在Java中使用GeoTools解析POI数据并存储到PostGIS实战
CSDN 2024-10-01 11:35:01 阅读 64
目录
前言
一、POI数据相关介绍
1、原始数据说明
2、空间数据库表设计
二、POI数据存储的设计与实现
1、对应的数据模型对象的设计
2、属性表数据和空间信息的读取
3、实际运行结果
三、总结
前言
POI点,全称为Point of Interest(兴趣点),是指一切被抽象为点要素的空间地理实体,尤其是与人们生活密切相关的地理要素,如小区、餐馆、商场、车站等。POI是地理信息数据的一部分,用于丰富地图内容,提供用户所需的地理信息,POI数据在地图应用、导航系统、位置服务、市场营销、城市规划等领域有着广泛应用。
POI数据涵盖了丰富的地理信息和属性特征,能够反映出一个地区的商业、文化、交通等各方面的特色,每个POI点主要包含四方面的信息:名称、类别、坐标、分类。(1)名称:POI的名称或标题。(2)地址:POI的详细地址。(3)经纬度坐标:POI的地理位置坐标,通过经纬度坐标将现实世界中的地点与数字世界进行关联。(4)分类:POI所属的类别。(5)描述:关于POI的详细描述。(6)联系方式:如电话、网址等。(7)附加信息:如营业时间、用户评价、图片等。可以看出,POI数据的核心要素在于其地理位置信息和属性描述。POI数据的特点有多样性(涵盖多种类型的地理实体)、动态性(POI信息会随时间变化而更新)、空间性(具有明确的地理位置)、可查询性(用户可以根据需求检索特定的POI)。
因此,可以看出,学会管理并正确的使用POI数据,对于我们进行城市规划、导航服务、位置服务、智慧旅游、智慧应急等方面有重要的应用。在我们应用这些数据之前,需要先将POI数据管理起来。本文即在这样的场景下产生。与GDAL的shp数据处理方式不同,在GeoTools中的处理方法有一定的不同。文章分享的方法可以在分布式环境中利用Mybatis-Plus这种ORM框架进行快速的空间数据批量插入。与GeoTools官方提供的PostGIS数据读写相比,本文分享的方法将更加方便,易于与其它项目进行集成。
一、POI数据相关介绍
在讲解如何利用GeoTools进行数据管理时,我们先对POI数据进行简单的说明。POI数据不仅包含丰富的空间位置信息,同时包含很丰富的分类,以餐饮类的POI为例,我们可以分为大类、中类和小类。
1、原始数据说明
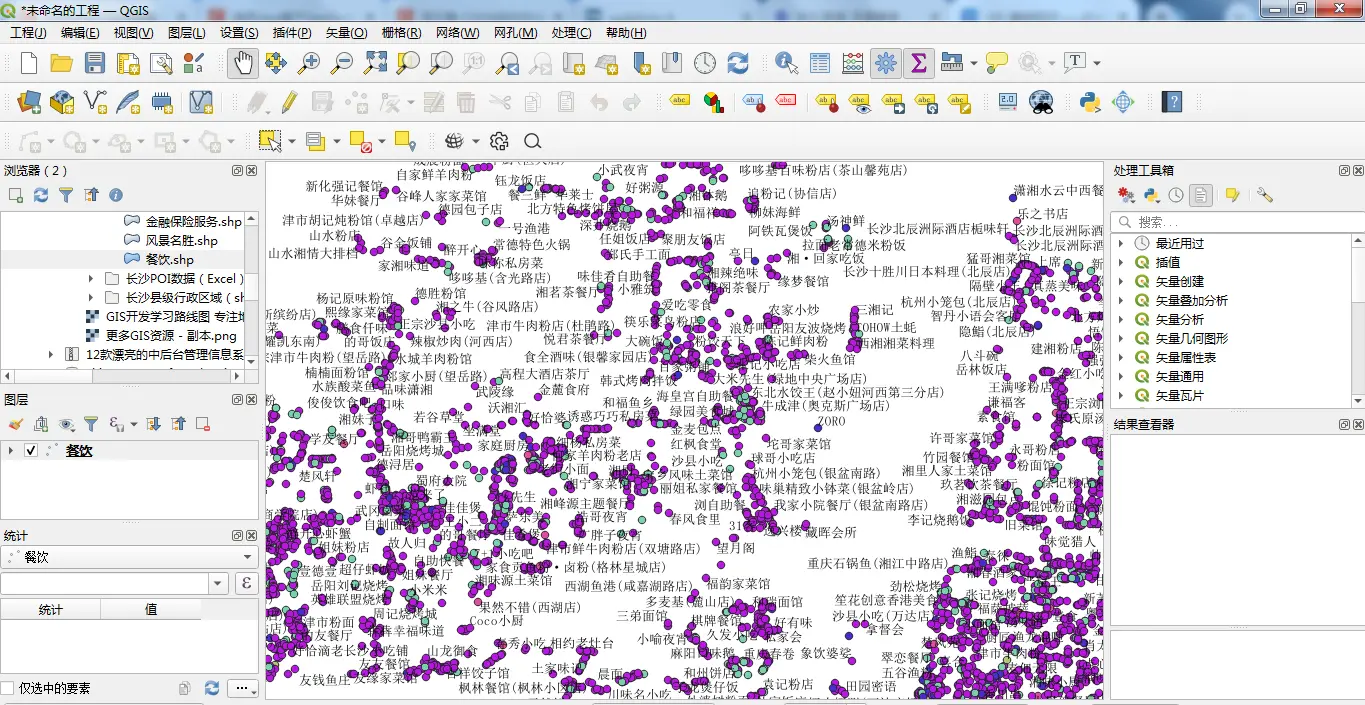
按照大类分为餐饮服务、中类分为中餐厅、西餐、烧烤,小类可以分为湘菜、川菜等。
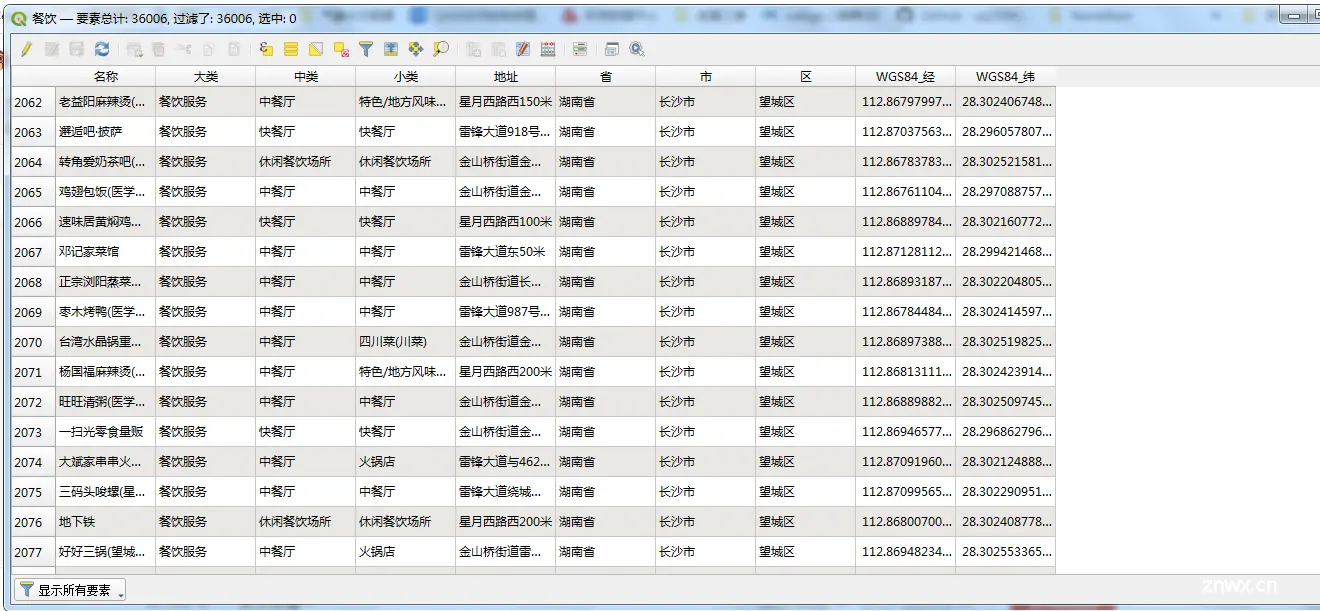
在这里,从行政区划上,我们把POI按照其归属进行了划分。在后续的统计中可以充分的利用这些数据。 这里的数据也是从互联网上抓取的数据,大多数的POI数据都是有标准的大类、中类、小类。当然,在拿到的部分POI数据,比如商业住宅的数据,
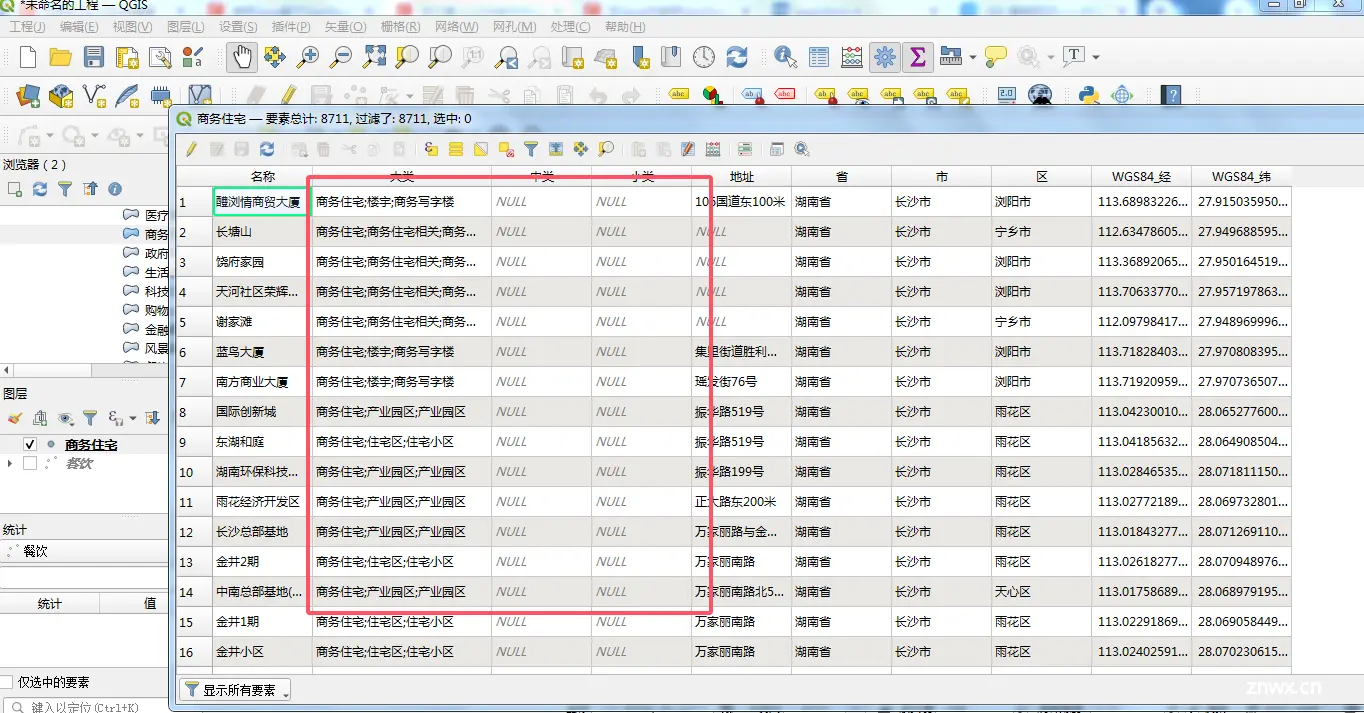
在商务住宅的POI数据中,所有的分类数据都集中到了大类这个字段,而另外两个字段比如中类和小类则是空的。其它的数据都是正确的,因此我们需要对商务住宅这个大类的数据进行简单的分拆。然后对应到具体的大类、中类、小类上面。
2、空间数据库表设计
在上一篇博客中,我们对POI信息表的空间数据属性字段有了具体的了解。与Shapefile等空间数据表相同,在PostGIS空间数据库中,我们也需要设计对应的空间表来存储对应的空间数据。
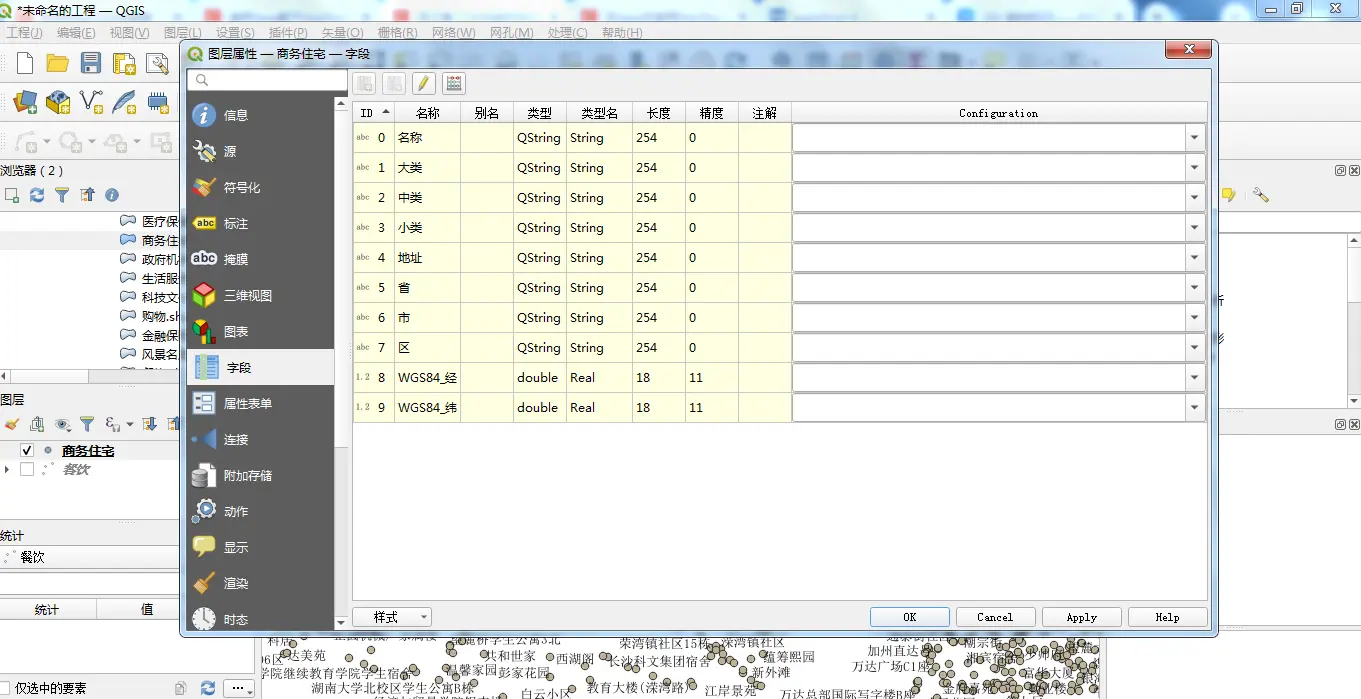
以上就是Shapefile中的属性字段信息,按照一一映射的原则,我们在PostGIS当中也同样的来设计对应的空间表。
大家可以使用自己熟悉的工具来进行表结构的设计,然后在数据库客户端软件中进行创建表结构即可。这里同样将数据表的表结构贴出来,供大家参考:
<code>CREATE TABLE "public"."biz_poi_info" (
"pk_id" int8 NOT NULL,
"name" varchar(255) COLLATE "pg_catalog"."default",
"main_category" varchar(255) COLLATE "pg_catalog"."default",
"type" varchar(255) COLLATE "pg_catalog"."default",
"subtype" varchar(255) COLLATE "pg_catalog"."default",
"address" varchar(255) COLLATE "pg_catalog"."default",
"province_name" varchar(255) COLLATE "pg_catalog"."default",
"city_name" varchar(255) COLLATE "pg_catalog"."default",
"area_name" varchar(255) COLLATE "pg_catalog"."default",
"lon_wgs84" numeric(18,11),
"lat_wgs84" numeric(18,11),
"geom" "public"."geometry",
"year" int4,
"create_by" int8,
"create_time" timestamp(6),
"update_by" int8,
"update_time" timestamp(6),
CONSTRAINT "pk_biz_poi_info" PRIMARY KEY ("pk_id")
);
CREATE INDEX "idx_biz_poi_info_geom" ON "public"."biz_poi_info" USING gist (
"geom" "public"."gist_geometry_ops_2d"
);
COMMENT ON COLUMN "public"."biz_poi_info"."pk_id" IS 'pk_id';
COMMENT ON COLUMN "public"."biz_poi_info"."name" IS '名称';
COMMENT ON COLUMN "public"."biz_poi_info"."main_category" IS '大类,比如:餐饮服务';
COMMENT ON COLUMN "public"."biz_poi_info"."type" IS '中类,比如:中餐';
COMMENT ON COLUMN "public"."biz_poi_info"."subtype" IS '小类';
COMMENT ON COLUMN "public"."biz_poi_info"."address" IS '地址';
COMMENT ON COLUMN "public"."biz_poi_info"."province_name" IS '省';
COMMENT ON COLUMN "public"."biz_poi_info"."city_name" IS '市';
COMMENT ON COLUMN "public"."biz_poi_info"."area_name" IS '区';
COMMENT ON COLUMN "public"."biz_poi_info"."year" IS '年份';
COMMENT ON COLUMN "public"."biz_poi_info"."create_by" IS '创建人';
COMMENT ON COLUMN "public"."biz_poi_info"."create_time" IS '创建时间';
COMMENT ON COLUMN "public"."biz_poi_info"."update_by" IS '更新人';
COMMENT ON COLUMN "public"."biz_poi_info"."update_time" IS '更新时间';
COMMENT ON TABLE "public"."biz_poi_info" IS '保存兴趣点信息表';
以上就是对POI数据进行简单的介绍,以及对POI数据的时空数据表的物理模型和表结构进行了讲解。请注意,在进行空间数据库设计的时候,请务必安装PostGIS的扩展,否则上面的SQL将无法运行,为了在后面的空间分析和查询的服务中发挥出更好的性能,我们给Geometry字段建立空间索引。
二、POI数据存储的设计与实现
在介绍完POI的属性表结构和空间数据库物理表模型之后,我们来具体讲解如何使用GeoTools来进行属性的读取,并调用Mybatis-Plus的批量入库代码,将2020年星城长沙的POI数据进行入库操作。
1、对应的数据模型对象的设计
众所周知,在面向对象的设计中,我们需要给数据库模型的表设计一个对应的实体类,这里简称为实体类。一般字段与数据库物理表是一一对应的。这里我们直接给出原始的代码:
package com.yelang.project.extend.earthquake.domain;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.math.BigDecimal;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.annotation.TableField;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.annotation.TableId;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.annotation.TableName;
import com.yelang.framework.handler.PgGeometryTypeHandler;
import com.yelang.framework.web.domain.BaseEntity;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Getter;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Setter;
import lombok.ToString;
@TableName(value = "biz_poi_info", autoResultMap = true)
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
@Setter
@Getter
@ToString
/**
* - 兴趣点信息表实体类
* @author 夜郎king
*
*/
public class PoiInfo extends BaseEntity implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -9163178655131959272L;
@TableId(value = "pk_id")
private Long pkId;// 主键
private String name;// 名称
@TableField(value = "main_category")
private String mainCategory;// 大类,比如:餐饮服务
private String type;// 中类,比如:中餐
private String subtype;// 小类
private String address;// 地址
@TableField(value = "province_name")
private String provinceName;// 省
@TableField(value = "city_name")
private String cityName;// 市
@TableField(value = "area_name")
private String areaName;// 区
@TableField(value = "lon_wgs84")
private BigDecimal lonWgs84;
@TableField(value = "lat_wgs84")
private BigDecimal latWgs84;
@TableField(typeHandler = PgGeometryTypeHandler.class)
private String geom;
@TableField(exist = false)
private String geomJson;
private Integer year;// 年份
public PoiInfo(String name, String mainCategory, String type, String subtype, String address, String provinceName,
String cityName, String areaName, BigDecimal lonWgs84, BigDecimal latWgs84, String geom, Integer year) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.mainCategory = mainCategory;
this.type = type;
this.subtype = subtype;
this.address = address;
this.provinceName = provinceName;
this.cityName = cityName;
this.areaName = areaName;
this.lonWgs84 = lonWgs84;
this.latWgs84 = latWgs84;
this.geom = geom;
this.year = year;
}
}
熟悉博主代码风格的小伙伴一定知道,在处理空间数据时,我们需要将Wkt格式的字符数据转为PostGIS认识的Geometry字段,因此在这里就需要自定义typeHandler来进行处理。在上面的代码中标识符如下:
@TableField(typeHandler = PgGeometryTypeHandler.class)
2、属性表数据和空间信息的读取
在定义好模型实体之后,我们将介绍如何使用GeoTools来进行属性数据和空间信息的读取。通过这两个信息要素,构成完成的一条空间基本信息。在本文的例子中,我们需要指定属性来进行解析,比如需要将“地址”这个属性对应到address中,因此我们需要类似于Jdbc的ResultSet的处理方式,需要手动的进行数据的对应。下面贴出具体的解析代码:
@Test
public void Read2PostGIS() throws IOException, FactoryException {
// 指定Shapefile的文件路径
//String shpFile = "C:/BaiduDownload/长沙市2020年POI数据集/长沙市2020年POI数据集/长沙POI数据(.shp)/风景名胜.shp";
String shpFile = "C:/BaiduDownload/长沙市2020年POI数据集/长沙市2020年POI数据集/长沙POI数据(.shp)/住宿服务.shp";
//FileDataStore dataStore = FileDataStoreFinder.getDataStore(new File(shpFile));
ShapefileDataStore shapefileDataStore = new ShapefileDataStore(new File(shpFile).toURI().toURL());
shapefileDataStore.setCharset(Charset.forName("UTF-8"));// 设置中文字符编码
// 获取特征类型
SimpleFeatureType featureType = shapefileDataStore.getSchema(shapefileDataStore.getTypeNames()[0]);
CoordinateReferenceSystem crs = featureType.getGeometryDescriptor().getCoordinateReferenceSystem();
System.out.println("坐标参考系统:" + crs);
Integer epsgCode = CRS.lookupEpsgCode(crs, true);
SimpleFeatureSource featureSource = shapefileDataStore.getFeatureSource();
SimpleFeatureCollection simpleFeatureCollection=featureSource.getFeatures();
SimpleFeatureIterator itertor = simpleFeatureCollection.features();
//遍历featurecollection
List<PoiInfo> list = new ArrayList<PoiInfo>();
Date now = new Date();
while (itertor.hasNext()){
SimpleFeature feature = itertor.next();
Property nameProperty = feature.getProperty("名称");
String name = (String)nameProperty.getValue();
Property mainCategoryProperty = feature.getProperty("大类");
String mainCategory = (String) mainCategoryProperty.getValue();
Property typeProperty = feature.getProperty("中类");
String type = (String)typeProperty.getValue();
Property subtypeProperty = feature.getProperty("小类");
String subtype = subtypeProperty != null ? (String)subtypeProperty.getValue() : "";
Property addressProperty = feature.getProperty("地址");
String address = (String)addressProperty.getValue();
Property provinceNameProperty = feature.getProperty("省");
String provinceName = (String)provinceNameProperty.getValue();
Property cityNameProperty = feature.getProperty("市");
String cityName = (String)cityNameProperty.getValue();
Property areaNameProperty = feature.getProperty("区");
String areaName = (String)areaNameProperty.getValue();
Property lonWgs84Property = feature.getProperty("WGS84_经");
BigDecimal lonWgs84 = new BigDecimal(String.valueOf(lonWgs84Property.getValue()));
Property latWgs84Property = feature.getProperty("WGS84_纬");
BigDecimal latWgs84 = new BigDecimal(String.valueOf(latWgs84Property.getValue()));
// 获取空间字段
org.locationtech.jts.geom.Geometry geometry = (org.locationtech.jts.geom.Geometry) feature.getDefaultGeometry();
// 创建WKTWriter对象
WKTWriter wktWriter = new WKTWriter();
// 将Geometry对象转换为WKT格式的字符串
String wkt = wktWriter.write(geometry);
String geom = "SRID=" + epsgCode +";" + wkt;//拼接srid,实现动态写入code>
PoiInfo poi = new PoiInfo(name, mainCategory, type, subtype, address, provinceName, cityName, areaName, lonWgs84, latWgs84, geom, 2020);
poi.setCreateTime(now);
poi.setUpdateTime(now);
list.add(poi);
}
if(list.size() > 0) {
// poiService.saveBatch(list,500);
}
System.out.println(list.size());
}
在上面的代码中,请注意在Geometry字段的属性设置时,我们为了能动态的设置空间对象的SRID,需要动态将解析出来的空间参考编码设置到WKT字符串中,方便在数据处理时可以动态的设置。看到很多朋友在介绍相关的博客值,总是在设置方法将4326这个SRID设置为静态的,这样的处理方式不够灵活。
在第一节中我们曾将讲过,在商务住宅这类POI中,数据的制作方将大类、中类、小类进行了合并,也因此导致了在数据中只有一列,这里举一个合并的例子:
商务住宅;楼宇;商住两用楼宇|商务住宅;楼宇;商务写字楼
在上面的例子当中,我们就需要特殊处理,正常的大类、中类、小类三类组合起来都是三个长度的标准分类,上面的分类就不是,因此我们将最后的字符全部合并起来,当成当前分类的小类。毕竟这种情况不多,当然我们后续可以对数据进行一个集中的清理。数据转换的逻辑:
String mainCategory = (String) mainCategoryProperty.getValue();;
String [] splitMainCategory = mainCategory.split(";");
String type = "";
String subtype ="";
//商务住宅的POI要特殊处理、从大类中分解出中类和小类
if(splitMainCategory.length == 3) {
mainCategory = splitMainCategory[0];
type = splitMainCategory[1];
subtype = splitMainCategory[2];
}else if(splitMainCategory.length > 3) {
mainCategory = splitMainCategory[0];
type = splitMainCategory[1];
for(int i = 2;i <splitMainCategory.length;i++ ) {
subtype += splitMainCategory[i];
}
}else {
Property typeProperty = feature.getProperty("中类");
type = (String)typeProperty.getValue();
Property subtypeProperty = feature.getProperty("小类");
subtype = subtypeProperty != null ? (String)subtypeProperty.getValue() : "";
}
3、实际运行结果
最后我们使用Junit来调用上述的代码实现POI数据的批量插入,由于篇幅有限,关于在Mybatis-Plus中如何批量插入数据的代码不再赘述。读取时的数据显示如下:

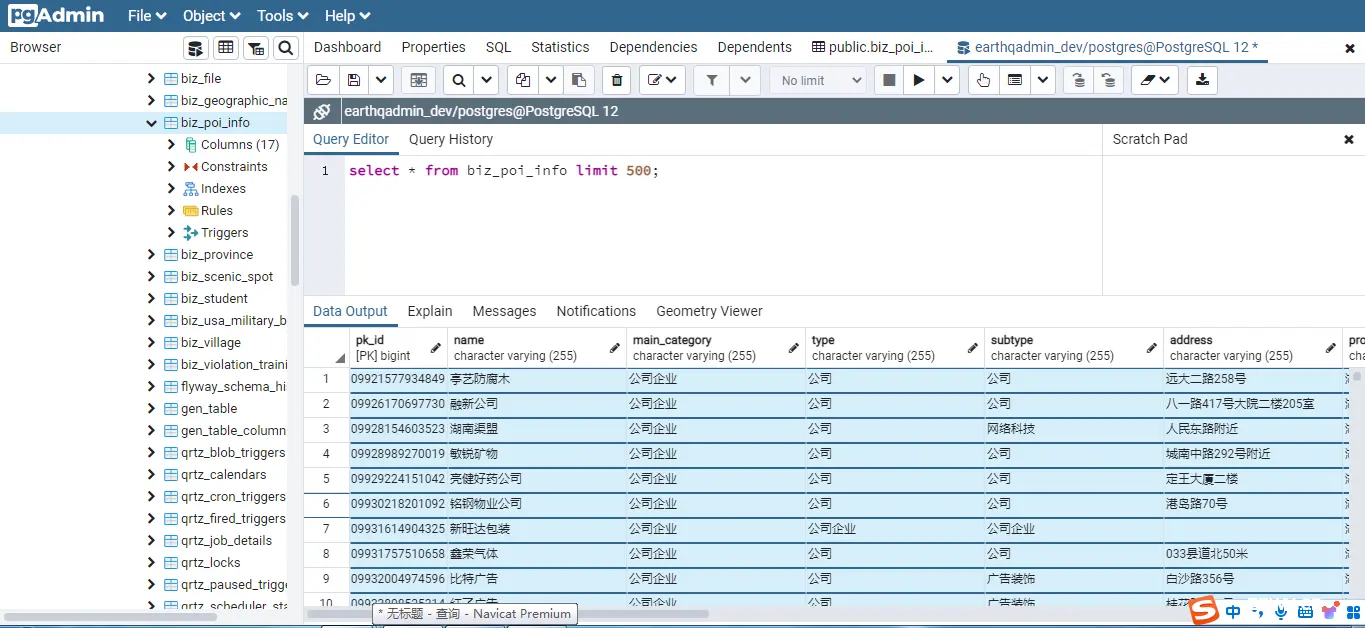
可以看到数据已经成功的加载到内存中,等待批量录入的空间数据库中。下面我们来看下空间数据库中的情况。 在PgAdmin中执行查询语句可以看到如下的结果:
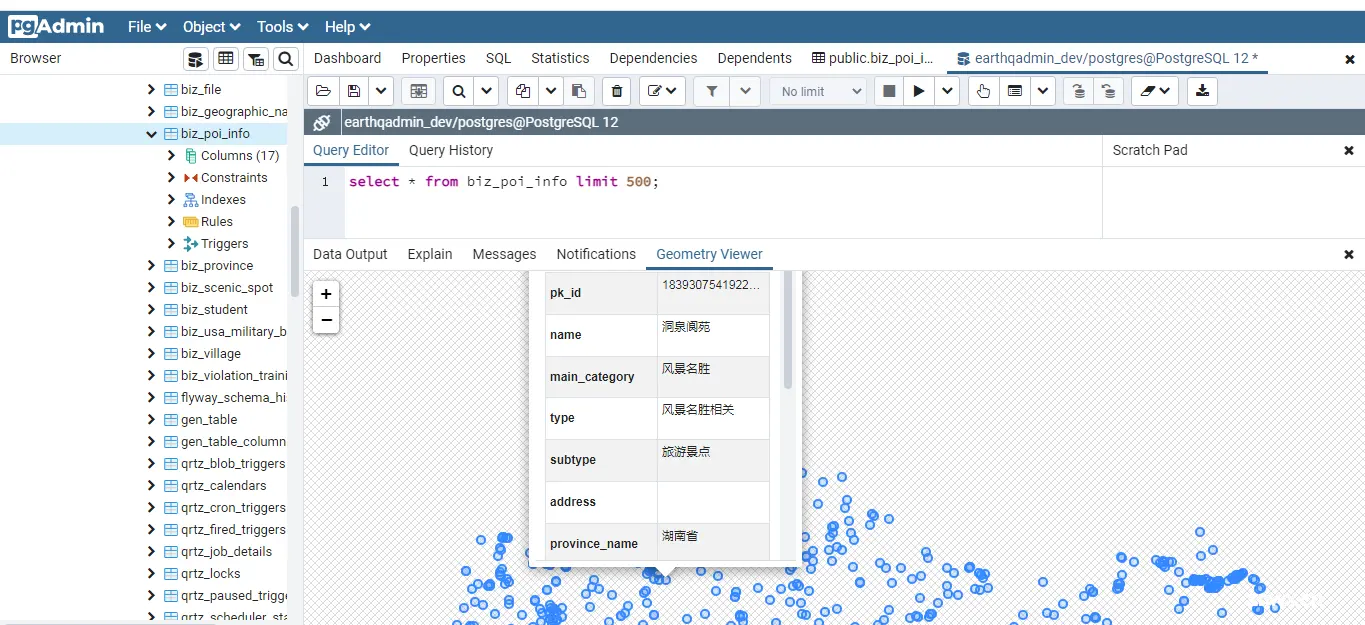
如果能看到以上结果说明,数据已经成功的插入到数据库中,在PgAdmin当中,还可以直接看到空间数据的分布,可以点击查看属性信息。
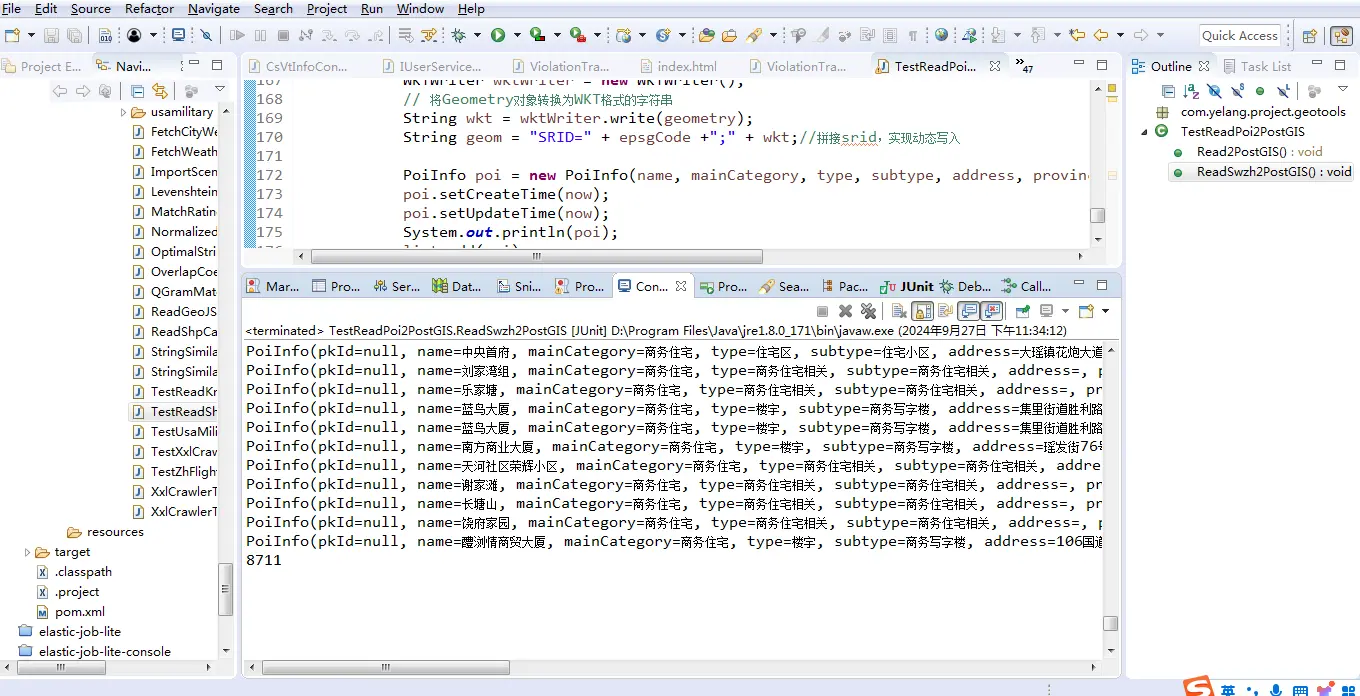
以上步骤就是如何在Java中调用GeoTools进行POI数据入库实例。
三、总结
以上就是本文的主要内容,本文主要讲解在Java开发环境,如何使用Geotools来进行数据的解析与存储,与GDAL的shp数据处理方式不同,在GeoTools中的处理方法有一定的不同。文章分享的方法可以在分布式环境中利用Mybatis-Plus这种ORM框架进行快速的空间数据批量插入。与GeoTools官方提供的PostGIS数据读写相比,本文分享的方法将更加方便,易于与其它项目进行集成。行文仓促,定有不足之处,还恳请各位专家朋友不吝赐教,万分感谢。
声明
本文内容仅代表作者观点,或转载于其他网站,本站不以此文作为商业用途
如有涉及侵权,请联系本站进行删除
转载本站原创文章,请注明来源及作者。