【C++/STL】list(常见接口、模拟实现、反向迭代器)
秦jh_ 2024-06-26 14:05:13 阅读 61
🌈个人主页:秦jh_-CSDN博客
🔥 系列专栏:https://blog.csdn.net/qinjh_/category_12575764.html?spm=1001.2014.3001.5482

目录
前言
list的常见接口
对迭代器的封装
节点
重载->
const迭代器
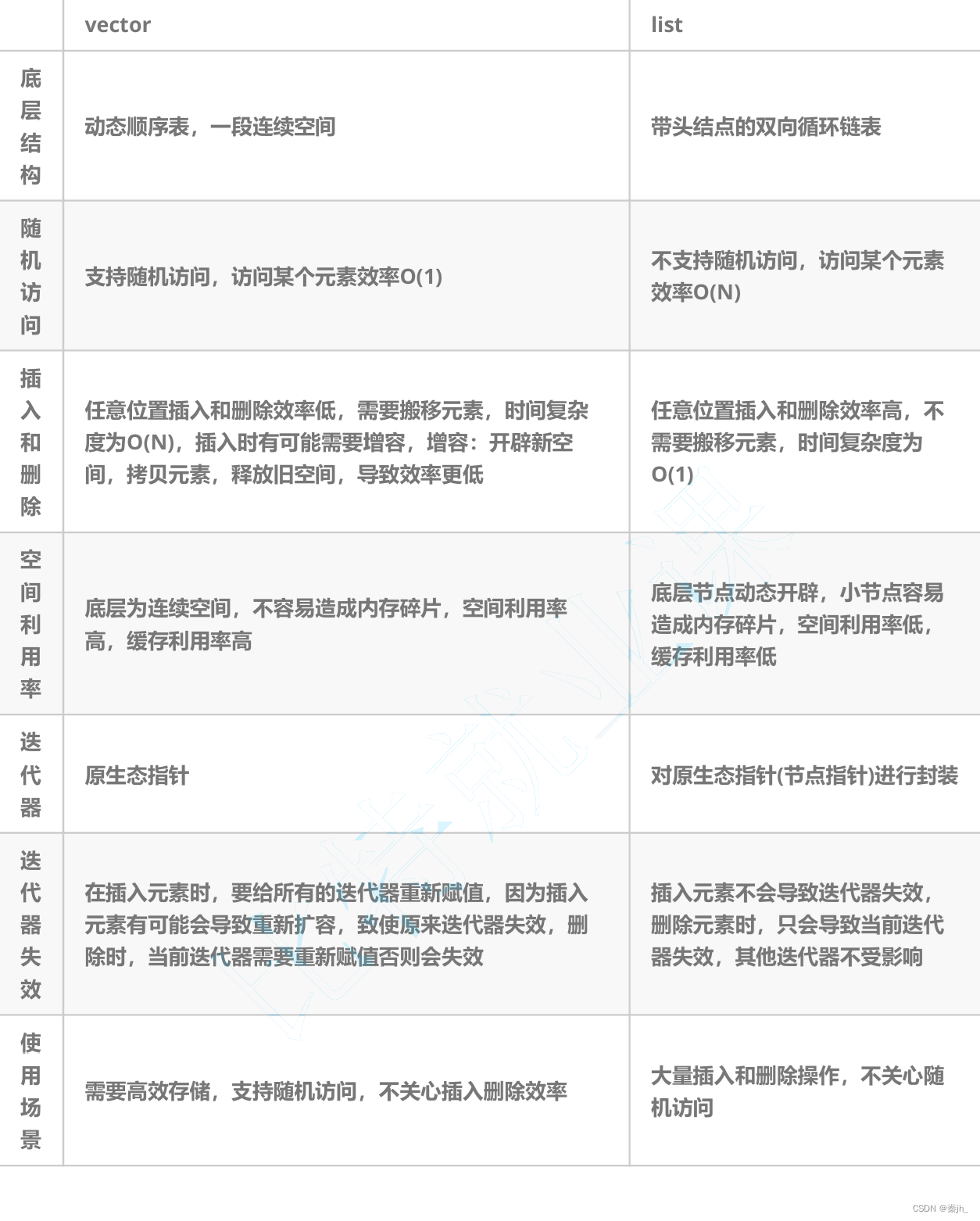
list与vector的对比
反向迭代器
反向迭代器完整代码
list完整代码
前言
💬 hello! 各位铁子们大家好哇。
今日更新了list的相关内容
🎉 欢迎大家关注🔍点赞👍收藏⭐️留言📝
list的底层是双向链表结构,双向链表中每个元素存储在互不相关的独立节点中,在节点中通过指针指向其前一个元素和后一个元素。
list的常见接口





对迭代器的封装

因为list的空间不是连续的,不能用原生指针,必须对其进行封装。
节点

重载->


当数据是自定义类型时,想通过->访问,就必须重载。
const迭代器



用const迭代器,需要重新弄一个类,而const迭代器跟普通迭代器基本一样,只修改了部分,如果为此就重新弄一个类,代码就太冗余了。
下面是进行的优化:


本质相当于写了一个类模板,编译器实例化生成了两个类。
list与vector的对比
反向迭代器
反向迭代器的++就是正向迭代器的--,反向迭代器的--就是正向迭代器的++,因此反向迭代器的实现可以借助正向迭代器,即:反向迭代器内部可以包含一个正向迭代器,对正向迭代器的接口进行 包装即可。


反向迭代器完整代码
#pragma once
//所以容器的反向迭代器
//迭代器适配器
namespace qjh
{
//vector<T>::iterator
template<class Iterator,class Ref,class Ptr> //给谁的正向迭代器,就适配出对应的反向迭代器
struct ReverseIterator
{
typedef ReverseIterator<Iterator, Ref, Ptr> Self;
Iterator _it;
ReverseIterator(Iterator it)
:_it(it)
{}
Ref operator*()
{
Iterator tmp = _it; //不能修改_it,得用临时变量放回
return *(--tmp);
}
Ptr operator->()
{
//return _it->;
//return _it.operator->();
return &(operator*());
}
Self& operator++()
{
--_it;
return *this;
}
Self& operator--()
{
++_it;
return *this;
}
bool operator!=(const Self& s)
{
return _it != s._it;
}
};
}
list完整代码
#pragma once
#include<assert.h>
#include"ReverseIterator.h"
namespace qjh
{
template<class T>
struct ListNode //需要全部被公开,用struct
{
ListNode<T>* _next;
ListNode<T>* _prev;
T _data;
ListNode(const T& x=T())
:_next(nullptr)
,_prev(nullptr)
,_data(x)
{}
};
template<class T,class Ref,class Ptr>
struct ListIterator //对指针进行封装,因为结点的空间不是连续的
{
typedef ListNode<T> Node;
typedef ListIterator<T,Ref,Ptr> Self;
Node* _node;
ListIterator(Node* node)
:_node(node)
{}
//*it
//T& operator*()
Ref operator*()
{
return _node->_data;
}
//T* operator->()
Ptr operator->()
{
return&_node->_data;
}
//++it
Self& operator++()
{
_node = _node->_next;
return *this;
}
//it++
Self& operator++(int)
{
Self tmp(*this);
_node = _node->_next;
return tmp;
}
//--it
Self& operator--()
{
_node = _node->_prev;
return *this;
}
//it--
Self& operator--(int)
{
Self tmp(*this);
_node = _node->_prev;
return tmp;
}
bool operator!=(const Self& it)
{
return _node != it._node;
}
bool operator==(const Self& it)
{
return _node == it._node;
}
};
//template<class T>
//struct ListConstIterator //对指针进行封装,因为结点的空间不是连续的
//{
//typedef ListNode<T> Node;
//typedef ListConstIterator<T> Self;
//Node* _node;
//ListConstIterator(Node* node)
//:_node(node)
//{}
////*it
//const T& operator*()
//{
//return _node->_data;
//}
//const T* operator->()
//{
//return&_node->_data;
//}
////++it
//Self& operator++()
//{
//_node = _node->_next;
//return *this;
//}
////it++
//Self& operator++(int)
//{
//Self tmp(*this);
//_node = _node->_next;
//return tmp;
//}
////--it
//Self& operator--()
//{
//_node = _node->_prev;
//return *this;
//}
////it--
//Self& operator--(int)
//{
//Self tmp(*this);
//_node = _node->_prev;
//return tmp;
//}
//bool operator!=(const Self& it)
//{
//return _node != it._node;
//}
//bool operator==(const Self& it)
//{
//return _node == it._node;
//}
//};
template<class T>
class list
{
typedef ListNode<T> Node;
public:
/*typedef ListIterator<T> iterator;
typedef ListConstIterator<T> const_iterator;*/
typedef ListIterator<T,T&,T*> iterator;
typedef ListIterator<T,const T&,const T*> const_iterator;
typedef ReverseIterator<iterator, T&, T*> reverse_iterator;
typedef ReverseIterator<const_iterator, const T&, const T*> const_reverse_iterator;
reverse_iterator rbegin()
{
return reverse_iterator(end());
}
reverse_iterator rend()
{
return reverse_iterator(begin());
}
iterator begin()
{
return iterator(_head->_next);
}
iterator end()
{
return iterator(_head);
}
//const迭代器需要迭代器指向的内容不能修改!const iterator不是我们需要的const迭代器
//const 迭代器本身可以++等操作
const_iterator begin() const
{
return const_iterator(_head->_next);
}
const_iterator end() const
{
return const_iterator(_head);
}
void empty_init()
{
_head = new Node;
_head->_next = _head;
_head->_prev = _head;
_size = 0;
}
list()
{
empty_init();
}
list(initializer_list<int> il)
{
empty_init();
for (auto& e : il)
{
push_back(e);
}
}
//lt2(lt1)
list(const list<T>& lt)
{
empty_init();
for (auto& e : lt)
{
push_back(e);
}
}
void swap(list<T>& lt)
{
std::swap(_head, lt._head);
std::swap(_size, lt._size);
}
//lt1=lt3
list<T>& operator=(list<T> lt)
{
swap(lt);
return *this;
}
void clear()
{
iterator it = begin();
while (it != end())
{
it = erase(it);
}
}
~list()
{
clear();
delete _head;
_head = nullptr;
}
//void push_back(const T& x)
//{
//Node* newnode = new Node(x);
//Node* tail = _head->_prev;
//tail->_next = newnode;
//newnode->_prev = tail;
//newnode->_next = _head;
//_head->_prev = newnode;
//}
void push_back(const T& x)
{
insert(end(), x);
}
void push_front(const T& x)
{
insert(begin(), x);
}
void pop_back()
{
erase(--end());//迭代器不能-1,只能用--
}
void pop_front()
{
erase(begin());
}
void insert(iterator pos, const T& val)
{
Node* cur = pos._node;
Node* newnode = new Node(val);
Node* prev = cur->_prev;
prev->_next = newnode;
newnode->_prev = prev;
newnode->_next = cur;
cur->_prev = newnode;
_size++;
}
iterator erase(iterator pos) //节点失效了,需要返回下一个节点
{
Node* cur = pos._node;
Node* prev = cur->_prev;
Node* next = cur->_next;
prev->_next = next;
next->_prev = prev;
delete cur;
_size--;
return iterator(next); //匿名对象
}
size_t size() const
{
return _size;
}
bool empty()
{
return _size == 0;
}
private:
Node* _head;
size_t _size;
};
void test_list1()
{
list<int> lt;
lt.push_back(1);
lt.push_back(2);
lt.push_back(3);
lt.push_back(4);
lt.push_back(5);
list<int>::iterator it = lt.begin();
while (it != lt.end())
{
cout << *it << " ";
++it;
}
cout << endl;
lt.push_front(10);
lt.push_front(20);
lt.push_front(30);
for (auto e : lt)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
lt.pop_back();
lt.pop_back();
lt.pop_front();
lt.pop_front();
for (auto e : lt)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
struct A
{
int _a1;
int _a2;
A(int a1 = 0, int a2 = 0)
:_a1(a1)
,_a2(a2)
{}
};
void test_list2()
{
list<A> lt;
A aa1(1, 1);
A aa2 = { 1, 1 };
lt.push_back(aa1);
lt.push_back(aa2);
lt.push_back(A(2,2));
lt.push_back({3,3});
lt.push_back({4,4});
list<A>::iterator it = lt.begin();
while (it != lt.end())
{
//cout << (*it)._a1 << ":" << (*it)._a2 << endl;
//cout << it->_a1 << ":" << it->_a2 << endl; //如果要遍历自定义类型,就要重载->,编译器为了可读性,省略了一个->
cout << it.operator->()->_a1 << ":" << it.operator->()->_a2 << endl;
++it;
}
cout << endl;
}
void PrintList(const list<int>& clt)
{
list<int>::const_iterator it = clt.begin();
while (it != clt.end())
{
//*it += 10;
cout << *it << " ";
++it;
}
cout << endl;
}
void test_list3()
{
list<int> lt;
lt.push_back(1);
lt.push_back(2);
lt.push_back(3);
lt.push_back(4);
lt.push_back(5);
PrintList(lt);
list<int> lt1(lt);
PrintList(lt1);
}
}
声明
本文内容仅代表作者观点,或转载于其他网站,本站不以此文作为商业用途
如有涉及侵权,请联系本站进行删除
转载本站原创文章,请注明来源及作者。