一文搞定WeakHashMap
cnblogs 2024-09-19 08:09:14 阅读 100
写在前面
在缓存场景下,由于内存是有限的,不能缓存所有对象,因此就需要一定的删除机制,淘汰掉一些对象。这个时候可能很快就想到了各种Cache数据过期策略,目前也有一些优秀的包提供了功能丰富的Cache,比如Google的Guava Cache,它支持数据定期过期、LRU、LFU等策略,但它仍然有可能会导致有用的数据被淘汰,没用的数据迟迟不淘汰(如果策略使用得当的情况下这都是小概率事件)。
现在有种机制,可以让Cache里不用的key数据自动清理掉,用的还留着,不会出现误删除。而WeakHashMap 就适用于这种缓存的场景,因为它有自清理机制!
如果让你手动实现一种自清理的HashMap,可以怎么做?首先肯定是想办法先知道某个Key肯定没有在用了,然后清理掉HashMap中没有在用的对应的K-V。在JVM里一个对象没用了是指没有任何其他有用对象直接或者间接执行它,具体点就是在GC过程中它是GCRoots不可达的。而某个弱引用对象所指向的对象如果被判定为垃圾对象,Jvm会将该弱引用对象放到一个ReferenceQueue里,只需要看下这个Queue里的内容就知道某个对象还有没有用了。
WeakHashMap概述
从WeakHashMap名字也可以知道,这是一个弱引用的Map,当进行GC回收时,弱引用指向的对象会被GC回收。
WeakHashMap正是由于使用的是弱引用,因此它的对象可能被随时回收。更直观的说,当使用 WeakHashMap 时,即使没有显示的添加或删除任何元素,也可能发生如下情况:
调用两次size()方法返回不同的值;
两次调用isEmpty()方法,第一次返回false,第二次返回true;
两次调用containsKey()方法,第一次返回true,第二次返回false,尽管两次使用的是同一个key;
两次调用get()方法,第一次返回一个value,第二次返回null,尽管两次使用的是同一个对象。

从上图可以看出:
WeakHashMap继承于AbstractMap,并且实现了Map接口。
WeakHashMap是哈希表,但是它的键是"弱键"。WeakHashMap中保护几个重要的成员变量:table, size, threshold, loadFactor, modCount, queue。
table是一个Entry[]数组类型,而Entry实际上就是一个单向链表。哈希表的"key-value键值对"都是存储在Entry数组中的。
size是Hashtable的大小,它是Hashtable保存的键值对的数量。
threshold是Hashtable的阈值,用于判断是否需要调整Hashtable的容量。threshold的值="容量*加载因子"。
loadFactor就是加载因子。
modCount是用来实现fail-fast机制的
queue保存的是“已被GC清除”的“弱引用的键”。
基本用法
<code>WeakHashMap < String, String > weakHashMap = new WeakHashMap < > (10);
String key0 = new String("str1");
String key1 = new String("str2");
String key2 = new String("str3");
// 存放元素
weakHashMap.put(key0, "data1");
weakHashMap.put(key1, "data2");
weakHashMap.put(key2, "data3");
System.out.printf("weakHashMap: %s\n", weakHashMap);
// 是否包含某key
System.out.printf("contains key str1 : %s\n", weakHashMap.containsKey(key0));
System.out.printf("contains key str2 : %s\n", weakHashMap.containsKey(key1));
// 移除key
weakHashMap.remove(key0);
System.out.printf("weakHashMap after remove: %s\n", weakHashMap);
// 这意味着"弱键"key1再没有被其它对象引用,调用gc时会回收WeakHashMap中与key1对应的键值对
key1 = null;
// 内存回收,这里会回收WeakHashMap中与"key0"对应的键值对
System.gc();
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
// 遍历WeakHashMap
for (Map.Entry < String, String > m: weakHashMap.entrySet()) {
System.out.printf("next : %s >>> %s\n", m.getKey(), m.getValue());
}
// 打印WeakHashMap的实际大小
System.out.printf("after gc WeakHashMap size: %s\n", weakHashMap.size());
底层源码
构造器
// 默认构造函数。
WeakHashMap()
// 指定“容量大小”的构造函数
WeakHashMap(int capacity)
// 指定“容量大小”和“加载因子”的构造函数
WeakHashMap(int capacity, float loadFactor)
// 包含“子Map”的构造函数
WeakHashMap(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> map)
从WeakHashMap的继承关系上来看,可知其继承AbstractMap,实现了Map接口。其底层数据结构是Entry数组,Entry的数据结构如下:
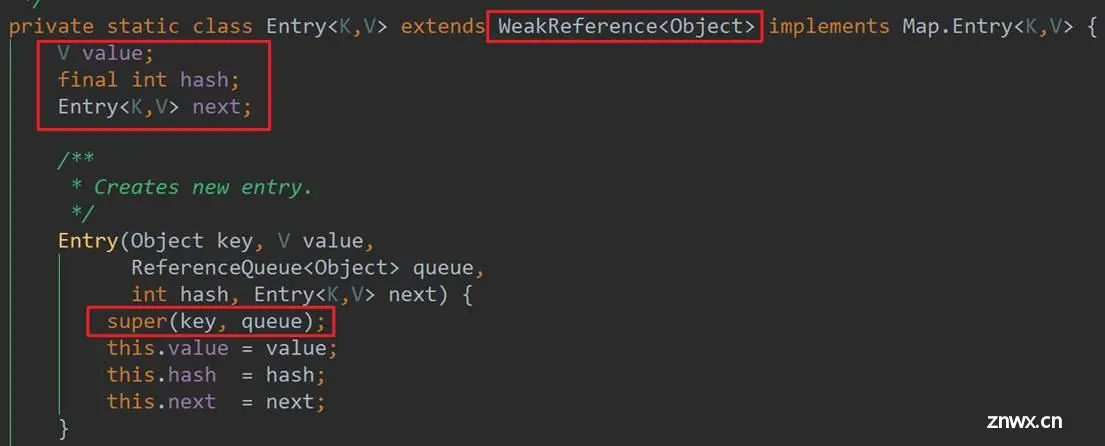
从源码上可知,Entry的内部并没有存储key的值,而是通过调用父类的构造方法,传入key和ReferenceQueue(这里与ThreadLocal类似),最终key和queue会关联到Reference中,这里是GC时,清除key的关键,这里大致看下Reference的源码:
<code>private static class ReferenceHandler extends Thread {
private static void ensureClassInitialized(Class <? > clazz) {
try {
Class.forName(clazz.getName(), true, clazz.getClassLoader());
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
throw (Error) new NoClassDefFoundError(e.getMessage()).initCause(e);
}
}
static {
// pre-load and initialize InterruptedException and Cleaner classes
// so that we don't get into trouble later in the run loop if there's
// memory shortage while loading/initializing them lazily.
ensureClassInitialized(InterruptedException.class);
ensureClassInitialized(Cleaner.class);
}
ReferenceHandler(ThreadGroup g, String name) {
super(g, name);
}
public void run() {
// 注意这里为一个死循环
while (true) {
tryHandlePending(true);
}
}
}
static boolean tryHandlePending(boolean waitForNotify) {
Reference < Object > r;
Cleaner c;
try {
synchronized(lock) {
if (pending != null) {
r = pending;
// 'instanceof' might throw OutOfMemoryError sometimes
// so do this before un-linking 'r' from the 'pending' chain...
c = r instanceof Cleaner ? (Cleaner) r : null;
// unlink 'r' from 'pending' chain
pending = r.discovered;
r.discovered = null;
} else {
// The waiting on the lock may cause an OutOfMemoryError
// because it may try to allocate exception objects.
if (waitForNotify) {
lock.wait();
}
// retry if waited
return waitForNotify;
}
}
} catch (OutOfMemoryError x) {
// Give other threads CPU time so they hopefully drop some live references
// and GC reclaims some space.
// Also prevent CPU intensive spinning in case 'r instanceof Cleaner' above
// persistently throws OOME for some time...
Thread.yield();
// retry
return true;
} catch (InterruptedException x) {
// retry
return true;
}
// Fast path for cleaners
if (c != null) {
c.clean();
return true;
}
// 加入对列
ReferenceQueue <? super Object > q = r.queue;
if (q != ReferenceQueue.NULL) q.enqueue(r);
return true;
}
static {
ThreadGroup tg = Thread.currentThread().getThreadGroup();
for (ThreadGroup tgn = tg; tgn != null; tg = tgn, tgn = tg.getParent());
// 创建handler
Thread handler = new ReferenceHandler(tg, "Reference Handler");
/* If there were a special system-only priority greater than
* MAX_PRIORITY, it would be used here
*/
// 线程优先级最大
handler.setPriority(Thread.MAX_PRIORITY);
// 设置为守护线程
handler.setDaemon(true);
handler.start();
// provide access in SharedSecrets
SharedSecrets.setJavaLangRefAccess(new JavaLangRefAccess() {@
Override
public boolean tryHandlePendingReference() {
return tryHandlePending(false);
}
});
}
put()
public V put(K key, V value) {
// 确定key值,允许key为null
Object k = maskNull(key);
// 获取器hash值
int h = hash(k);
// 获取tab
Entry <K, V> [] tab = getTable();
// 确定在tab中的位置 简单的&操作
int i = indexFor(h, tab.length);
// 遍历,是否要进行覆盖操作
for (Entry <K, V> e = tab[i]; e != null; e = e.next) {
if (h == e.hash && eq(k, e.get())) {
//已经存在,则覆盖旧值
V oldValue = e.value;
if (value != oldValue)
e.value = value;
return oldValue;
}
}
//不是旧值,就新建Entry
// 修改次数自增
modCount++;
// 取出i上的元素
Entry <K, V> e = tab[i];
// 构建链表,新元素在链表头
tab[i] = new Entry <> (k, value, queue, h, e);
// 检查是否需要扩容
if (++size >= threshold)
resize(tab.length * 2);
return null;
}
WeakHashMap的put操作与HashMap相似,都会进行覆盖操作(相同key),但是注意插入新节点是放在链表头;注意这里和HashMap不太一样的地方,HashMap会在链表太长的时候会将链表转换为红黑树,防止极端情况下hashcode冲突导致的性能问题,但在WeakHashMap中没有树化。
上述代码中还要一个关键的函数getTable
resize操作
WeakHashMap的扩容操作:在size大于阈值的时候,WeakHashMap也对做resize的操作,也就是把tab扩大一倍。WeakHashMap中的resize比HashMap中的resize要简单好懂些,但没HashMap中的resize优雅。
WeakHashMap中resize有另外一个额外的操作,就是expungeStaleEntries(),因为key可能被GC掉,所以在扩容时也需要考虑这种情况
void resize(int newCapacity) {
Entry<K,V>[] oldTable = getTable();
// 原数组长度
int oldCapacity = oldTable.length;
if (oldCapacity == MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) {
threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
return;
}
// 创建新的数组
Entry<K,V>[] newTable = newTable(newCapacity);
// 数据转移
transfer(oldTable, newTable);
table = newTable;
/*
* If ignoring null elements and processing ref queue caused massive
* shrinkage, then restore old table. This should be rare, but avoids
* unbounded expansion of garbage-filled tables.
*/
// 确定扩容阈值
if (size >= threshold / 2) {
threshold = (int)(newCapacity * loadFactor);
} else {
// 清除被GC的value
expungeStaleEntries();
// 数组转移
transfer(newTable, oldTable);
table = oldTable;
}
}
private void transfer(Entry<K,V>[] src, Entry<K,V>[] dest) {
// 遍历原数组
for (int j = 0; j < src.length; ++j) {
// 取出元素
Entry<K,V> e = src[j];
src[j] = null;
// 链式找元素
while (e != null) {
Entry<K,V> next = e.next;
Object key = e.get();
// key被回收的情况
if (key == null) {
e.next = null; // Help GC
e.value = null; // " "
size--;
} else {
// 确定在新数组的位置
int i = indexFor(e.hash, dest.length);
// 插入元素 注意这里为头插法,会倒序
e.next = dest[i];
dest[i] = e;
}
e = next;
}
}
}
过期元素(弱引用)清除
该函数的主要作用就是清除Entry的value,该Entry是在GC清除key的过程中入队的。
private void expungeStaleEntries() {
// 从队列中取出被GC的Entry
for (Object x; (x = queue.poll()) != null;) {
synchronized(queue) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Entry <K, V> e = (Entry <K, V> ) x;
// 确定元素在队列中的位置
int i = indexFor(e.hash, table.length);
// 取出数组中的第一个元素 prev
Entry <K, V> prev = table[i];
Entry <K, V> p = prev;
// 循环
while (p != null) {
Entry <K, V> next = p.next;
// 找到
if (p == e) {
// 判断是否是链表头元素 第一次时
if (prev == e)
// 将next直接挂在i位置
table[i] = next;
else
// 进行截断
prev.next = next;
// Must not null out e.next;
// stale entries may be in use by a HashIterator
e.value = null; // Help GC
size--;
break;
}
// 更新prev和p
prev = p;
p = next;
}
}
}
}
当某个key失去所有强应用之后,其key对应的WeakReference对象会被放到queue里,有了queue就知道需要清理哪些Entry了。这里也是整个WeakHashMap里唯一加了同步的地方。
除了上文说的到resize中调用了expungeStaleEntries(),size()、getTable()中也调用了这个清理方法,这就意味着几乎所有其他方法都间接调用了清理。
总结
- WeakHashMap非同步,默认容量为16,扩容因子默认为0.75,底层数据结构为Entry数组(数组+链表)。
- WeakHashMap中的弱引用key会在下一次GC被清除,注意只会清除key,value会在每次调用expungeStaleEntries()的操作中清除。
- 注意:使用WeakHashMap做缓存时,如果只有它的key只有WeakHashMap本身在用,而在WeakHashMap之外没有对该key的强引用,那么GC时会回收这个key对应的entry。所以WeakHashMap不能用做主缓存,合适的用法应该是用它做二级的内存缓存,即过期缓存数据或者低频缓存数据
缺点
非线程安全:关键修改方法没有提供任何同步,多线程环境下肯定会导致数据不一致的情况,所以使用时需要多注意。
单纯作为Map没有HashMap好:HashMap在Jdk8做了好多优化,比如单链表在过长时会转化为红黑树,降低极端情况下的操作复杂度。但WeakHashMap没有相应的优化,有点像jdk8之前的HashMap版本。
不能自定义ReferenceQueue:WeakHashMap构造方法中没法指定自定的ReferenceQueue,如果用户想用ReferenceQueue做一些额外的清理工作的话就行不通了。如果即想用WeakHashMap的功能,也想用ReferenceQueue,就得自己实现一套新的WeakHashMap了。
使用场景
Tomcat的源码里,实现缓存时会用到WeakHashMap
阿里Arthas:阿里开源的Java诊断工具中使用了WeakHashMap做类-字节码的缓存。
// 类-字节码缓存
private final static Map<Class<?>/*Class*/, byte[]/*bytes of Class*/> classBytesCache
= new WeakHashMap<Class<?>, byte[]>();
关于作者
来自一线程序员Seven的探索与实践,持续学习迭代中~
本文已收录于我的个人博客:https://www.seven97.top
公众号:seven97,欢迎关注~
声明
本文内容仅代表作者观点,或转载于其他网站,本站不以此文作为商业用途
如有涉及侵权,请联系本站进行删除
转载本站原创文章,请注明来源及作者。