FastAPI快速入门2 Pydantic&错误处理
pythontesting 2024-06-15 09:09:00 阅读 73
2.1 Pydantic简介
Pydantic使用python类型注解进行数据验证和配置管理。这是一款能让您更精确地处理数据结构的工具。例如,到目前为止,我们一直依赖字典来定义项目中的典型配方。有了Pydantic,我们可以这样定义配方:
from pydantic import BaseModel
class Recipe(BaseModel):
id: int
label: str
source: str
raw_recipe = {'id': 1, 'label': 'Lasagna', 'source': 'Grandma Wisdom'}
structured_recipe = Recipe(**raw_recipe)
print(structured_recipe.id)
#> 1
Recipe 类继承自Pydantic BaseModel,我们可以使用标准Python类型提示来定义每个预期字段及其类型。
除了使用类型模块的标准类型外,您还可以像这样递归地使用Pydantic模型:
from pydantic import BaseModel
class Car(BaseModel):
brand: str
color: str
gears: int
class ParkingLot(BaseModel):
cars: List[Car] # recursively use `Car`
spaces: int
结合这些功能,您可以定义非常复杂的对象。这只是Pydantic功能的皮毛,以下是对其优势的快速总结:
- 无需学习新的微语言(这意味着它能很好地与集成开发环境/精简器配合使用)
- 既可用于 "验证该请求/响应数据",也可用于加载配置
- 验证复杂的数据结构--Pydantic 提供极为精细的验证器
- 可扩展--您可以创建自定义数据类型
- 可与Python数据类一起使用
- 速度非常快
2.2 Pydantic与FastAPI结合使用
ch02/main.py
from fastapi import FastAPI, APIRouter, Query
from typing import Optional
from schemas import RecipeSearchResults, Recipe, RecipeCreate
from recipe_data import RECIPES
app = FastAPI(title="Recipe API", openapi_url="/openapi.json")
api_router = APIRouter()
@api_router.get("/", status_code=200)
def root() -> dict:
"""
Root GET
"""
return {"msg": "Hello, World!"}
# Updated using to use a response_model
# https://fastapi.tiangolo.com/tutorial/response-model/
@api_router.get("/recipe/{recipe_id}", status_code=200, response_model=Recipe)
def fetch_recipe(*, recipe_id: int) -> dict:
"""
Fetch a single recipe by ID
"""
result = [recipe for recipe in RECIPES if recipe["id"] == recipe_id]
if result:
return result[0]
# Updated using the FastAPI parameter validation `Query` class
# # https://fastapi.tiangolo.com/tutorial/query-params-str-validations/
@api_router.get("/search/", status_code=200, response_model=RecipeSearchResults)
def search_recipes(
*,
keyword: Optional[str] = Query(
None,
min_length=3,
openapi_examples={
"chickenExample": {
"summary": "A chicken search example",
"value": "chicken",
}
},
),
max_results: Optional[int] = 10
) -> dict:
"""
Search for recipes based on label keyword
"""
if not keyword:
# we use Python list slicing to limit results
# based on the max_results query parameter
return {"results": RECIPES[:max_results]}
results = filter(lambda recipe: keyword.lower() in recipe["label"].lower(), RECIPES)
return {"results": list(results)[:max_results]}
# New addition, using Pydantic model `RecipeCreate` to define
# the POST request body
@api_router.post("/recipe/", status_code=201, response_model=Recipe)
def create_recipe(*, recipe_in: RecipeCreate) -> dict:
"""
Create a new recipe (in memory only)
"""
new_entry_id = len(RECIPES) + 1
recipe_entry = Recipe(
id=new_entry_id,
label=recipe_in.label,
source=recipe_in.source,
url=recipe_in.url,
)
RECIPES.append(recipe_entry.dict())
return recipe_entry
app.include_router(api_router)
if __name__ == "__main__":
# Use this for debugging purposes only
import uvicorn
uvicorn.run(app, host="0.0.0.0", port=8001, log_level="debug")
ch02/schemas.py:
from pydantic import BaseModel, HttpUrl
from typing import Sequence
class Recipe(BaseModel):
id: int
label: str
source: str
url: HttpUrl
class RecipeSearchResults(BaseModel):
results: Sequence[Recipe]
class RecipeCreate(BaseModel):
label: str
source: str
url: HttpUrl
submitter_id: int
/recipe/{recipe_id} 已更新为包含response_model字段。在这里,我们通过Pydantic来定义JSON响应的结构。
新的食谱类继承自pydantic BaseModel,每个字段都使用标准类型提示进行定义,除了 url 字段,它使用了 Pydantic HttpUrl helper。这将强制执行预期的 URL 组件,例如方案(http 或 https)的存在。
我们在 /search endpointsearch 端点响应中添加了响应模型 RecipeSearchResults。我们引入了 FastAPI Query 类,它允许我们为查询参数添加额外的验证和要求,例如最小长度。请注意,由于我们设置了示例字段,因此当您"尝试"时,文档页面上会显示该示例字段。
RecipeSearchResults 类使用Pydantic的递归功能定义了一个字段,该字段指向我们之前定义的另一个Pydantic 类,即Recipe类。我们指定结果字段将是一个Recipes的Sequence(这是一个支持 len 和 getitem 的可迭代类)。
为了将函数设置为处理POST请求,我们只需调整api_router装饰器。请注意,我们还将HTTP status_code设置为 201,因为我们正在创建资源。
recipe_in 字段是 POST 请求正文。通过指定 Pydantic 模式,我们能够自动验证传入的请求,确保其主体符合我们的模式。
为了持久保存创建的配方,我们正在进行原始列表追加。当然,这只是一个玩具示例,在服务器重启时不会持久化数据。在本系列的后面,我们将介绍数据库。
RecipeCreate 模式包含一个新字段:submitter_id,因此我们要将它与 Recipe 模式区分开来。
请务必在本地通过交互式文档运行应用程序时尝试创建一些新菜谱。
参考资料
- 软件测试精品书籍文档下载持续更新 https://github.com/china-testing/python-testing-examples 请点赞,谢谢!
- 本文涉及的python测试开发库 谢谢点赞! https://github.com/china-testing/python_cn_resouce
- python精品书籍下载 https://github.com/china-testing/python_cn_resouce/blob/main/python_good_books.md
- Linux精品书籍下载 https://www.cnblogs.com/testing-/p/17438558.html
2.3 错误处理
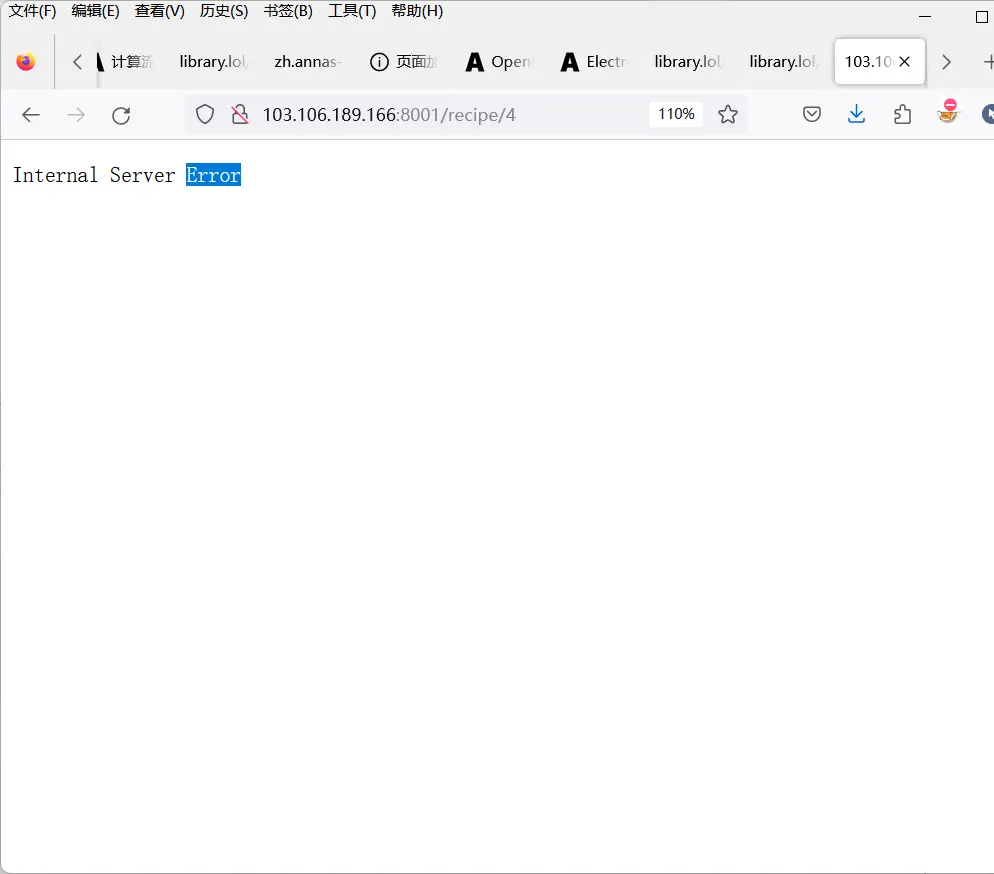
- 错误处理之前:
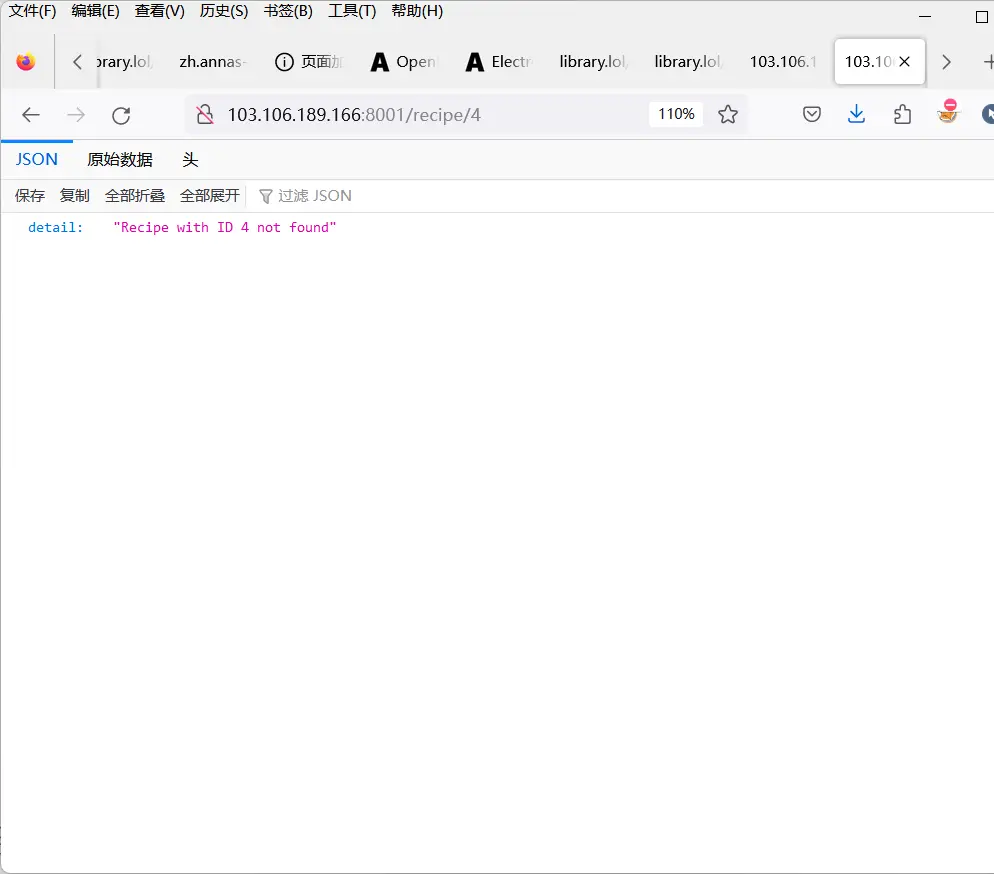
- 新增错误处理
ch02/main2.py
from fastapi import FastAPI, APIRouter, Query, HTTPException # 1
# skipping...
@api_router.get("/recipe/{recipe_id}", status_code=200, response_model=Recipe)
def fetch_recipe(*, recipe_id: int) -> Any:
"""
Fetch a single recipe by ID
"""
result = [recipe for recipe in RECIPES if recipe["id"] == recipe_id]
if not result:
# the exception is raised, not returned - you will get a validation
# error otherwise.
# 2
raise HTTPException(
status_code=404, detail=f"Recipe with ID {recipe_id} not found"
)
return result[0]
声明
本文内容仅代表作者观点,或转载于其他网站,本站不以此文作为商业用途
如有涉及侵权,请联系本站进行删除
转载本站原创文章,请注明来源及作者。