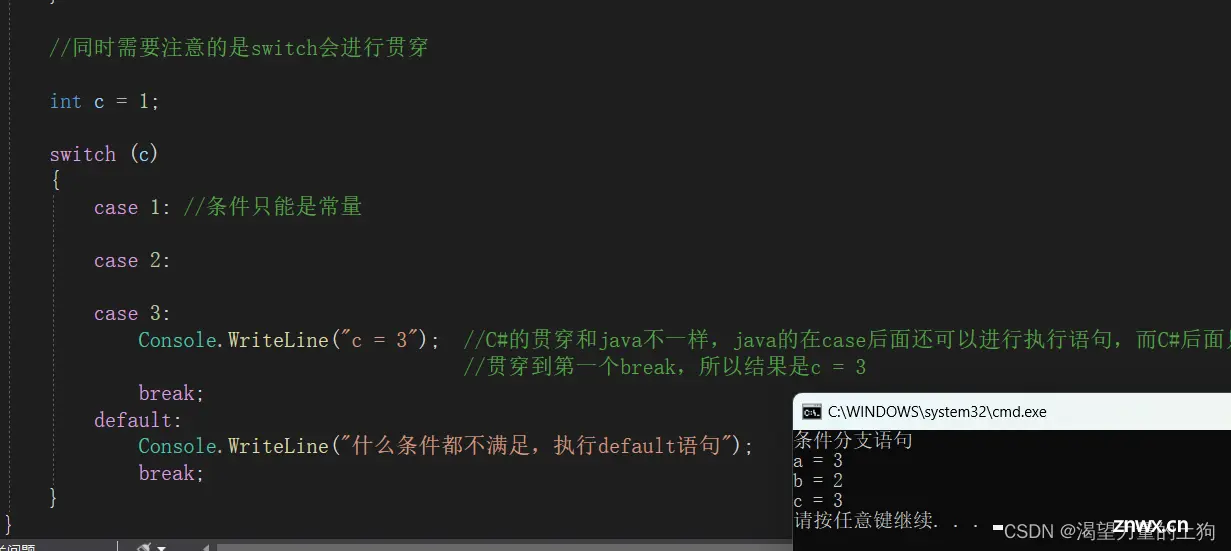
//同时需要注意的是switch会进行贯穿
int c = 1;
switch (c)
{
case 1: //条件只能是常量
case 2:
case 3:
Console.WriteLine("c = 3"); //C#的贯穿和java不一样,java的在case后面还可以进行执行语句,而C#后面只能像上述所写
//贯穿到第一个break,所以结果是c = 3
break;
default:
Console.WriteLine("什么条件都不满足,执行default语句");
break;
}
循环语句
while语句
写循环语句的时候一般要避免写死循环(条件一直为真) 还会造成程序卡死
但是有时候也会用到死循环
<code>using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace CSharp入门_循环语句
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("循环语句");
//while语句
//while (true)
//{
// Console.WriteLine("这是一个死循环");
//}
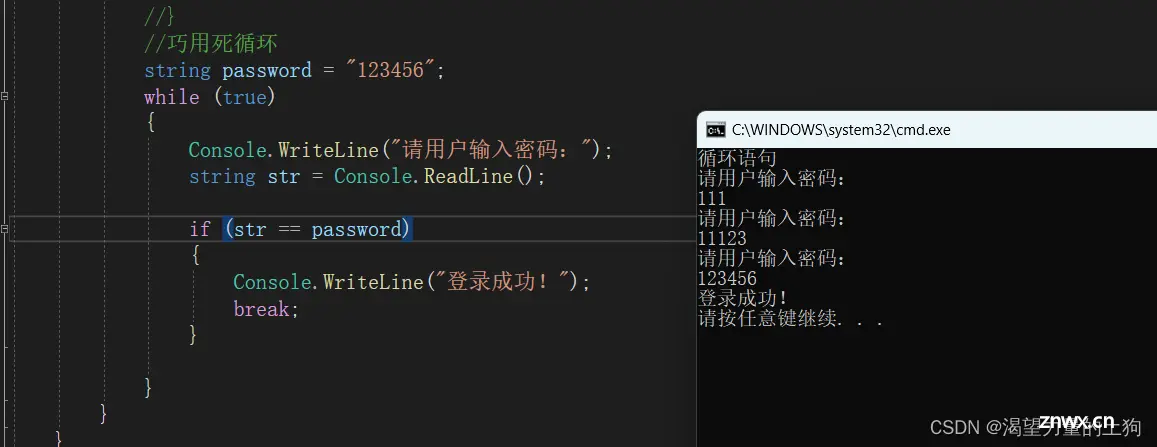
//巧用死循环
string password = "123456";
while (true)
{
Console.WriteLine("请用户输入密码:");
string str = Console.ReadLine();
if (str == password)
{
Console.WriteLine("登录成功!");
break;
}
}
}
}
}
<code>using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace CSharp入门_循环语句
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("循环语句");
//while语句
//while (true)
//{
// Console.WriteLine("这是一个死循环");
//}
//巧用死循环
string password = "123456";
while (true)
{
Console.WriteLine("请用户输入密码:");
string str = Console.ReadLine();
if (str == password)
{
Console.WriteLine("登录成功!");
break;//跳出循环
}
}
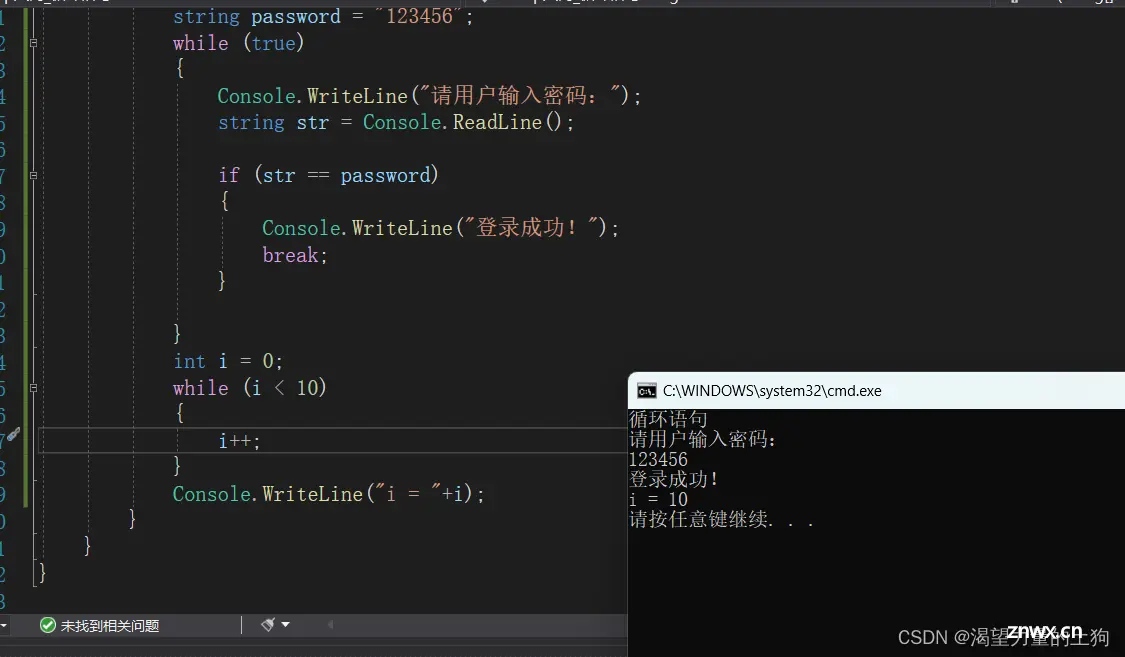
int i = 0;
while (i < 10)
{
i++;
}
Console.WriteLine("i = "+i);
}
}
}
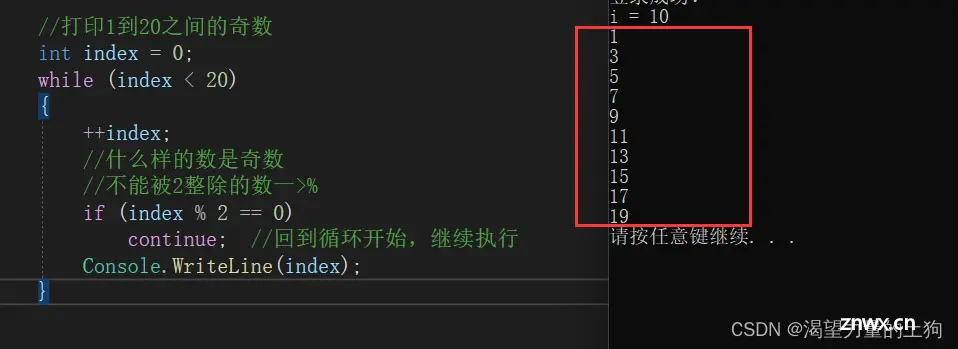
<code> //打印1到20之间的奇数
int index = 0;
while (index < 20)
{
++index;
//什么样的数是奇数
//不能被2整除的数一>%
if (index % 2 == 0)
continue; //回到循环开始,继续执行
Console.WriteLine(index);
}
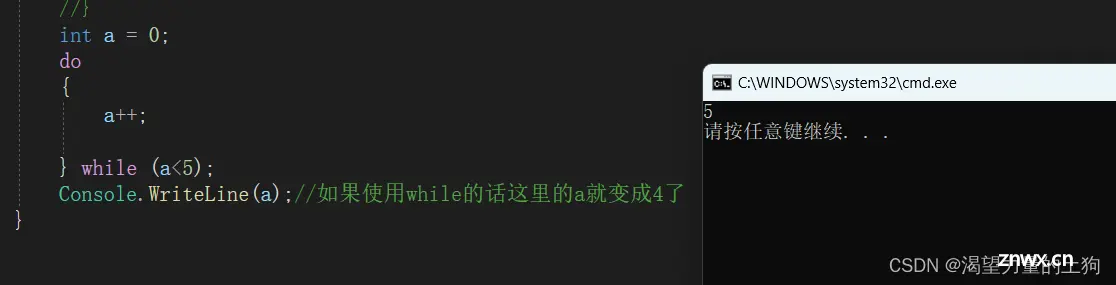
do while语句 (使用较少)
do while语句和while的不同在于do while是先执行一次再进行判断,其他基本一致。
do
{
a++;
} while (a<5);
Console.WriteLine(a);//如果使用while的话这里的a就变成4了
需要注意一点的是:continue在该语句中使用的时候是跳转到while进行判断,而不是从上到下
for循环 (最常用)
for循环特别适合在某个范围内进行取值的操作,一般while能做的,for循环都可以做
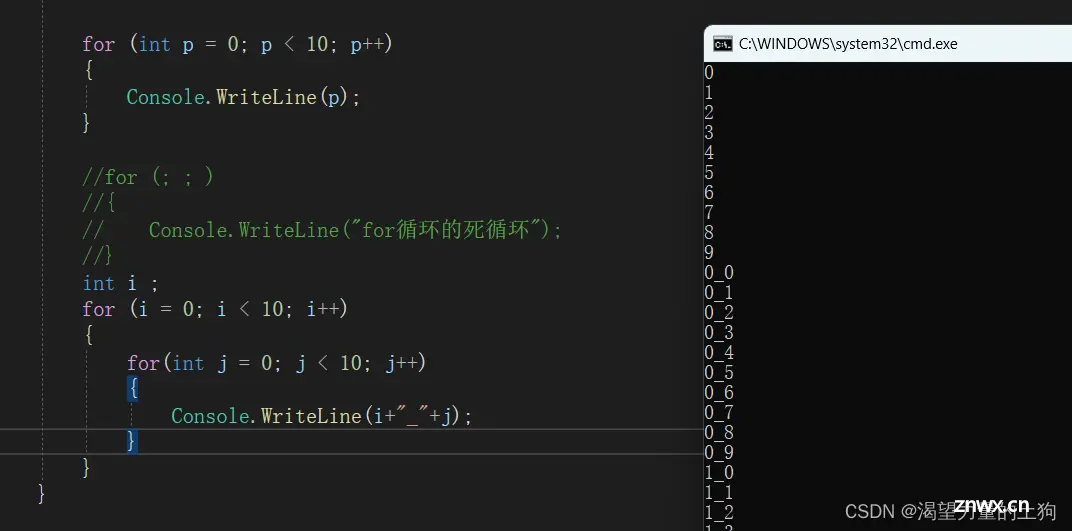
<code> for (int p = 0; p < 10; p++)
{
Console.WriteLine(p);
}
//for (; ; )
//{
// Console.WriteLine("for循环的死循环");
//}
int i ;
for (i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
for(int j = 0; j < 10; j++)
{
Console.WriteLine(i+"_"+j);
}
}
补充内容
<code>//输入一个键并赋值
char c = Console.ReadKey().KeyChar;
//输入一个键并赋值 且不在控制台显示
char c = Console.ReadKey(true).KeyChar;
//清除控制台
Console.Clear();
//设置光标位置 控制台左上角为0,0 右侧是x正方向 下方是y正方向
Console.SetCursorPosition(10,5);
//设置文字颜色
Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.Red;
//设置背景色 配合Clear使用 填充窗口颜色
Console.BackgroundColor = ConsoleColor.White;
Console.Clear();
//光标显隐
Console.CursorVisible = false;
//关闭控制台
Environment.Exit(0);
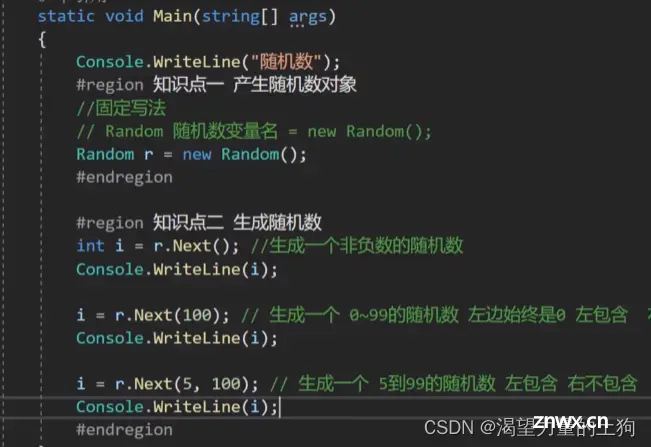
随机数
好了,C#(CSharp)入门教程到这里就基本结束了,全程都由本人在线学习进行敲的代码,可以直接拿来实验,多敲代码,才能掌握的更好哈!加油,接着学!
声明
本文内容仅代表作者观点,或转载于其他网站,本站不以此文作为商业用途
如有涉及侵权,请联系本站进行删除
转载本站原创文章,请注明来源及作者。