再探GraphRAG:如何提升LLM总结能力?
Florian 2024-08-08 08:13:00 阅读 55
本文对GraphRAG的灵感来源、能力透视、应用场景都做了比较优秀的解读,同时也对图技术的应用价值做了深入探讨,相信会给大家带来不一样的收获。

作者:王振亚
编者语:
自微软发布GraphRAG之后,相关解读文层出不穷,其中不乏优秀的内容。比如前段时间转载薛明同学的《微软GraphRAG框架源码解读》让大家对GraphRAG的开源代码有了快速的认识。这次我们分享一下来自蚂蚁技术同学王振亚的对GraphRAG如何提升LLM总结能力的思考,作者对GraphRAG的灵感来源、能力透视、应用场景都做了比较优秀的解读,同时也对图技术的应用价值做了深入探讨,相信此文会给大家带来不一样的收获。
注:本文经作者全权授权转载。
GraphRAG是一种基于知识图谱的检索增强生成方法。微软在7月初开源了GraphRAG项目,一个月左右的时间内,它已经获得了13k 的 stars。
相对于通常的 RAG ,GraphRAG在从多个非结构化文档中进行高层次总结和摘要方面表现更佳。例如,对于关于环境问题的文章集合,GraphRAG能更好地回答“这些文章的最主要的5个主题是什么?”这类问题。此类问题没有直接相关的文档可供 RAG 召回,因此通常的 RAG 对于这类问题很难处理。
在GraphRAG之前,也有相关方案处理此类问题。例如,《RAPTOR: RECURSIVE ABSTRACTIVE PROCESSING FOR TREE-ORGANIZED RETRIEVAL》论文中提到的方法,通过对文档进行聚类,并基于不同的抽象层级进行多个层级的聚类,聚类后进行摘要总结,以供后续的 RAG 召回。文章后续部分对 RAPTOR 进行了详细介绍。
GraphRAG的方法与 RAPTOR 方法有何不同?除了摘要总结类问题,GraphRAG在什么问题处理中也具备优势?GraphRAG目前有什么不足?GraphRAG的设计给我们设计 RAG 系统带来了哪些启示?
本文围绕上述问题,对GraphRAG进行分析和介绍。文章开始部分对GraphRAG解决的问题和设计初衷做简单介绍,第二章节主要围绕GraphRAG的原理和概念展开,最后一部分是一些观点和想法。
GraphRAG并没有“原创性”的创新,而是巧妙地组合了之前已经存在的技术。涉及的技术包括 LLM 、知识图谱、社区检测与聚合算法,还使用了一些 Map-Reduce 的思想。
GraphRAG的设计精髓可以用其对应论文《From Local to Global: A Graph RAG Approach to Query-Focused Summarization》中的一句话概括:“Use the natural modularity of graphs to partition data for global summarization.”
下文会围绕这句话,进行展开解释。
1. Why GraphRAG?
1.1 GraphRAG在解决什么问题?
引用 GraphRAG: Advanced Data Retrieval for Enhanced Insights 文中表述:
1. Complex Information Traversal: It excels at connecting different pieces of information to provide new, synthesized insights.
2. Holistic Understanding: It performs better at understanding and summarizing large data collections, offering a more comprehensive grasp of the information.
第二点 “Holistic Understanding” 是文章开始提到的“摘要总结”能力,即处理 QFS ( query focused summarization ) 问题的能力,需要跨多个文档进行高层次的总结和抽象。GraphRAG的论文中主要表述了这一点,并且通过分析其代码,可以看到大量设计也是围绕这一能力展开。
第一点是通过知识图谱提升的能力。GraphRAG在构建知识图谱时(下一章节将详细介绍),通过知识图谱将分布在不同文章和信息片段中的信息关联起来。在查询时,能召回相关的预料信息,而通常的 RAG 由于没有预先构建的知识图谱,无法完全召回所需的预料。对于需要结合多个语料才能回答的问题,GraphRAG表现更佳。
论文中主要讨论的是摘要总结能力的增强,GraphRAG的评估也是围绕这一能力进行的。“Complex Information Traversal” 能力结合多个片段信息,提供新的洞察力,在进行 QFS 时也会用到。
1.2 不能使用超大上下文的 LLM 进行摘要总结么?
Claude 3 模型上下文为 200K ,可以直接将所有文章一次性提供给 LLM 进行摘要总结么?这样做有两个问题。
一是上下文大小的限制,200K 的 token 限制在处理大量语料时仍可能不够。成千上万篇独立文档的 token 数量很容易超过这一限制。而且,每次处理几十万 token 的时间和计算成本都过高。后文会介绍,GraphRAG采用分层摘要,即中间数据在一次计算后可以重复使用。
二是目前的 LLM 随着上下文变长,会表现出“找不到重点”或“忽略一些信息”的问题。GraphRAG论文中对此有所表述:
The challenge remains, however, for query-focused abstractive summarization over an entire corpus. Such volumes of text can greatly exceed the limits of LLM context windows, and the expansion of such windows may not be enough given that information can be “lost in the middle” of longer contexts (Kuratov et al., 2024; Liu et al., 2023).
1.3 与 RAPTOR 相比,有何差异?
RAPTOR 设计初衷,也是为了解决 QFS 问题,实现的原理,参考RAPTOR论文:

RAPTOR 在 query 前先进行多层树的构建,其构建的几点说明如下:
- 由最底层的 Text chunk 向上进行聚类,聚类后使用 LLM 进行 summary ,节点中保存 summary 后的信息。
- 聚类是“soft clustering”的:一个 Text chunk 可以被聚类到多个组中。
- 聚类是基于 embedding 的 vector 进行的。
- 聚类算法先使用了 Uniform Manifold Approximation and Projection (UMAP) 对 vector 进行降维,然后使用类似 Gaussian Mixture Models (GMMs) 的方法进行聚类。
通过这样构建一个多层的树,用户在进行 query 时,可以基于不同问题的层次,使用树的不同层生成的 summary 信息放入 LLM 的上下文中进行推理回答,从而对一些相对抽象、总结类的问题提供更好的回答。
RAPTOR 与GraphRAG相比,最大差异是什么?差异在于聚类的方式不同。GraphRAG是通过构建知识图谱,然后基于图谱间节点的关联关系进行多层聚类(“Use the natural modularity of graphs to partition data for global summarization”),而 RAPTOR 的聚类还是基于 embedding 后的结果进行的聚类。
两者究竟在效果上有多大差异,暂未找到直接的数据比对。但是从原理上分析,个人倾向于GraphRAG的方式。从之前使用传统 RAG 方式的项目实践来看,目前 embedding 召回的效果并不理想。如果 embedding 效果不理想,那么基于 embedding 的聚类从理论上分析也会存在不少问题(这些都只是个人分析,实践中需要进行对比评估)。
GraphRAG是如何构建知识图谱,以及如何基于图谱节点关系进行聚合?下一章节会展开介绍。
2. GraphRAG介绍
前文提到,GraphRAG与 RAPTOR 类似,需要预先对文档进行处理,进行分层聚类和总结,在 Query 时使用构建出的数据放入 LLM 上下文进行推理。GraphRAG可以分为 Indexing 和 Query 两个部分。
2.1 Indexing
2.1.1 基本流程
类似于基于倒排算法的搜索引擎,搜索引擎需要对所有爬取到的文档进行切词、构建倒排索引,以便后续的关键词搜索阶段使用。GraphRAG也需要对所有文档进行处理,但不是通过切词构建倒排索引,而是使用 LLM 基于特殊 prompt 处理,提取实体和关系,构建知识图谱。
构建知识图谱的目的,并不仅仅是为了在进行 RAG 推理时增加 LLM 上下文的关联关系,而是为了进行多层的聚类,为更好地回答用户的 QFS 问题准备中间数据。
GraphRAG内置了一套完整的 pipeline,在 indexing 阶段,主要流程如下:
- 基于原始文本提取实体、关系和 claims (实体与其他实体之间关系的具体描述)。
- 对实体进行 community detection (社区检测,可以简单理解为聚类)。
- 在多个粒度级别生成 community summaries 和 community reports (比 summaries 更详细)。
- 将实体 embedding 到图向量空间中。
- 将文本片段 embedding 到文本向量空间中。
构建出的知识图谱结构可视化后的 Demo:

几点说明:
- 相同颜色的是同一个 community 。
- community 是分层的,左侧是高一层级的 communities,颜色的个数相对右侧的 Sub-communities 会少很多。这点与 RAPTOR 中的分层类似。
- 与 RAPTOR 类似,也是由下向上进行的聚类。
- 算法使用的是 Leiden。
2.1.2 Indexing Dataflow分析
参考官方文档:Indexing Dataflow,主要过程如下:

不再详细展开,不少阶段通过名字能了解大概功能,如需详细了解可以直接参考官方文档。几个从名字可能看不出在做何处理、需要关注的点说明如下:
- Phase 3: Graph Augmentation 阶段,对图的结构进行了一次 embedding( Node2Vec algorithm ),方便在后续的 Query 阶段能召回相关联的信息。
- Phase 4: Community Summarization 阶段,同样对 Community Summarization 进行了 embedding,也是为后续的 query 做召回使用。
- Phase 5: Document Processing 阶段,把 Text Units 与 Document 的关联关系保存到图谱中。这样在后续 LLM 推理时,上下文中有此关系,输出的结果可以明确说明是基于哪些文档生成的。一方面可以在测评时基于原始文档判断 LLM 生成的内容是否有幻觉,另一方面在需要进一步了解详细信息时可以直接链接过去查看。
- Phase 6: Network Visualization 阶段,由于生成的图谱一般不是一个平面图(可以通过在平面上绘制其顶点和边而不出现边的交叉),通过使用 UMAP(一种降维技术)操作将非平面图映射到平面上,可以更直观地观察和理解数据的结构和模式。
2.2 Query
与 RAPTOR 相比,GraphRAG在 query 时也会根据问题使用不同的聚类层级。但不同的是,GraphRAG定义了两种差异非常大的 query 方式。
一种是 Local Search ,用于处理具体的、相对关注细节的问题。这种 query 时使用的上下文内容主要是知识图谱中的内容和原始的 Text Units 。把这些信息合并后,一次构建上下文调用 LLM 进行推理。
另一种是 Global Search ,主要用于处理摘要总结类、相对抽象的问题。query 时使用 Community Report ,由于 Community Report 的 token 量大,无法一次放入上下文中,为了避免信息丢失,采用了 Map-Reduce 的方式。
下面对这两种方式做简单介绍。
2.2.1 Local Search

从上面的 dataflow 可以看出,上下文中的内容种类非常多。首先,使用用户 query 从知识图谱中通过 embedding 方式获取相关的实体,然后将实体相关的多种信息进行排序,选取部分放入上下文中,具体包括:
- 关联的原始文本(Text Units)
- 实体关联的 Community Reports
- 相关联的实体(Entities)
- 实体相关的关系信息
- 实体的属性(Covariates,例如,实体是苹果,颜色可以理解为一个属性)
再加上会话历史,一次 query 使用的 token 比通常的 RAG 方式要多不少。
构造上下文的代码 build_context,和 dataflow 中一致。构造 context 后推理使用的 prompt 如下:
<code>"""Local search system prompts."""
LOCAL_SEARCH_SYSTEM_PROMPT = """
---Role---
You are a helpful assistant responding to questions about data in the tables provided.
---Goal---
Generate a response of the target length and format that responds to the user's question, summarizing all information in the input data tables appropriate for the response length and format, and incorporating any relevant general knowledge.
If you don't know the answer, just say so. Do not make anything up.
Points supported by data should list their data references as follows:
"This is an example sentence supported by multiple data references [Data: <dataset name> (record ids); <dataset name> (record ids)]."
Do not list more than 5 record ids in a single reference. Instead, list the top 5 most relevant record ids and add "+more" to indicate that there are more.
For example:
"Person X is the owner of Company Y and subject to many allegations of wrongdoing [Data: Sources (15, 16), Reports (1), Entities (5, 7); Relationships (23); Claims (2, 7, 34, 46, 64, +more)]."
where 15, 16, 1, 5, 7, 23, 2, 7, 34, 46, and 64 represent the id (not the index) of the relevant data record.
Do not include information where the supporting evidence for it is not provided.
---Target response length and format---
{response_type}
---Data tables---
{context_data}
---Goal---
Generate a response of the target length and format that responds to the user's question, summarizing all information in the input data tables appropriate for the response length and format, and incorporating any relevant general knowledge.
If you don't know the answer, just say so. Do not make anything up.
Points supported by data should list their data references as follows:
"This is an example sentence supported by multiple data references [Data: <dataset name> (record ids); <dataset name> (record ids)]."
Do not list more than 5 record ids in a single reference. Instead, list the top 5 most relevant record ids and add "+more" to indicate that there are more.
For example:
"Person X is the owner of Company Y and subject to many allegations of wrongdoing [Data: Sources (15, 16), Reports (1), Entities (5, 7); Relationships (23); Claims (2, 7, 34, 46, 64, +more)]."
where 15, 16, 1, 5, 7, 23, 2, 7, 34, 46, and 64 represent the id (not the index) of the relevant data record.
Do not include information where the supporting evidence for it is not provided.
---Target response length and format---
{response_type}
Add sections and commentary to the response as appropriate for the length and format. Style the response in markdown.
"""
其中 {context_data} 为占位符变量,具体值为上述 dataflow 构造出的 context。
一次 Local Search 调用一次 LLM 即可,但 Global Search 一次 Query 可能会调用十几次 LLM,下面分析下 Global Search 是如何处理的。
2.2.2 Global Search
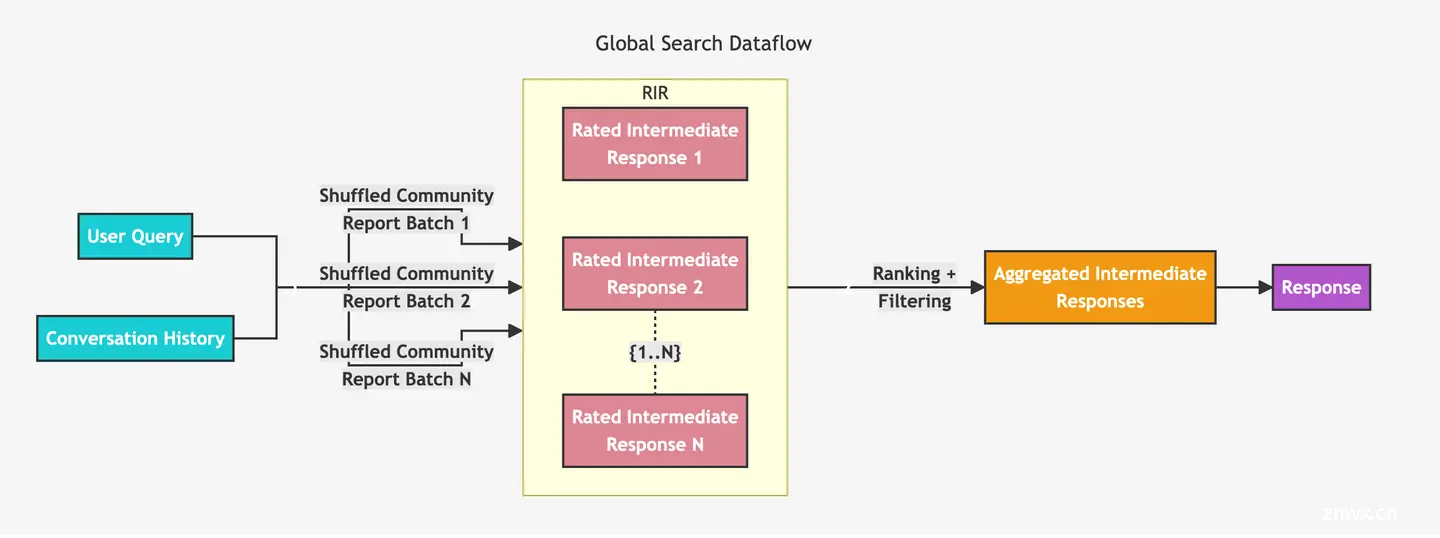
前文提到,Global Search 使用的 context 与 Local Search 差异很大。Global Search 使用特定层次的 Community Report 的集合。由于单个上下文可能无法容纳这些 Community Reports,需要进行 MapReduce 操作:
- 把 Community Reports 切分为多个部分,然后每个部分基于用户 query 使用 LLM 并发进行推理,每个部分总结几个主要的总结点。在推理总结时,会让 LLM 生成权重,方便最后进行 reduce 操作。
- 把每个部分推理的结果进行合并,将所有总结点进行 reduce 操作——再次使用 LLM 进行摘要总结。
map 阶段的 prompt:
<code>"""System prompts for global search."""
MAP_SYSTEM_PROMPT = """
---Role---
You are a helpful assistant responding to questions about data in the tables provided.
---Goal---
Generate a response consisting of a list of key points that responds to the user's question, summarizing all relevant information in the input data tables.
You should use the data provided in the data tables below as the primary context for generating the response.
If you don't know the answer or if the input data tables do not contain sufficient information to provide an answer, just say so. Do not make anything up.
Each key point in the response should have the following element:
- Description: A comprehensive description of the point.
- Importance Score: An integer score between 0-100 that indicates how important the point is in answering the user's question. An 'I don't know' type of response should have a score of 0.
The response should be JSON formatted as follows:
{{
"points": [
{{"description": "Description of point 1 [Data: Reports (report ids)]", "score": score_value}},
{{"description": "Description of point 2 [Data: Reports (report ids)]", "score": score_value}}
]
}}
The response shall preserve the original meaning and use of modal verbs such as "shall", "may" or "will".
Points supported by data should list the relevant reports as references as follows:
"This is an example sentence supported by data references [Data: Reports (report ids)]"
**Do not list more than 5 record ids in a single reference**. Instead, list the top 5 most relevant record ids and add "+more" to indicate that there are more.
For example:
"Person X is the owner of Company Y and subject to many allegations of wrongdoing [Data: Reports (2, 7, 64, 46, 34, +more)]. He is also CEO of company X [Data: Reports (1, 3)]"
where 1, 2, 3, 7, 34, 46, and 64 represent the id (not the index) of the relevant data report in the provided tables.
Do not include information where the supporting evidence for it is not provided.
---Data tables---
{context_data}
---Goal---
Generate a response consisting of a list of key points that responds to the user's question, summarizing all relevant information in the input data tables.
You should use the data provided in the data tables below as the primary context for generating the response.
If you don't know the answer or if the input data tables do not contain sufficient information to provide an answer, just say so. Do not make anything up.
Each key point in the response should have the following element:
- Description: A comprehensive description of the point.
- Importance Score: An integer score between 0-100 that indicates how important the point is in answering the user's question. An 'I don't know' type of response should have a score of 0.
The response shall preserve the original meaning and use of modal verbs such as "shall", "may" or "will".
Points supported by data should list the relevant reports as references as follows:
"This is an example sentence supported by data references [Data: Reports (report ids)]"
**Do not list more than 5 record ids in a single reference**. Instead, list the top 5 most relevant record ids and add "+more" to indicate that there are more.
For example:
"Person X is the owner of Company Y and subject to many allegations of wrongdoing [Data: Reports (2, 7, 64, 46, 34, +more)]. He is also CEO of company X [Data: Reports (1, 3)]"
where 1, 2, 3, 7, 34, 46, and 64 represent the id (not the index) of the relevant data report in the provided tables.
Do not include information where the supporting evidence for it is not provided.
The response should be JSON formatted as follows:
{{
"points": [
{{"description": "Description of point 1 [Data: Reports (report ids)]", "score": score_value}},
{{"description": "Description of point 2 [Data: Reports (report ids)]", "score": score_value}}
]
}}
"""
从上面 prompt 可以看出输出的结果是JSON格式的:
{
{
"points": [
{
{
"description": "Description of point 1 [Data: Reports (report ids)]",
"score": score_value
}
},
{
{
"description": "Description of point 2 [Data: Reports (report ids)]",
"score": score_value
}
}
]
}
}
reduce 阶段的 prompt:
"""Global Search system prompts."""
REDUCE_SYSTEM_PROMPT = """
---Role---
You are a helpful assistant responding to questions about a dataset by synthesizing perspectives from multiple analysts.
---Goal---
Generate a response of the target length and format that responds to the user's question, summarize all the reports from multiple analysts who focused on different parts of the dataset.
Note that the analysts' reports provided below are ranked in the **descending order of importance**.
If you don't know the answer or if the provided reports do not contain sufficient information to provide an answer, just say so. Do not make anything up.
The final response should remove all irrelevant information from the analysts' reports and merge the cleaned information into a comprehensive answer that provides explanations of all the key points and implications appropriate for the response length and format.
Add sections and commentary to the response as appropriate for the length and format. Style the response in markdown.
The response shall preserve the original meaning and use of modal verbs such as "shall", "may" or "will".
The response should also preserve all the data references previously included in the analysts' reports, but do not mention the roles of multiple analysts in the analysis process.
**Do not list more than 5 record ids in a single reference**. Instead, list the top 5 most relevant record ids and add "+more" to indicate that there are more.
For example:
"Person X is the owner of Company Y and subject to many allegations of wrongdoing [Data: Reports (2, 7, 34, 46, 64, +more)]. He is also CEO of company X [Data: Reports (1, 3)]"
where 1, 2, 3, 7, 34, 46, and 64 represent the id (not the index) of the relevant data record.
Do not include information where the supporting evidence for it is not provided.
---Target response length and format---
{response_type}
---Analyst Reports---
{report_data}
---Goal---
Generate a response of the target length and format that responds to the user's question, summarize all the reports from multiple analysts who focused on different parts of the dataset.
Note that the analysts' reports provided below are ranked in the **descending order of importance**.
If you don't know the answer or if the provided reports do not contain sufficient information to provide an answer, just say so. Do not make anything up.
The final response should remove all irrelevant information from the analysts' reports and merge the cleaned information into a comprehensive answer that provides explanations of all the key points and implications appropriate for the response length and format.
The response shall preserve the original meaning and use of modal verbs such as "shall", "may" or "will".
The response should also preserve all the data references previously included in the analysts' reports, but do not mention the roles of multiple analysts in the analysis process.
**Do not list more than 5 record ids in a single reference**. Instead, list the top 5 most relevant record ids and add "+more" to indicate that there are more.
For example:
"Person X is the owner of Company Y and subject to many allegations of wrongdoing [Data: Reports (2, 7, 34, 46, 64, +more)]. He is also CEO of company X [Data: Reports (1, 3)]"
where 1, 2, 3, 7, 34, 46, and 64 represent the id (not the index) of the relevant data record.
Do not include information where the supporting evidence for it is not provided.
---Target response length and format---
{response_type}
Add sections and commentary to the response as appropriate for the length and format. Style the response in markdown.
"""
NO_DATA_ANSWER = (
"I am sorry but I am unable to answer this question given the provided data."
)
GENERAL_KNOWLEDGE_INSTRUCTION = """
The response may also include relevant real-world knowledge outside the dataset, but it must be explicitly annotated with a verification tag [LLM: verify]. For example:
"This is an example sentence supported by real-world knowledge [LLM: verify]."
"""
prompt 中 “Note that the analysts' reports provided below are ranked in the descending order of importance.” 表示在给到 LLM 前,已经把 map 阶段的信息根据评分进行降序排列。
以上是 Global Search 的主要过程。除了进行不同层次问题的 Query,由于使用了知识图谱,GraphRAG还可以进行问题推荐,下一小节简单分析此能力。
2.3 Question Generation
由于使用知识图谱,构建了复杂的关系连接,还可以使用这些连接进行问题推荐。例如用户提问 “杭州旅游去哪里?” 可以基于图谱中的关系推荐出类似“杭州有哪些美食/历史名人?”的问题。
在GraphRAG之前,不少推荐系统中已利用知识图谱进行推荐。稍有差异的是,GraphRAG使用了 LLM 生成和一些独特的上下文。在GraphRAG中,问题推荐使用的上下文与 Local Search 一样,使用的 prompt 如下:
"""Question Generation system prompts."""
QUESTION_SYSTEM_PROMPT = """
---Role---
You are a helpful assistant generating a bulleted list of {question_count} questions about data in the tables provided.
---Data tables---
{context_data}
---Goal---
Given a series of example questions provided by the user, generate a bulleted list of {question_count} candidates for the next question. Use - marks as bullet points.
These candidate questions should represent the most important or urgent information content or themes in the data tables.
The candidate questions should be answerable using the data tables provided, but should not mention any specific data fields or data tables in the question text.
If the user's questions reference several named entities, then each candidate question should reference all named entities.
---Example questions---
"""
2.4 小结
通过几个问题简单总结,结束本章节的介绍。
2.4.1 GraphRAG、RAG、RAPTOR 有何区别?
| GraphRAG | RAG | RAPTOR | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 适用场景 | 1. 具体问题 2. 总结类问题 | 1. 具体问题 2. 总结类问题效果差 | 总结类问题 |
| 预处理 | 1. 使用 LLM 构建知识图谱 2. 知识图谱中的节点进行 embedding 3. 基于知识图谱使用社区聚类算法与 LLM 构建多层的 community 结构,并进行 embedding | 文本切片,embedding处理 | 1. 构建多层的 cluster 2. 对cluster 中的文本 embedding |
| 预处理成本 | 1. 非常高,需要把所有文本切片通过 LLM 构建知识图谱 2. 构建 community 也需要使用 LLM | 低,只需要低成本的 embedding | 高,需要把所有的文本 LLM 进行多层 summary |
| Query | 1. 有显著的两种Query,Local Search、Global Search 2. Global Search 需要通过并发MR,多次调用 LLM | 1. 单一方式 Query一次 2. Query 一次 LLM | 1. 单一方式,但可以通过不同层级的 cluster 进行 2. 一次 Query 一次 LLM |
| Query 成本 | 1. Local Search 高(需要多种信息的上下文 2. Global Search 非常高,大量上下文,多次 LLM | 低,embedding 出的文本放入上下文即可 | 一般,cluster 中内容放入上下文 |
2.4.2 GraphRAG构建的知识图谱与一般知识图谱有何区别?
| GraphRAG构建的知识图谱 | 一般的知识图谱 | |
|---|---|---|
| 构建方式 | 使用 LLM 构建 | 一般通过机器学习算法 |
| 节点、边 | 实体、关系的model中,有详细的description、description的 Embedding,可参考代码:entity、relationship | 一般是简单的description ,没有 embedding 信息 |
| 推理 | 可以把关系、实体、及其描述放到 LLM 的上下文中,使用 LLM 来进行“间接”推理 | 推理的时候有规范的输入要求,比如“中国” + “国旗”作为具体推理条件 |
| 如何使用 | 1. 基于知识图谱,使用社区聚类算法,构建多层的 community 2. 推荐问题生成 | 比较宽泛,如搜索引擎优化、推荐、金融风控中的反洗钱与欺诈识别 |
3. 一些想法与观点
3.1 正确性优于响应时间
这个观点在之前介绍 Agency Workflow(TODO) 时有所提及,而在学习GraphRAG过程中再次思考了这个问题。GraphRAG的 Indexing 构建过程和 Query 过程都可以理解为是一种 workflow。
查看官方文档的 Global Query 部分时,看到采用 Map-Reduce 方式,第一反应是“耗时”(MR 与耗时长没有必然关系,只是日常 QDPS 做离线分析相对较慢,形成了自己的认知谬误)。耗时长不一定是问题,就像 QDPS 做离线数据分析一样,需要平衡准确性、成本与耗时。
“正确性优于响应时间”应是部分 LLM 产品的设计理念,但很少有 LLM 产品是基于这一理念设计的。不少产品设计中,过多关注响应时间,而忽视了用户体验的另一个重要维度——准确性。
然而,将“正确性优于响应时间”的理念付诸实践,可能会遇到以下挑战:
- 产品设计团队的接受度:响应时间可能从原先的秒级延长到分钟甚至小时级别。对于产品设计人员来说,在其他产品都追求秒级响应时,设计出一个响应时间为分钟级别的产品无疑面临巨大挑战。
- 高成本问题:如果一个任务需要 LLM 进行多环节、多次迭代的推理,这会消耗大量计算资源,每次任务的成本可能高达几十元人民币,从而带来不小的成本压力。
- 用户体验保障:随着响应时间的增加,如何尽可能维持良好的用户体验成为一大问题。是提供给用户多种选择(即选择响应时间长但准确率更高,或响应时间短但质量一般的选项),还是改变产品交互方式,采用离线处理?
“正确性优于响应时间”并不只是一个技术上的折中策略,随着 LLM 应用越来越普及,这会成为越来越多产品的设计理念。在用户通过使用这种“高耗时”产品得到质量更好、准确率更高的结果后,“正确性优于响应时间”也会被用户慢慢接受为一种产品设计。
3.2 Graph 可以用于实现 Query 改写
在不少对话中,为了实现更好效果,会对用户 query 进行改写。有一种改写方式类似“扩展”,比如“介绍下杭州”这类问题,会把这个问题先拆成几个小问题,比如“杭州的地理信息”、“杭州的经济情况”、“杭州的历史文化信息”,然后分别用这三个问题做 embedding,把 embedding 的信息放入 LLM 进行推理,而不是直接使用“介绍下杭州”的 embedding 向量匹配去召回文本,这样有可能召回不到,或召回的信息不全面。
将一个大问题拆成几个小问题,召回语料并进行 summary 的方式,也能提高使用 RAG 提高摘要总结类问题的全面性。而拆解问题时,也可以利用知识图谱中的实体关系。
3.3 图是 QA 库最佳的数据结构
在 LLM 之前,对话机器人会维护很多“意图”到“标准回答”的映射。当前不少使用 LLM 的对话机器人,为了防止 LLM 幻觉、提高性能,在用户输入的意图非常明确的情况下,也会维护不少 QA 问题(问题——标准答案的一对文本),在能够意图或语义匹配时,能快速返回。
这种人工维护的 QA 库,QA 之间的关系,使用图是最佳的数据结构。一般 QA 也是围绕一些主题(实体)多层次、多个方面的问题。在使用 LLM 能力的情况下,无论是进行相关问题的推荐、用户 query 的扩充,还是摘要总结类的回答,使用图结构都可以容易获取更多关联的上下文,从而在使用 LLM 推理时得到更好的结果。
3.4 GraphRAG的适用场景
3.4.1 数据分析:趋势分析/舆情感知
对大量文本进行趋势分析非常适合使用GraphRAG。通过由下至上构建知识图谱,可以很容易发现热点趋势、新增的主题,并且通过社区聚类,还能给出非常系统的趋势说明和分析。
3.4.2 专业领域对客机器人
专业领域的知识往往是系统的、多层结构的。如果要对专业问题进行深入回答,不仅需要高质量的语料,还需要能表示语料之间的关系,从而回答不同层次的问题。专业领域的知识相对有限,构建类似的知识图谱成本可控。
4. 总结
本文介绍了GraphRAG的基本原理与解决的问题。
这种对大量分散材料进行分析、总结的场景,在 LLM 的上下文能力有重大突破之前,GraphRAG是少有的、非常实用的方案。
如果工作中涉及对大量文本提取观点、感知趋势,GraphRAG是非常值得投入时间研究的项目。
以上,感谢阅读。
5. 参考
- Github地址:https://github.com/microsoft/graphrag
- 论文地址:https://arxiv.org/pdf/2404.16130
- 微软Blog:https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/research/blog/graphrag-unlocking-llm-discovery-on-narrative-private-data/
- 官方文档:https://microsoft.github.io/graphrag/
- GraphRAG介绍:https://bhavikjikadara.medium.com/graphrag-advanced-data-retrieval-for-enhanced-insights-bcef777404d2
- RAPTOR论文:https://arxiv.org/pdf/2401.18059
- LangChain实现RAPTOR:https://github.com/langchain-ai/langchain/blob/master/cookbook/RAPTOR.ipynb
- LangChain实现RAPTOR视频:https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=jbGchdTL7d0
声明
本文内容仅代表作者观点,或转载于其他网站,本站不以此文作为商业用途
如有涉及侵权,请联系本站进行删除
转载本站原创文章,请注明来源及作者。