【JAVA】javadoc,如何生成标准的JAVA API文档
_BugMan 2024-06-30 15:35:09 阅读 78

目录
1.什么是JAVA DOC
2.标签
3.命令
1.什么是JAVA DOC
当我们写完JAVA代码,别人要调用我们的代码的时候要是没有API文档是很痛苦的,只能跟进源码去一个个的看,一个个方法的猜,并且JAVA本来就不是一个重复造轮子的游戏,一般一些常用的轮子早就已经早好了,直接拿来用就是。但是拿来用的时候往往由于API文档的缺失或者不规范,造成使用上的很多痛苦,大家在很多实际工作中经常也会遇到类似的场景:
公司多年累积下来的工具类或者提供底层能力的公共模块里面积累了很多能力,公司为了代码规范也要求我们尽量去调用这些工具类或者公共模块。但是:
没有API文档或者文档写的很烂
参数列表动不动就很长,数十个甚至几十个参数
参数列表没有注释,出现一些莫名其妙的参数,都不知道怎么传
方法名也不能见名知意
造成往往要用这些公共能力的时候甚至还要去读源码
有读源码这个时间,可能自己都重新写了一个了,而且自己写的,可能比祖传下来的那些工具类还更“清爽”一些。于是系统内越来越多工具类堆积,重复造的轮子越来越多,“屎山”越堆越高。
即使有时候我们有API文档,但是各类API文档,格式,内容都不相同,没有统一的规范,读起来其实也很慢。所以有没有一个统一的规范喃?JAVA官方其实早就想到了这个问题,在JDK1.1发布的时候就附带了JAVA DOC,支持用标签注释的方式给各个方法做好规范的说明,然后用JAVA命令一键生成可视化的HTML页面作为API。
2.标签
标签是JAVA DOC的核心,用什么标签,JAVA DOC最后就会对应生成哪些API文档内容:
@author:
/**
* @author John Doe
*/
public class MyClass {
}
@version:
/**
* @version 1.0.1
*/
public class MyClass {
}
@param:
/**
* Concatenates two strings.
* @param string1 The first string to concatenate.
* @param string2 The second string to concatenate.
* @return The concatenated string.
*/
public String concatenateStrings(String string1, String string2) {
return string1 + string2;
}
@return:
/**
* Returns the sum of two integers.
* @param num1 The first integer.
* @param num2 The second integer.
* @return The sum of num1 and num2.
*/
public int add(int num1, int num2) {
return num1 + num2;
}
@throws 或 @exception: 描述方法可能抛出的异常。
/**
* Divides two numbers and throws an exception if the divisor is zero.
* @param dividend The number to be divided.
* @param divisor The divisor.
* @return The result of the division.
* @throws ArithmeticException If the divisor is zero.
*/
public double safeDivide(double dividend, double divisor) {
if (divisor == 0) {
throw new ArithmeticException("Divisor cannot be zero.");
}
return dividend / divisor;
}
@see:
/**
* See {@link java.util.ArrayList} for more information on dynamic arrays.
*/
public class MyDynamicArray {
}
@link: 创建一个链接到其他类、方法或字段的链接。
/**
* This method uses the {@link java.util.Collections#shuffle(List)} method to randomize the list.
*/
public void shuffleList(List<?> list) {
Collections.shuffle(list);
}
@since: 指定该元素是从哪个版本开始引入的。
/**
* A utility class for working with dates.
* @since 1.5
*/
public class DateUtils {
}
@deprecated: 标记不再推荐使用的元素。
/**
* Old method that should not be used anymore.
* @deprecated Use the {@link #newMethod()} instead.
*/
@Deprecated
public void oldMethod() {
}
@inheritDoc: 继承父类或接口的 JavaDoc。
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*/
@Override
public void someMethod() {
// Implementation
}
@parametricType: 用于描述泛型类型参数。
/**
* Represents a generic collection.
* @param <E> The type of elements in this collection.
*/
public class MyCollection<E> {
}
@serialField 和 @serialData: 用于序列化类的字段和数据。
/**
* A serializable class.
* @serialField name The name of the object.
* @serialData The length of the name.
*/
@Serial
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
private String name;
// serialization logic
3.命令
javadoc命令用于生成API文档,其支持多种参数:
javadoc [options] [source files]
常用参数:
-d <directory>: 指定输出目录,存放生成的 HTML 文件。-sourcepath <pathlist>: 指定源文件路径,可以是多个路径,用分隔符(如冒号或分号)分隔。-subpackages <packagename>: 递归处理指定包及其子包下的所有类。-classpath <classpath>: 设置类路径,用于解析类型引用。-encoding <encoding>: 指定源文件的字符编码。-charset <charset>: 指定生成文档时使用的字符集。-windowtitle <text>: 设置文档窗口标题。-doctitle <text>: 设置文档页面的标题。-overview <filename>: 指定概述文件,用于文档的首页内容。-exclude <patternlist>: 指定要排除的包或类的模式列表。-private: 包含私有成员的文档。-protected: 默认行为,包含受保护和公开成员的文档。-public: 只包含公共成员的文档。
示例:
假设你有一个名为 com.example 的包,位于 /src/main/java 目录下,你想生成包含所有公共和受保护成员的 API 文档,并将输出文件保存在 /docs/api 目录下,同时指定字符编码为 UTF-8,可以使用以下命令:
javadoc -encoding UTF-8 -charset UTF-8 -d /docs/api -sourcepath /src/main/java -subpackages com.example
搞一个类来把注解都用上,然后生成API文档看看:
package com.eryi.config;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* @author John Doe
* @version 1.0.0
* @since 2022-04-01
* @deprecated Since version 1.1.0, use the {@link BetterFileManager} instead.
* This class provides basic file management operations.
*/
@Deprecated
public class FileManager {
/**
* @param filePath The path of the file to check.
* @return True if the file exists, false otherwise.
* @see File#exists()
* @throws NullPointerException If the filePath is null.
*/
public boolean fileExists(String filePath) {
if (filePath == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("FilePath cannot be null.");
}
File file = new File(filePath);
return file.exists();
}
/**
* @param fileName The name of the file to create.
* @param content The content to write into the file.
* @return The newly created file.
* @throws IOException If there's any issue creating or writing to the file.
* @see File#createNewFile()
* @see FileWriter
*/
public File createFileWithContent(String fileName, String content) throws IOException {
File file = new File(fileName);
if (!file.createNewFile()) {
throw new IOException("Failed to create file: " + fileName);
}
try (FileWriter writer = new FileWriter(file)) {
writer.write(content);
}
return file;
}
/**
* A sample file path constant.
* @since 1.0.0
*/
@Deprecated
public static final String SAMPLE_FILE_PATH = "resources/sample.txt";
/**
* @param args Command-line arguments (not used in this example).
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
FileManager fileManager = new FileManager();
System.out.println("Does sample file exist? " + fileManager.fileExists(SAMPLE_FILE_PATH));
}
}
直接JAVADOC:
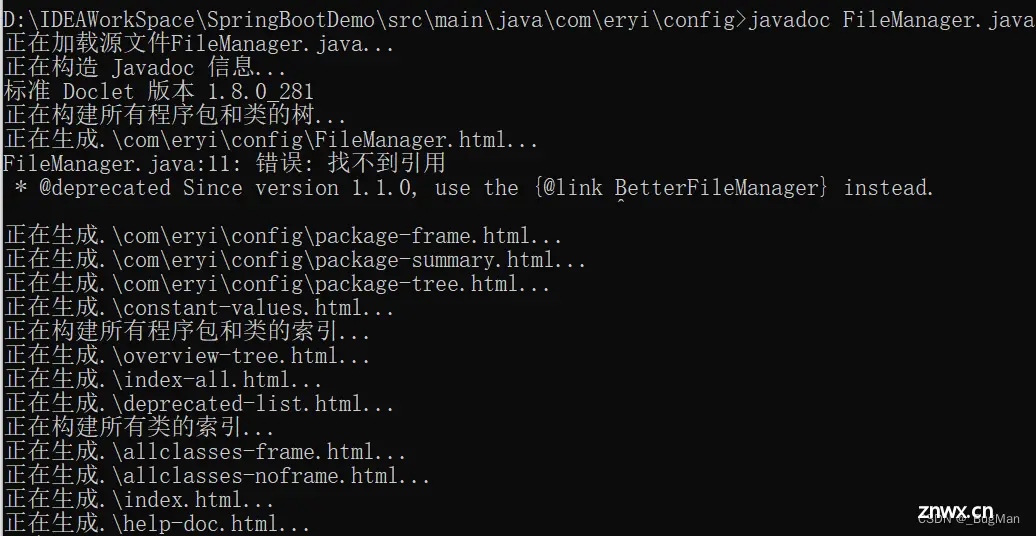
会在路径下生成一堆东西,需要用的只有index.html,其它的都是为了支持这个index.html的资源文件而已:
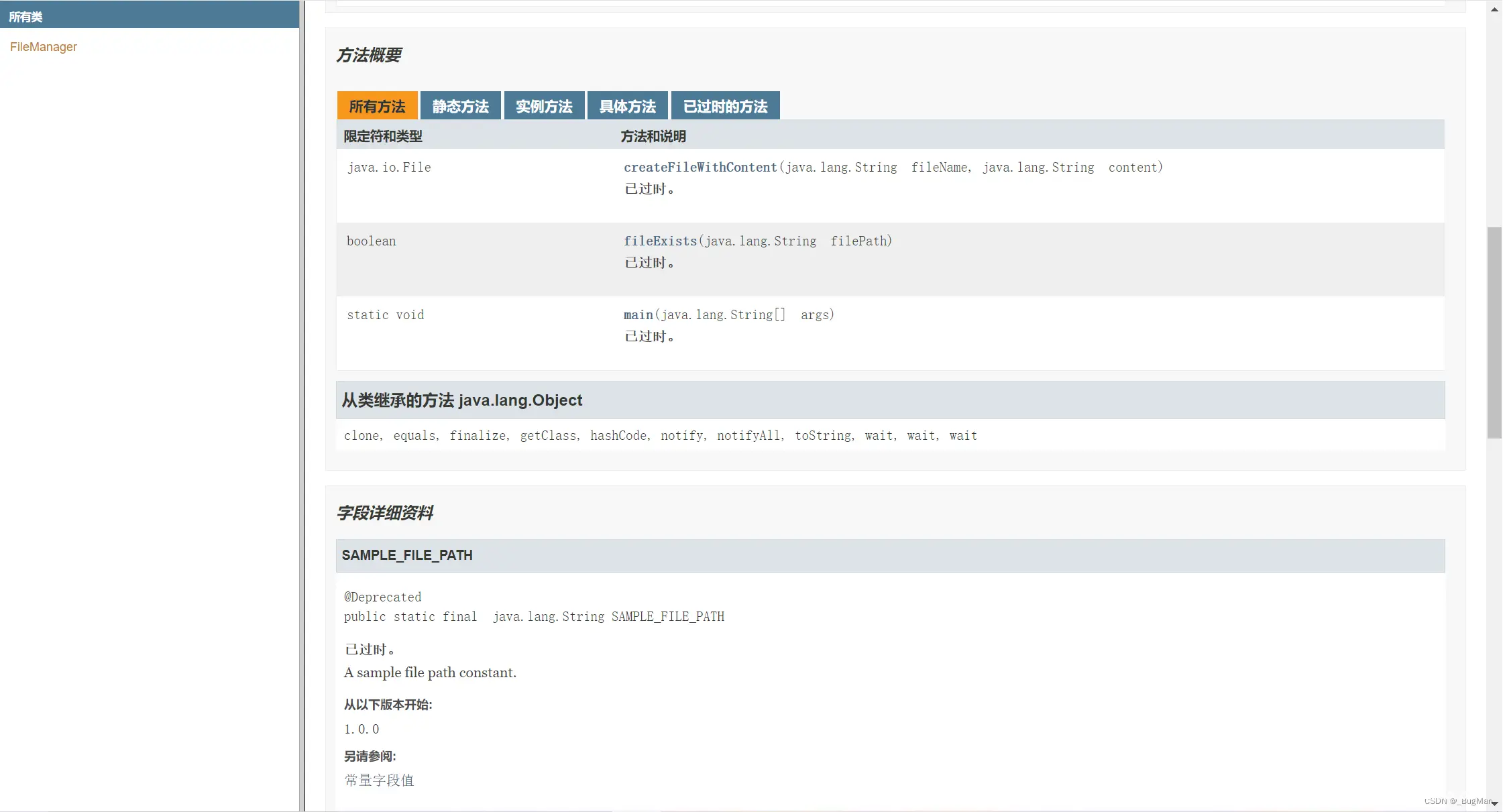
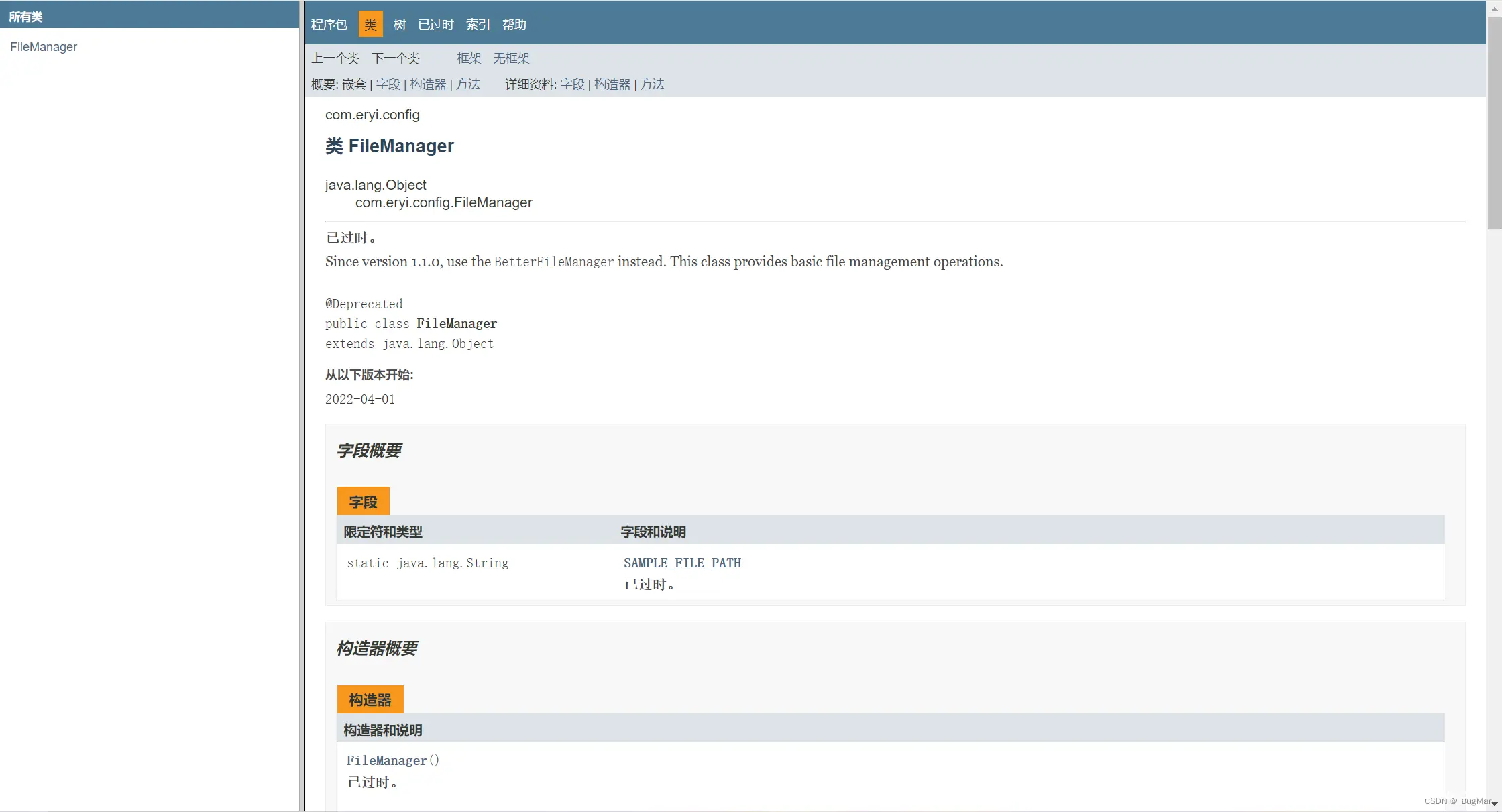
看看效果:
可以看到关于这个类的什么都有:
声明
本文内容仅代表作者观点,或转载于其他网站,本站不以此文作为商业用途
如有涉及侵权,请联系本站进行删除
转载本站原创文章,请注明来源及作者。