U4字符串以及正则表达式
cnblogs 2024-10-21 08:09:06 阅读 74
Unit4字符串以及正则表达式
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| capitalize() | 把首字符转换为大写。 |
| casefold() | 把字符串转换为小写。 |
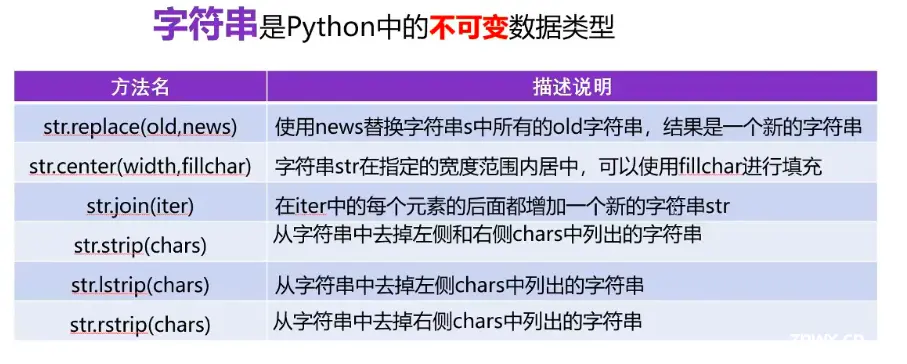
| center() | 返回居中的字符串。 |
| count() | 返回指定值在字符串中出现的次数。 |
| encode() | 返回字符串的编码版本。 |
| endswith() | 如果字符串以指定值结尾,则返回 true。 |
| expandtabs() | 设置字符串的 tab 尺寸。 |
| find() | 在字符串中搜索指定的值并返回它被找到的位置。 |
| format() | 格式化字符串中的指定值。 |
| format_map() | 格式化字符串中的指定值。 |
| index() | 在字符串中搜索指定的值并返回它被找到的位置。 |
| isalnum() | 如果字符串中的所有字符都是字母数字,则返回 True。 |
| isalpha() | 如果字符串中的所有字符都在字母表中,则返回 True。 |
| isdecimal() | 如果字符串中的所有字符都是小数,则返回 True。 |
| isdigit() | 如果字符串中的所有字符都是数字,则返回 True。 |
| isidentifier() | 如果字符串是标识符,则返回 True。 |
| islower() | 如果字符串中的所有字符都是小写,则返回 True。 |
| isnumeric() | 如果字符串中的所有字符都是数,则返回 True。 |
| isprintable() | 如果字符串中的所有字符都是可打印的,则返回 True。 |
| isspace() | 如果字符串中的所有字符都是空白字符,则返回 True。 |
| istitle() | 如果字符串遵循标题规则,则返回 True。 |
| isupper() | 如果字符串中的所有字符都是大写,则返回 True。 |
| join() | 把可迭代对象的元素连接到字符串的末尾。 |
| ljust() | 返回字符串的左对齐版本。 |
| lower() | 把字符串转换为小写。 |
| lstrip() | 返回字符串的左修剪版本。 |
| maketrans() | 返回在转换中使用的转换表。 |
| partition() | 返回元组,其中的字符串被分为三部分。 |
| replace() | 返回字符串,其中指定的值被替换为指定的值。 |
| rfind() | 在字符串中搜索指定的值,并返回它被找到的最后位置。 |
| rindex() | 在字符串中搜索指定的值,并返回它被找到的最后位置。 |
| rjust() | 返回字符串的右对齐版本。 |
| rpartition() | 返回元组,其中字符串分为三部分。 |
| rsplit() | 在指定的分隔符处拆分字符串,并返回列表。 |
| rstrip() | 返回字符串的右边修剪版本。 |
| split() | 在指定的分隔符处拆分字符串,并返回列表。 |
| splitlines() | 在换行符处拆分字符串并返回列表。 |
| startswith() | 如果以指定值开头的字符串,则返回 true。 |
| strip() | 返回字符串的剪裁版本。 |
| swapcase() | 切换大小写,小写成为大写,反之亦然。 |
| title() | 把每个单词的首字符转换为大写。 |
| translate() | 返回被转换的字符串。 |
| upper() | 把字符串转换为大写。 |
| zfill() | 在字符串的开头填充指定数量的 0 值。 |
常用方法1

<code>s1 = "HelloWorld"
new_s1 = s1.lower()
print(s1, new_s1)
s2 = new_s1.upper()
print(new_s1,s2)
#字符串的分割
e_mail = "zhl@qq.com"
lst = e_mail.split("@")
print("邮箱名:", lst[0],"邮箱服务器域名:",lst[1])
#统计出行次数
print(s1.count("l"))
#检索操作
print(s1.find("o"))#首次出现位置
print(s1.find("p"))#-1没有找到
print(s1.index("o"))
#print(s1.index("p"))#ValueError: substring not found
#判断前缀和后缀
print(s1.startswith("h"))
print(s1.startswith("H"))
print("demo.py".endswith(".py"))#True
print("text.txt".endswith(".txt"))#Ture
常用方法2
<code>s = "helloworld"
#替换
'''
def replace(self,
__old: str,
__new: str,
__count: SupportsIndex = ...) -> str
'''
new_s = s.replace("o","你好",1)#最后一个参数是替换次数,默认是全部替换
print(s,new_s)
'''
字符串在指定的宽度范围内居中
def center(self,
__width: SupportsIndex,
__fillchar: str = ...) -> str
'''
print(s.center(20))
print(s.center(20, "-"))
'''
去掉字符串左右的空格
def strip(self, __chars: str | None = ...) -> str
'''
s = " hello world "
print(s.strip())
print(s.lstrip())
print(s.rstrip())
#去掉指定的字符 与顺序无关
s3 = "dl_Helloworld"
print(s3.strip("ld"))
print(s3.lstrip("ld"))
print(s3.rstrip("ld"))
格式化

<code>name = "马冬梅"
age = 18
score = 98.4
print("name:%s,age:%d,score:%.1f"%(name,age,score))
#f-string
print(f"name:{name},age:{age},score{score}")
#format()
print("name:{0},age{1},score{2}".format(name,age,score))
详细格式
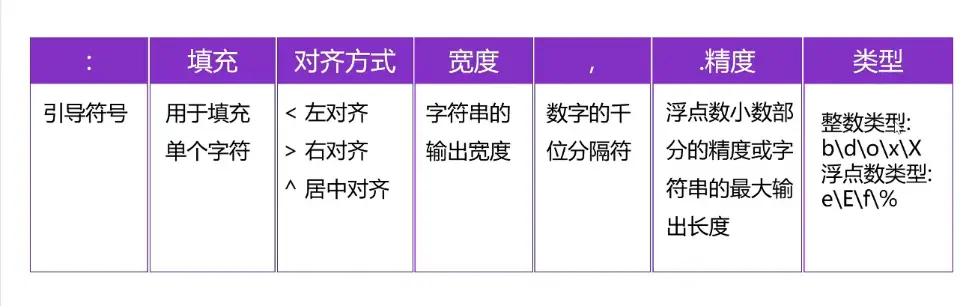
<code>s = "helloworld"
print("{0:*<20}".format(s))
print("{0:*>20}".format(s))
print("{0:*^20}".format(s))
#居中对齐
print(s.center(20,"*"))
#千位分隔符(只适用于整数和读点书
print("{0:,}".format(123456789))
print("{0:,}".format(123456789.312313))
print("{0:.2f}".format(123456789.312313))
print("{0:.5}".format(s))
#整数类型
a = 425
print(
"2进制:{0:b},8进制:{0:o},10进制:{0:d},16进制:{0:X},".format(a)
)
#科学计数法
pi = 3.1415926
print("{0:.2f},{0:.2E},{0:.2e},{0:.2%}".format(pi))
字符串的编码和解码

<code>
s = "伟大的人民"
#编码 str -> bytes
#默认UTF-8
scode = s.encode(errors="replace")code>
print(scode)
'''
def encode(self,
encoding: str = ...,
errors: str = ...) -> bytes
'''
scode_gbk= s.encode("gbk",errors="replace") #gbk中中文占两个字节code>
print(scode_gbk)
#编码中的出错问题
s2 = "✌ye耶"
#errors = strickt(default) or replace or ignore or xmlcharrefreplace
scode_error = s2.encode("gbk",errors='replace')code>
print(scode_error)
# 解码过程 bytes -》 str
print(bytes.decode(scode_gbk, "gbk"))
print(bytes.decode(scode, "utf-8"))
print(s2)
数据的验证
#阿拉伯数据判定
print("12345".isdigit())#True
print("一二三".isdigit())#False
print("0x123".isdigit())#False
print("Ⅰ".isdigit())#False
print("一1".isdigit())#False
print("="*20)
#所有字符都是数字
'''
def isnumeric(self) -> bool
Return True if the string is a numeric string, False otherwise.
A string is numeric if all characters in the string are numeric and there is at
least one character in the string.
'''
print("123".isnumeric())#True
print("一二三".isnumeric())#True
print("0b100".isnumeric())#Fakse
print("ⅠⅡⅢ".isnumeric())#True
print("壹贰叁".isnumeric())#True
print("="*20)
#所有字母都是字母(包含中文字符)
'''
def isalpha(self) -> bool
Return True if the string is an alphabetic string, False otherwise.
'''
print("hello你好".isalpha())#True
print("hello你好123".isalpha())#False
print("hello你好一二三".isalpha())#True
print("hello你好0b100".isalpha())#False
print("hello你好ⅠⅡⅢ".isalpha())#False
print("hello你好壹贰叁".isalpha())#True\
print("="*20)
#判断字符的大小写 判断是读取全部字母
print("hello你好".islower())
print("hellO你好".islower())
print("Hello你好".islower())
print("hello=".islower())
print("Hello=".isupper())
print("="*20)code>
# isspace
print(" ".isspace())
print("hello ".isspace())
print(" hello ".isspace())
字符串拼接
s1 = "hello"
s2 = "world"
#(1)
print(s1 + s2)
#join()
print("-".join([s1,s2]))
#直接拼接
print("hello""world")
#format
print("%s%s" % (s1,s2))
print(f"{s1}{s2}")
print("{0}{1}".format(s1,s2))
去重
s = "hello world"
new_s = ""
for item in s:
if item not in new_s:
new_s += item
print(new_s)
#使用索引
new_s2 = ""
for i in range(len(s)):
if s[i] not in new_s2:
new_s2 += s[i]
print(new_s2)
print(new_s2 == new_s)
print(id(new_s2))
print(id(new_s))
#通过集合
new_s3 = set(s)
print(new_s3)
lst = list(new_s3)
print(lst)
lst.sort(key=s.index)
print(lst)
print("".join(lst))
正则表达式
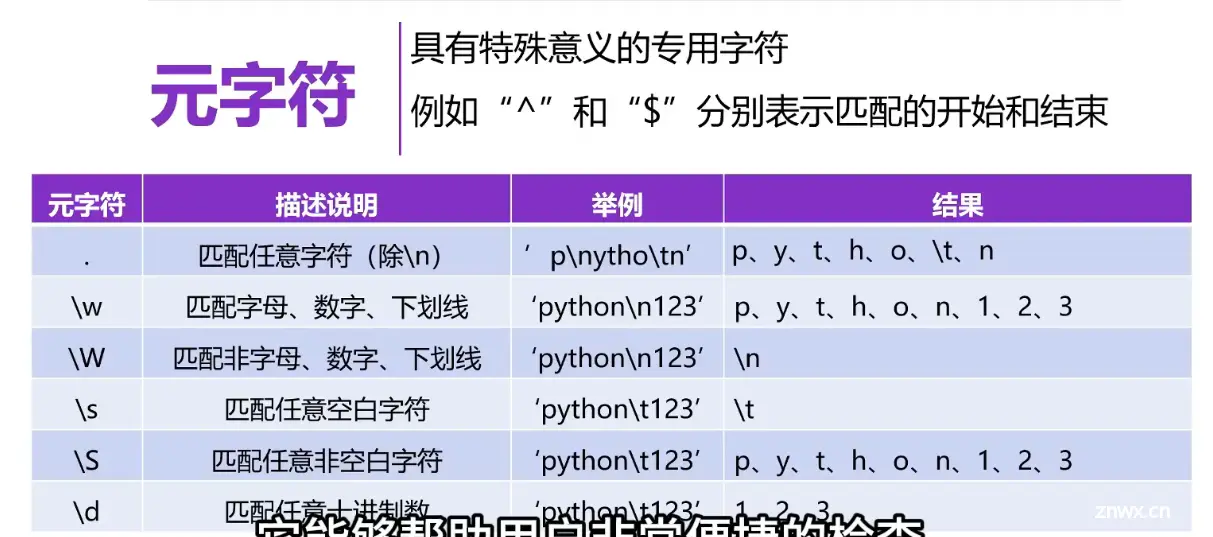
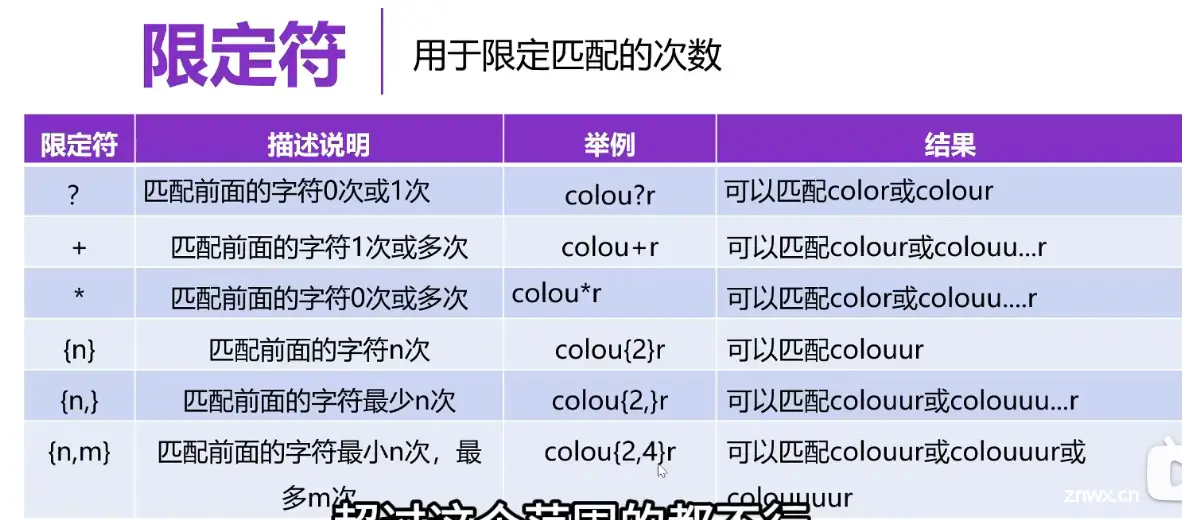
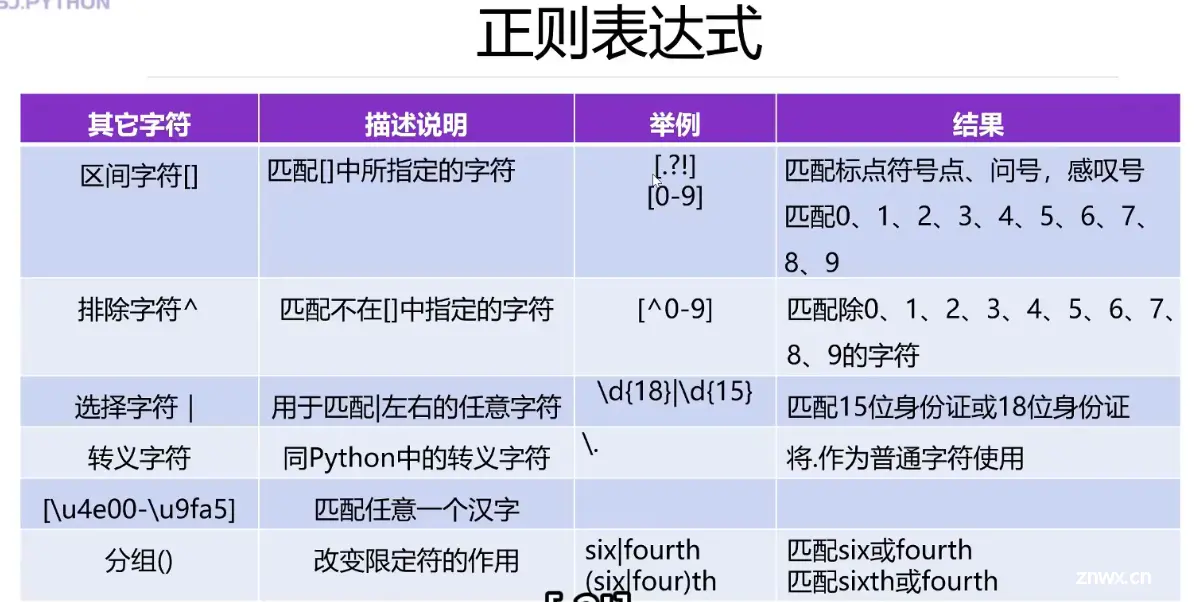
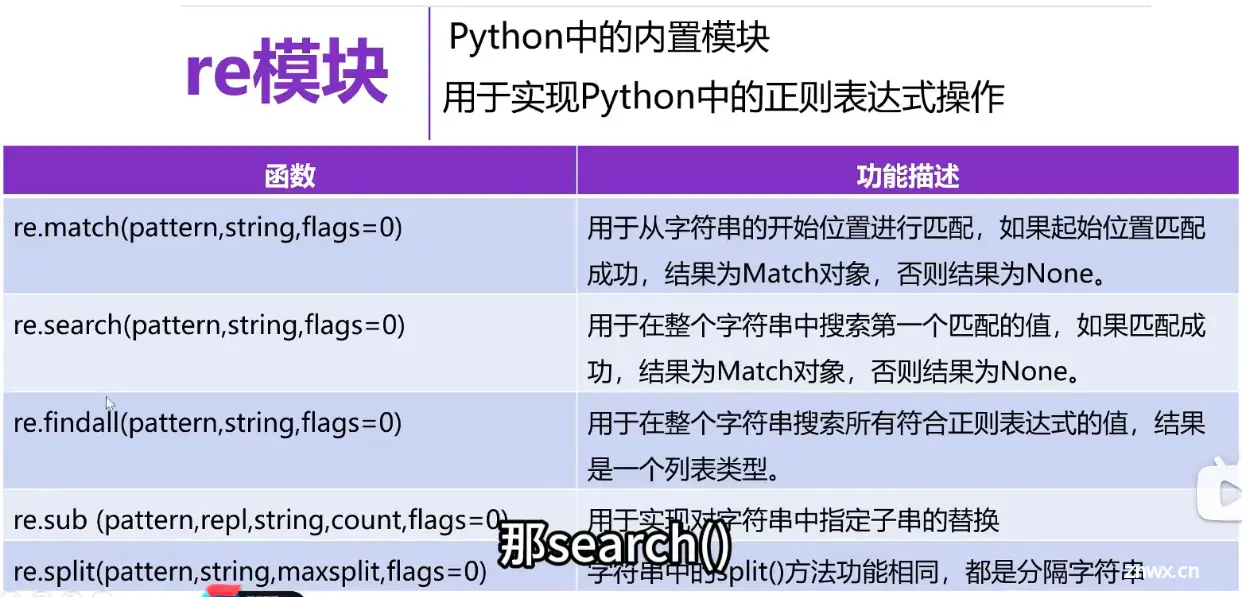
<code>import re #导入
pattern = '\d\.\d+' #限定符+ \d 0-9数字出现一次或多次
s = "I study Python3 every day"
match = re.match(pattern, s, re.I)
print(match) #None
s2 = "3.11Python I study every day"
match1 = re.match(pattern, s2)
print(match1)#<re.Match object; span=(0, 4), match='3.11'>code>
print("匹配值的起始位置:",match1.start())
print("匹配值的结束位置:",match1.end())
print("匹配值的区间的位置:",match1.span())
print("待匹配值的字符串:",match1.string)
print("匹配的数据:",match1.group())
'''
匹配值的起始位置: 0
匹配值的结束位置: 4
匹配值的区间的位置: (0, 4)
待匹配值的字符串: 3.11Python I study every day
匹配的数据: 3.11`
'''
#search
pattern = "\d\.\d+"
s = "I study python3.11 every day python2.7 i used"
match = re.search(pattern, s)
print(match)
s1 = "2.71I study python3.11 every day python i used"
match1 = re.search(pattern, s1)
print(match1)
#findall
lst = re.findall(pattern,s)
lst1 = re.findall(pattern,s1)
print(lst)
print(lst1)
#sub and split
import re
#sub()
pattern = "黑客|破解|反爬"
s = "我需要学习python,想当黑客,破解一些VIP视频,python可以实现无底线反爬吗"
'''
def sub(pattern, repl, string, count=0, flags=0):
"""Return the string obtained by replacing the leftmost
non-overlapping occurrences of the pattern in string by the
replacement repl. repl can be either a string or a callable;
if a string, backslash escapes in it are processed. If it is
a callable, it's passed the Match object and must return
a replacement string to be used."""
return _compile(pattern, flags).sub(repl, string, count)
'''
new_s = re.sub(pattern, "XXX", s)
print(new_s)
#split
s1 = "https://cn.bing.com/search?q=zhl&cvid=016dc0451cab427eaa8d8f04787fae17"
pattern1 = "[?|&]"
lst = re.split(pattern1,s1)
print(lst)
练习
Exer1
'''
判断车牌归属地
使用列表存储N个车牌号码,通过遍历列表以及字符串的切片操作判断车牌的归属地
'''
lst = ["湘A0001","京A0001","沪A0001","粤A0001"]
for item in lst:
area = item[0:1]
print(item, "归属地为:",area)
Exer2
'''
统计字符串中出现指定字符的次数
内容为 ”HelloPython,HelloJava,HelloC++“
用户从键盘录入要查询的字符,不区分大小写
要求统计出要查找的字符串出现的次数
'''
s1 = "HelloPython,HelloJava,HelloC++"
word = input("输入要统计的字符:")
print(f"{word}在{s1}一共出现了{s1.upper().count(word.upper())}")
Exer3
'''
格式化输出商品的名称和价格
使用列表存储一些商品数据,使用循环遍历输出商品的信息,要求对商品的编号进行格式化为6位
单价保存2位小鼠,并在前面添加人名币符号输出
'''
lst = [
["01","PC","MS",5000],
["02","car","BYD",50000],
["03","mp","NS",5],
["04","TV","TCL",500],
]
print("编号\t\t\t名称\t\t\t品牌\t\t\t单价")
for item in lst:
for i in item:
print(i,end="\t\t\t")code>
print()
#格式化操作
for item in lst:
item[0] = "0000" + item[0]
item[3] = "¥{0:.2f}".format(item[3])
print("编号\t\t\t\t名称\t\t\t\t品牌\t\t\t\t单价")
for item in lst:
for i in item:
print(i,end="\t\t\t")code>
print()
Exer4
'''
提取文本中所有图片的链接地址
'''
import random
import string
# 定义基础URL
base_url = "https://example.com/image"
# 定义可能的查询参数
params = {
"resolution": ["1080p", "720p", "4k"],
"format": ["jpg", "png", "gif"],
"quality": ["high", "medium", "low"],
"random": lambda: ''.join(random.choices(string.ascii_letters + string.digits, k=6))
}
# 生成随机查询参数
def generate_query_params():
query_params = []
for key, values in params.items():
if callable(values):
value = values()
else:
value = random.choice(values)
query_params.append(f"{key}={value}")
return "&".join(query_params)
# 生成完整的图片URL
def generate_complex_image_url():
query_string = generate_query_params()
return f"{base_url}?{query_string}"
# 生成并打印10个复杂的图片URL
for _ in range(10):
print(generate_complex_image_url())
import re
# 编译正则表达式模式
pattern = re.compile(r"\d+")
# 使用编译后的正则表达式对象进行匹配
text = "There are 123 apples and 456 oranges."
match = pattern.search(text)
if match:
print("Found:", match.group())
test_s = '"https://example.com/image?resolution=1080p&format=jpg&quality=high&random=abcdef","https://example.com/image?resolution=4k&format=jpg&quality=medium&random=saxkir","asd",sad,"asd",d"""""https://example.com/image?resolution=4k&format=jpg&quality=medium&random=driv3X",https://example.com/image?resolution=1080p&format=png&quality=low&random=xG7jqi'
# 使用捕获组
regex_pattern_with_groups = r'(https://example\.com/image\?resolution=(1080p|720p|4k)&format=(jpg|png|gif)&quality=(high|medium|low)&random=([a-zA-Z0-9]{6}))'
# 不使用捕获组
regex_pattern_without_groups = r'https://example\.com/image\?resolution=[0-9a-z]+&format=[0-9a-z]+&quality=[0-9a-z]+&random=[0-9a-zA-Z]{6}'
# 使用findall查找所有匹配的URL
lst_with_groups = re.findall(regex_pattern_with_groups, test_s)
lst_without_groups = re.findall(regex_pattern_without_groups, test_s)
# 打印所有匹配的URL
print("With groups:")
for item in lst_with_groups:
print(item) # item是一个元组
print("\nWithout groups:")
for item in lst_without_groups:
print(item) # item是整个匹配的字符串
声明
本文内容仅代表作者观点,或转载于其他网站,本站不以此文作为商业用途
如有涉及侵权,请联系本站进行删除
转载本站原创文章,请注明来源及作者。