STL详解 - string类
南风与鱼 2024-10-01 09:05:05 阅读 95

目录
编辑
一、为什么要学习string类
1.1 C语言中的字符串
1.2 面试题
🌳字符串相加https://leetcode.cn/problems/add-strings/description/
二、标准库中的string类
2.1 string类
2.2 string类的常用接口说明
1. string类对象的常见构造
2. string类对象的容量操作
3. string类对象的访问及遍历操作
4. string类对象的修改操作
5. string类非成员函数
6. vs和g++下string结构的说明
🌵vs下string的结构:
🌵g++下string的结构:
三、OJ习题
1. 仅仅反转字母
2. 找字符串中第一个只出现一次的字符
3. 字符串里面最后一个单词的长度
4. 验证一个字符串是否是回文串
5. 字符串相加
四、扩展阅读
🥤:面试中string的一种正确写法
🍺:STL中的string类怎么了
一、为什么要学习string类
1.1 C语言中的字符串
C语言中,字符串是以'\0'结尾的一些字符的集合,为了操作方便,C标准库中提供了一些str系列的库函数,但是这些库函数与字符串是分离开的,不太符合OOP的思想,而且底层空间需要用户自己管理,稍不留神可能还会越界访问。
1.2 面试题
🌳字符串相加

https://leetcode.cn/problems/add-strings/description/
在OJ中,有关字符串的题目基本以string类的形式出现,而且在常规工作中,为了简单、方便、快捷,基本都使用string类,很少有人去使用C库中的字符串操作函数。
二、标准库中的string类
学习C++中的string类非常重要,但是它的接口又非常的多,我们不可能将它们全部记住,并且也没这个必要,我们只需要熟练掌握平常工作中需要经常用到的一些接口就行了,剩下的可以通过查阅相关文档来了解string类的成员函数、用法和示例。
这里介绍两个网站,以供参考:
C++官方网站(cppreference):
网址:https://en.cppreference.com/w/优点:作为一个wiki风格的网站,提供了非常详尽和全面的C++语言参考资料。覆盖了C++标准库、语言特性、语法规则等方方面面。缺点:有些页面可能含有过多详细信息,对初学者难以理解。
cplusplus网站(推荐):
网址:http://www.cplusplus.com/优点:提供了C++语言的完整参考资料、教程和示例代码。有专门的页面介绍标准库函数、关键字和语法规则。缺点:部分资料可能有限,对一些高级语言特性和最新标准可能覆盖不够全面。
2.1 string类
string类的文档介绍

https://legacy.cplusplus.com/reference/string/string/?kw=string
字符串是表示字符序列的类。
标准的字符串类提供了对此类对象的支持,其接口类似于标准字符容器的接口,但添加了专门用于操作单字节字符字符串的设计特性。 string类是使用char(即作为它的字符类型,使用它的默认char_traits和分配器类型(关于模板的更多信息,请参阅basic_string)。 string类是basic_string模板类的一个实例,它使用char来实例化basic_string模板类,并用char_traits和allocator作为basic_string的默认参数(更多的模板信息请参考basic_string)。 注意,这个类独立于所使用的编码来处理字节:如果用来处理多字节或变长字符(如UTF-8)的序列,这个类的所有成员(如长度或大小)以及它的迭代器,将仍然按照字节(而不是实际编码的字符)来操作。
总结:
string是表示字符串的字符串类 。该类的接口与常规容器的接口基本相同,再添加了一些专门用来操作string的常规操作。string在底层实际是:basic_string模板类的别名,typedef basic_string<char, char_traits,allocator>string;
不能操作多字节或者变长字符的序列。
在使用string类时,必须包含#include头文件以及using namespace std;
2.2 string类的常用接口说明
1. string类对象的常见构造
🌵函数名称:constructor

https://legacy.cplusplus.com/reference/string/string/string/
using namespace std;
#include <string>
void test_string1()
{
string s0; // 默认构造,构造空的string类对象
string s1("hello world"); // 字符串构造
string s2(s1); // 拷贝构造
string s3(s1, 5, 3); // 将s1从第5个位置开始取3个字符
string s4(s1, 5, 10); // 将s1从第5个位置开始取10个字符
string s5(s1, 5); // 不给第三个参数,就默认是缺省值npos(npos是string里面的一个静态成员变量 static const size_t npos = -1),后边有多少取多少
string s6(10, '*');
cout << s0 << endl;
cout << s1 << endl;
cout << s2 << endl;
cout << s3 << endl;
cout << s4 << endl;
cout << s5 << endl;
cout << s6 << endl;
}
int main()
{
test_string1();
return 0;
}
2. string类对象的容量操作

🌳函数名称链接: (size + length + capacity + empty + clear + reserve + resize)
using namespace std;
#include <string>
void test_string()
{
string s1("hello world hello world hello world");
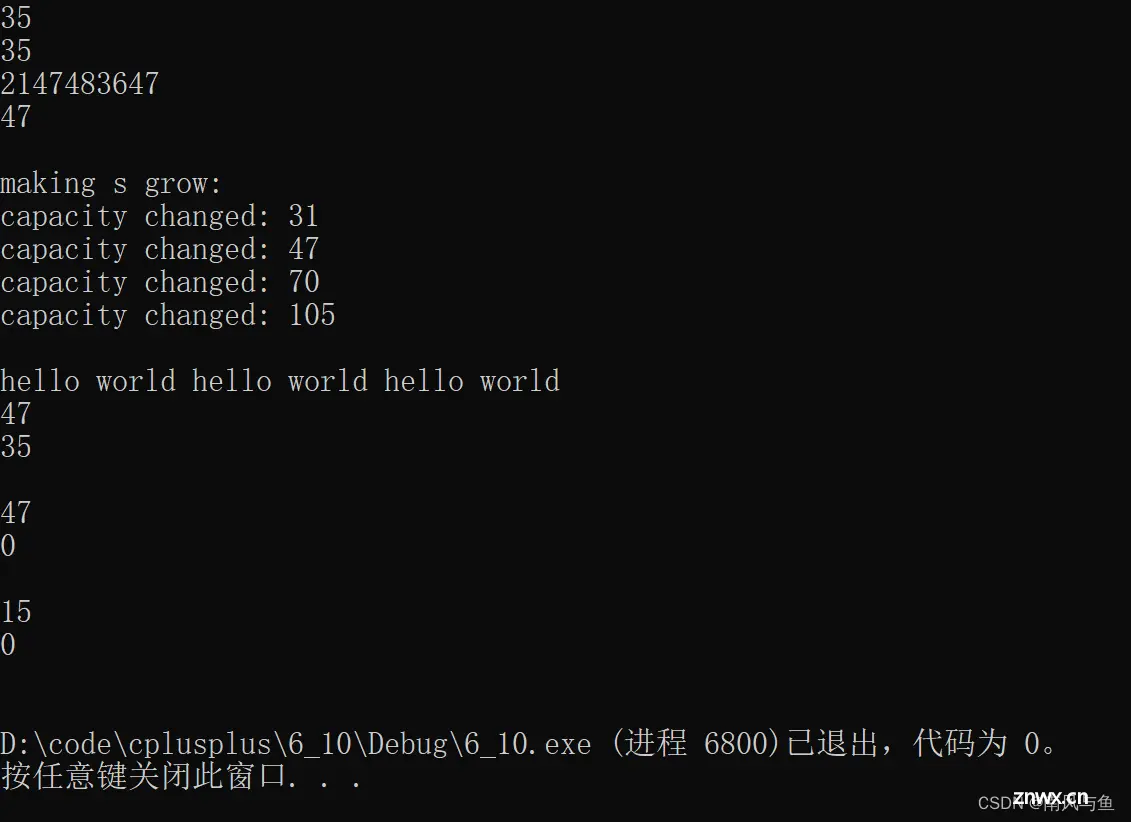
cout << s1.size() << endl;
cout << s1.length() << endl;
cout << s1.max_size() << endl;
cout << s1.capacity() << endl << endl;; // 不包含\0占用的空间
// 查看扩容机制
string s;
size_t sz = s.capacity();
cout << "making s grow:\n";
for (int i = 0; i < 100; ++i)
{
s.push_back('c'); // 自动扩容
if (sz != s.capacity())
{
sz = s.capacity();
cout << "capacity changed: " << sz << '\n';
}
}
cout << endl;
// clear只是清数据,不会清空间
cout << s1 << endl;
cout << s1.capacity() << endl;
cout << s1.size() << endl;
s1.clear();
cout << s1 << endl;
cout << s1.capacity() << endl;
cout << s1.size() << endl << endl;
// 缩容
// 但不会将string对象的容量缩减到0,因为它会
// 保留一定的冗余空间以提高字符串的操作效率
s1.shrink_to_fit();
cout << s1.capacity() << endl;
cout << s1.size() << endl << endl;
}
int main()
{
test_string();
return 0;
}

using namespace std;
#include <string>
void test_string()
{
// reserve是手动扩容,比capacity大才会扩容
// reserve用的比较多,因为如果我们知道要插入多少数据
// 就会提前开好空间,这样就避免了扩容,提高了效率
string s2("hello hello hello hello");
cout << s2.size() << endl;
cout << s2.capacity() << endl;
s2.reserve(200);
cout << s2.size() << endl;
cout << s2.capacity() << endl << endl;
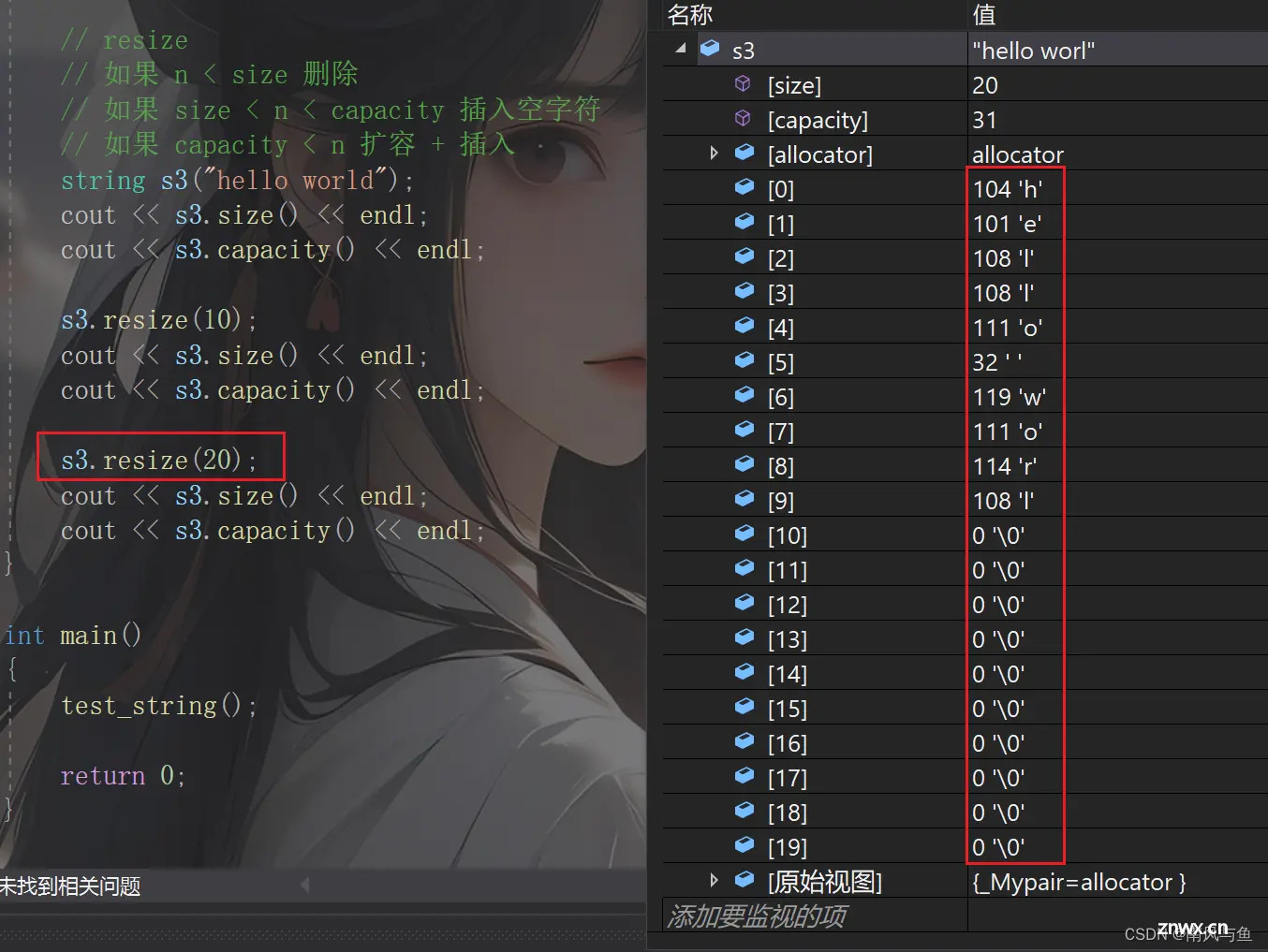
// resize
// 如果 n < size 删除
// 如果 size < n < capacity 插入空字符
// 如果 capacity < n 扩容 + 插入
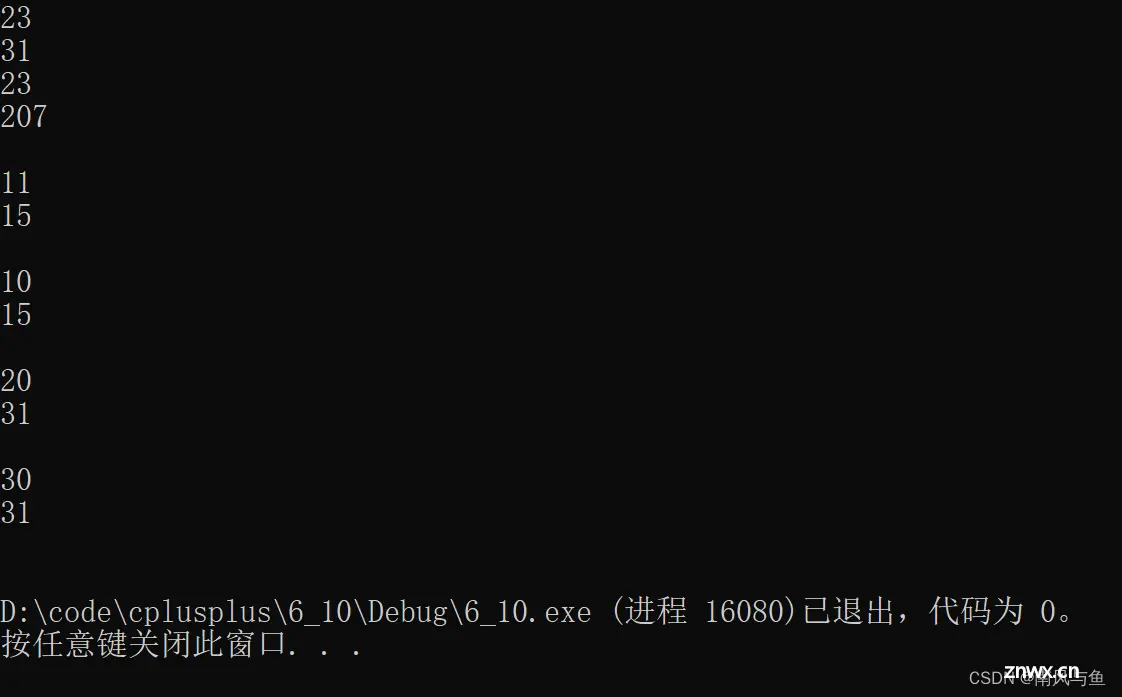
string s3("hello world");
cout << s3.size() << endl;
cout << s3.capacity() << endl << endl;
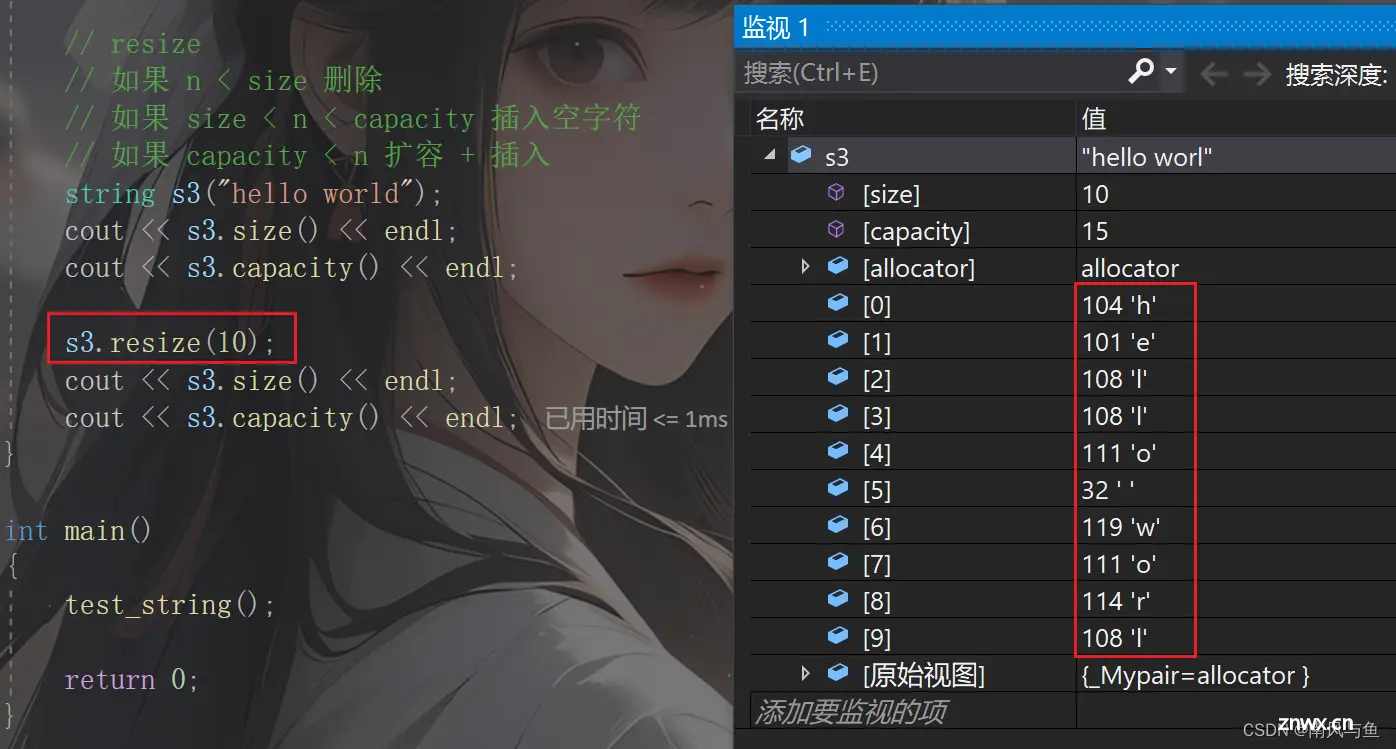
s3.resize(10);
cout << s3.size() << endl;
cout << s3.capacity() << endl << endl;
s3.resize(20);
cout << s3.size() << endl;
cout << s3.capacity() << endl << endl;
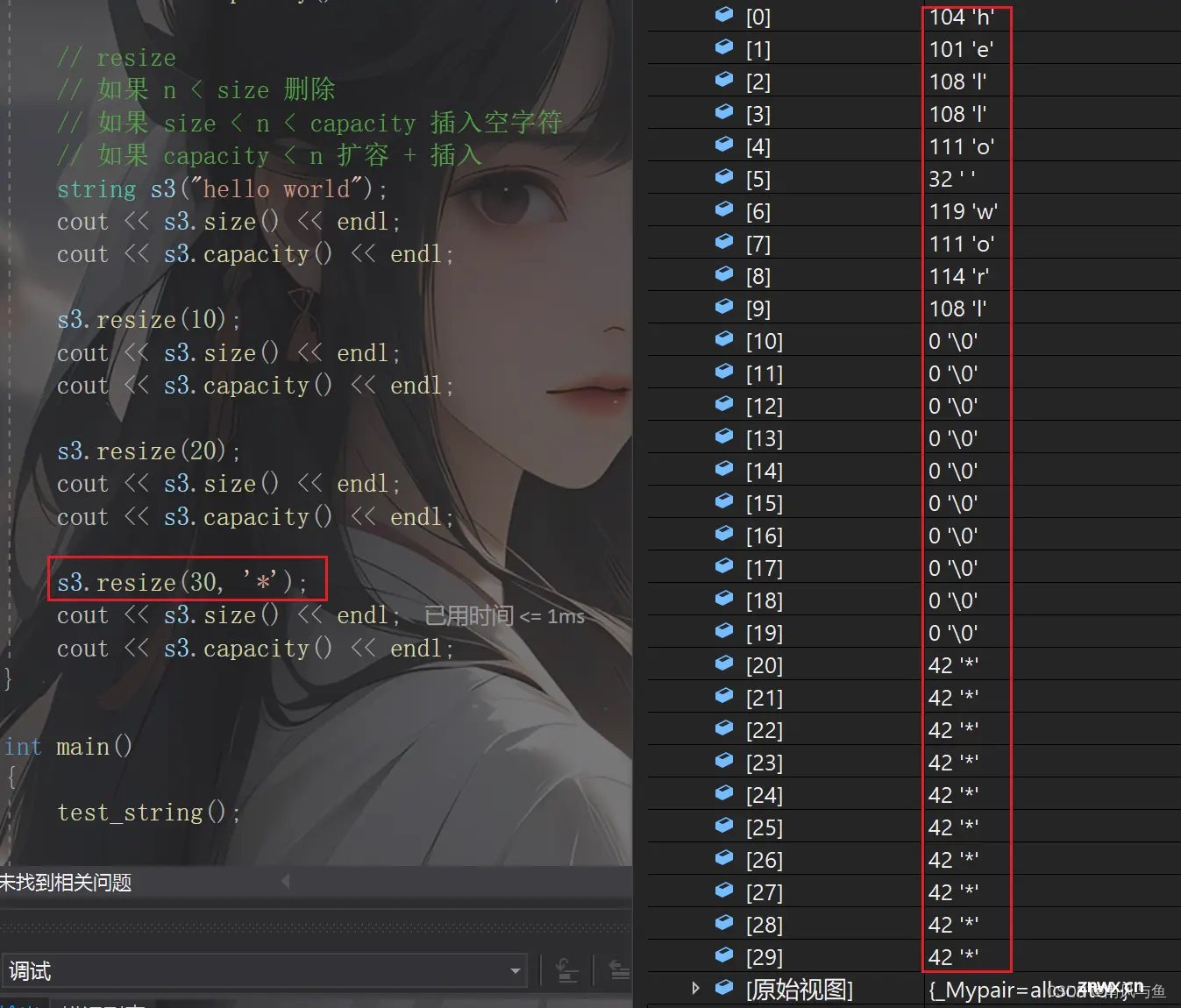
s3.resize(30, '*');
cout << s3.size() << endl;
cout << s3.capacity() << endl << endl;
}
int main()
{
test_string();
return 0;
}
注意:
size()与length()方法底层实现原理完全相同,引入size()的原因是为了与其他容器的接口保持一致,一般情况下基本都是用size()。
clear()只是将string中有效字符清空,不改变底层空间大小。
resize(size_t n) 与 resize(size_t n, char c)都是将字符串中有效字符个数改变到n个,不同的是当字符个数增多时:resize(n)用0来填充多出的元素空间,resize(size_t n, char c)用字符c来填充多出的元素空间。注意:resize在改变元素个数时,如果是将元素个数增多,可能会改变底层容量的大小,如果是将元素个数减少,底层空间总大小不变。
reserve(size_t res_arg=0):为string预留空间,不改变有效元素个数,当reserve的参数小于string的底层空间总大小时,reserver不会改变容量大小。
3. string类对象的访问及遍历操作


🌲函数名称:operator

https://legacy.cplusplus.com/reference/string/string/operator%5B%5D/
🌲函数名称:begin

https://legacy.cplusplus.com/reference/string/string/begin/ + end

https://legacy.cplusplus.com/reference/string/string/end/
using namespace std;
#include <string>
// string的三种遍历方式
void test_string()
{
string s1("hello world");
// 需要注意的以下三种方式除了遍历string对象,还可以修改string中的字符,
// 另外以下三种方式对于string而言,第一种使用最多
// 1. for+operator[]、下标 + []
for (size_t i = 0; i < s1.size(); i++)
{
cout << s1[i] << " ";
//cout << s1.operator[](i) << " ";
}
cout << endl;
// 修改
for (size_t i = 0; i < s1.size(); i++)
{
s1[i]++;
}
for (size_t i = 0; i < s1.size(); i++)
{
cout << s1[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
// 2.迭代器(区间是左闭右开)
// begin是第一个有效数据的迭代器
// end是最后一个位置的下一个位置(就是\0,因为\0不是有效字符)
string::iterator it = s1.begin();
while (it != s1.end())
{
cout << *it << " ";
++it;
}
cout << endl;
// 3.范围for
// 底层就是迭代器
for (auto e : s1)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
int main()
{
test_string();
return 0;
}

🌲函数名称:rbegin

https://legacy.cplusplus.com/reference/string/string/rbegin/ + rend

https://legacy.cplusplus.com/reference/string/string/rend/
using namespace std;
#include <string>
// 反向迭代器
void test_string()
{
string s("hello world");
// 可读可写
string::reverse_iterator rit = s.rbegin();
while (rit != s.rend())
{
cout << *rit << " ";
++rit;// 注意这儿是++
}
cout << endl;
// 只读
const string s1("hello world");
string::const_reverse_iterator rit1 = s1.rbegin();
while (rit1 != s1.rend())
{
cout << *rit1 << " ";
++rit1;
}
cout << endl;
}
int main()
{
test_string();
return 0;
}
🌳函数名称:operator[]

https://legacy.cplusplus.com/reference/string/string/operator%5B%5D/ + at

https://legacy.cplusplus.com/reference/string/string/at/
using namespace std;
#include <string>
void test_string()
{
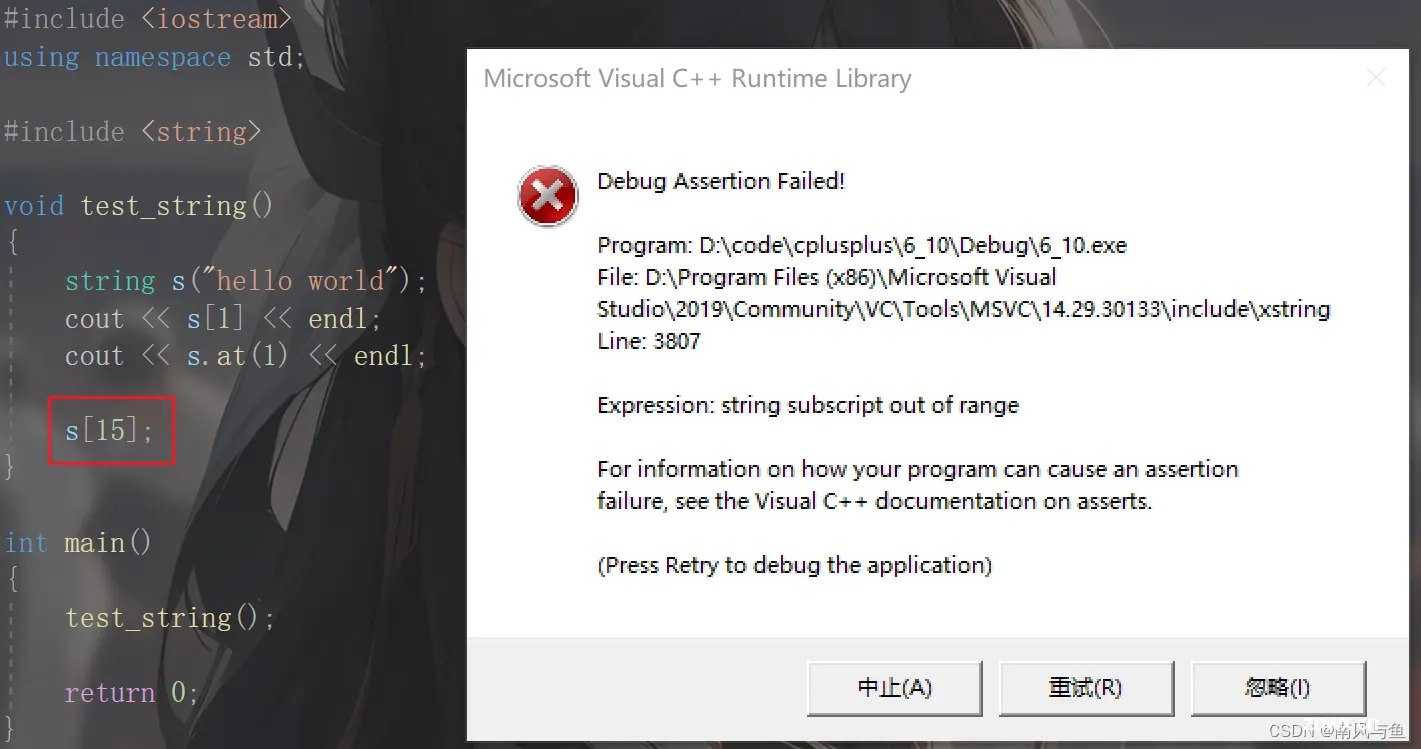
string s("hello world");
cout << s[1] << endl;
cout << s.at(1) << endl;
// []和at的不同在于对数组越界访问的报错不一样
/*s[15];
s.at(15);*/
}
int main()
{
test_string();
return 0;
}
4. string类对象的修改操作


🌳函数名称链接:push_back + append + operator+= + c_str + find + npos + rfind + substr
using namespace std;
#include <string>
void test_string()
{
string s("hello world");
// push_back:在尾部插入一个字符
s.push_back('!');
cout << s << endl;
// append:在尾部追加一个字符串
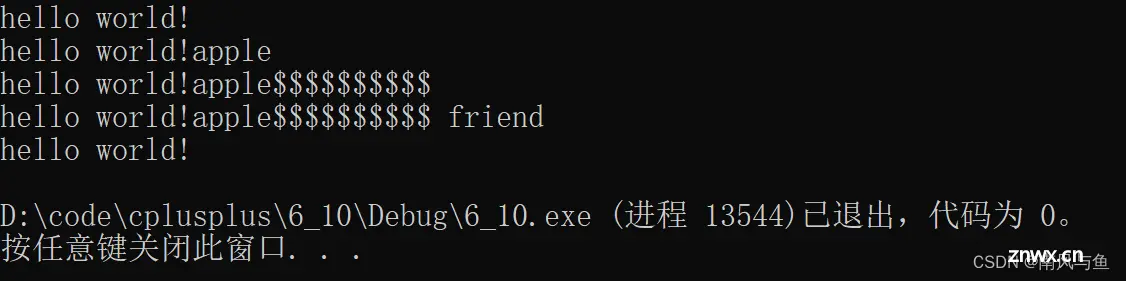
s.append("apple");
cout << s << endl;
// 在尾部插入n个字符
s.append(10, '$');
cout << s << endl;
string s1(" friend ");
/*s.append(s1);
cout << s << endl;*/
// 追加时头部只留一个空格,尾部不要空格
s.append(++s1.begin(), --s1.end());
cout << s << endl;
// operator+=:在字符串后边追加字符串
string s3("hello");
s3 += " ";
s3 += "world!";
cout << s3 << endl;
}
int main()
{
test_string();
return 0;
}
using namespace std;
#include <string>
void test_string()
{
string s("hello");
cout << s << endl;
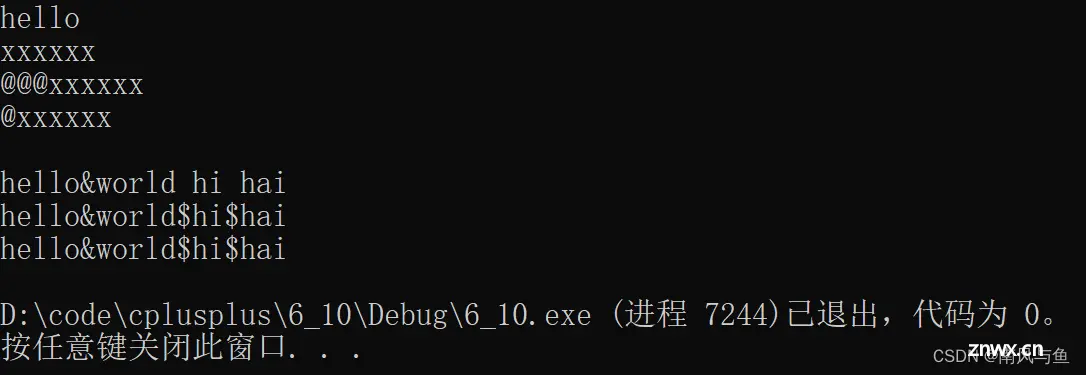
// assign:赋值(用一个值覆盖掉字符串)
s.assign("xxxxxx");
cout << s << endl;
// insert:在某个位置进行插入
s.insert(0, "@@@");// 在第0个位置插入@@@
cout << s << endl;
// erase :删除字符串中的字符
s.erase(1, 2);// 从第一个位置开始删除两个字符
cout << s << endl;
s.erase();// 全部删除(erase支持全缺省)
cout << s << endl;
// replace:替换字符串的一部分
string s1("hello world hi hai");
s1.replace(5, 1, "&");
cout << s1 << endl;
// 替换字符串中的空格
size_t pos = s1.find(' ');
while (pos != s1.npos)
{
s1.replace(pos, 1, "$");
pos = s1.find(' ');
}
cout << s1 << endl;
// 第二种方法
string s2;
for (auto ch : s1)
{
if (ch != ' ')
{
s2 += ch;
}
else
{
s2 += '$';
}
}
cout << s2 << endl;
}
int main()
{
test_string();
return 0;
}

#include <string>
using namespace std;
void test_string()
{
// c_str 返回c格式字符串
string s("hello world");
string filename("test.cpp");
FILE* fout = fopen(filename.c_str(), "r");
// find 从字符串pos位置从前往后找字符c,返回该字符在字符串中的位置
// substr 在str中从pos位置开始,截取n个字符,然后将其返回
// 拿到文件的后缀
string s1("test.txt");
size_t pos1 = s1.find('.');
if (pos1 != string::npos)
{
string suffix = s1.substr(pos1);
//string suffix = s1.substr(pos1, s1.size() - pos1);
cout << suffix << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "没有后缀" << endl;
}
// rfind 从字符串pos位置从后往前找字符c,返回该字符在字符串中的位置
// 获取文件后缀
string s2("file.c.tar.zip");
size_t pos2 = s2.rfind('.');
if (pos2 != string::npos)
{
string suffix = s2.substr(pos2);
cout << suffix << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "没有后缀" << endl;
}
string url1("https://legacy.cplusplus.com/reference/string/string/");
string url2("https://image.baidu.com/search/index?tn=baiduimage&ps=1&ct=201326592&lm=-1&cl=2&nc=1&ie=utf-8&dyTabStr=MCwxLDIsMyw3LDYsNCw1LDgsOQ%3D%3D&word=%E4%B9%A0%E8%BF%91%E5%B9%B3%E5%BC%BA%E8%B0%83%E4%B8%8D%E8%83%BD%E8%AE%A9%E4%BB%96%E4%BB%AC%E5%90%83%E4%BA%8F");
string protocal, domain, uri;
size_t i1 = url1.find(':');
if (i1 != string::npos)
{
string protocal = url1.substr(0, i1 - 0);
cout << protocal << endl;
}
size_t i2 = url1.find('/', i1 + 3);
if (i2 != string::npos)
{
string domain = url1.substr(i1 + 3, i2 - (i1 + 3));
cout << domain << endl;
string uri = url1.substr(i2 + 1);
cout << uri << endl;
}
}
int main()
{
test_string();
return 0;
}
注意:
在string尾部追加字符时,s.push_back(c) / s.append(1, c) / s += 'c'三种的实现方式差不多,一般情况下string类的+=操作用的比较多,+=操作不仅可以连接单个字符,还可以连接字符串。
对string操作时,如果能够大概预估到放多少字符,可以先通过reserve把空间预留好。
5. string类非成员函数


🌳函数名称链接:operator+ + relational operators + swap + operator>> + operator<< + getline
#include <string>
using namespace std;
void test_string()
{
// operator+
string s1 = "hello";
string s2 = " world";
string ret = s1 + s2;
cout << ret << endl;
// 支持string + 字符串, 也支持字符串 + string
string ret1 = s1 + "world";
string ret2 = "hello" + s2;
}
int main()
{
test_string();
return 0;
}

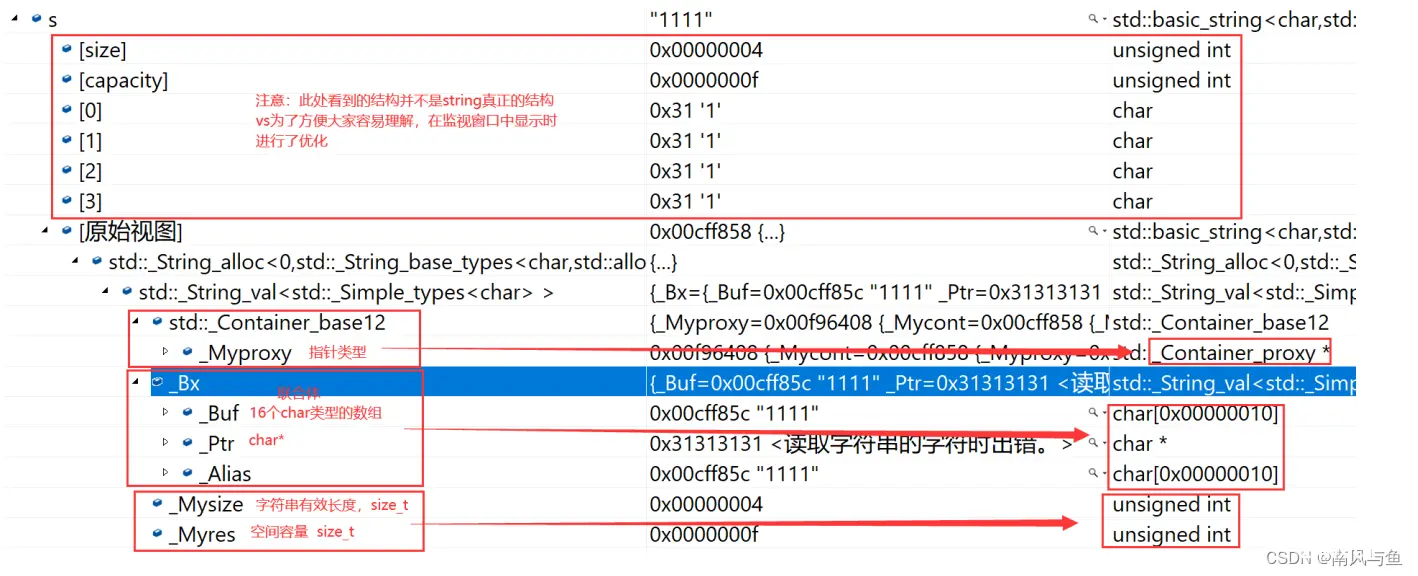
6. vs和g++下string结构的说明
注意:下述结构是在32位平台下进行验证,32位平台下指针占4个字节。
🌵vs下string的结构:
string总共占28个字节,内部结构稍微复杂一点,先是有一个联合体,联合体用来定义string中字符串的存储空间:
当字符串长度小于16时,使用内部固定的字符数组来存放。当字符串长度大于等于16时,从堆上开辟空间。
<code>union _Bxty
{ // storage for small buffer or pointer to larger one
value_type _Buf[_BUF_SIZE];
pointer _Ptr;
char _Alias[_BUF_SIZE]; // to permit aliasing
} _Bx;
这种设计也是有一定道理的,大多数情况下字符串的长度都小于16,那string对象创建好之后,内部已经有了16个字符数组的固定空间,不需要通过堆创建,效率高。
其次:还有一个size_t字段保存字符串长度,一个size_t字段保存从堆上开辟空间总的容量。
最后:还有一个指针做一些其他事情。
故总共占16+4+4+4=28个字节。
🌵g++下string的结构:
G++下,string是通过写时拷贝实现的,string对象总共占4个字节,内部只包含了一个指针,该指针将来指向一块堆空间,内部包含了如下字段:
空间总大小字符串有效长度引用计数
<code>struct _Rep_base
{
size_type _M_length;
size_type _M_capacity;
_Atomic_word _M_refcount;
}
指向堆空间的指针,用来存储字符串。
三、OJ习题
1. 仅仅反转字母

https://leetcode.cn/problems/reverse-only-letters/description/
class Solution
{
public:
bool isLetter(char ch)
{
if (ch >= 'a' && ch <= 'z')
return true;
if (ch >= 'A' && ch <= 'Z')
return true;
return false;
}
string reverseOnlyLetters(string S)
{
if (S.empty())
return S;
size_t begin = 0, end = S.size() - 1;
while (begin < end)
{
while (begin < end && !isLetter(S[begin]))
++begin;
while (begin < end && !isLetter(S[end]))
--end;
swap(S[begin], S[end]);
++begin;
--end;
}
return S;
}
};
2. 找字符串中第一个只出现一次的字符

https://leetcode.cn/problems/first-unique-character-in-a-string/description/
class Solution
{
public:
int firstUniqChar(string s)
{
int count[26] = { 0 };
// 统计每个字符出现的次数
for (auto ch : s)
{
count[ch - 'a']++;
}
// 按照字符次序从前往后找只出现一次的字符
for (int i = 0; i < s.size(); ++i)
{
if (1 == count[s[i] - 'a'])
return i;
}
return -1;
}
};
3. 字符串里面最后一个单词的长度

https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/8c949ea5f36f422594b306a2300315da?tpId=37&&tqId=21224&rp=5&ru=/activity/oj&qru=/ta/huawei/question-ranking
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string str;
// 不要使用cin>>line,因为会它遇到空格就结束了
// while(cin>>line)
while (getline(cin, str))
{
// 从后往前找第一个空格的位置
size_t pos = str.rfind(' ');
// 左开右闭,size是最后一个字符的下一个位置
// pos是空格的位置,+1刚好是最后一个单词的起始位置
cout << str.size() - (pos + 1) << endl;
}
//char ch = getchar();
//while (ch != '\n')
//{
// str += ch;
// ch = getchar();
//}
return 0;
}

4. 验证一个字符串是否是回文串

https://leetcode.cn/problems/valid-palindrome/description/
class Solution {
public:
bool isLetterOrNumber(char ch)
{
return (ch >= '0' && ch <= '9')
|| (ch >= 'a' && ch <= 'z')
|| (ch >= 'A' && ch <= 'Z');
}
bool isPalindrome(string s) {
// 先小写字母转换成大写,再进行判断
for (auto& ch : s)
{
if (ch >= 'a' && ch <= 'z')
ch -= 32;
}
int begin = 0, end = s.size() - 1;
while (begin < end)
{
while (begin < end && !isLetterOrNumber(s[begin]))
++begin;
while (begin < end && !isLetterOrNumber(s[end]))
--end;
if (s[begin] != s[end])
{
return false;
}
else
{
++begin;
--end;
}
}
return true;
}
};
5. 字符串相加

https://leetcode.cn/problems/add-strings/description/
class Solution
{
public:
string addStrings(string num1, string num2)
{
// 最后一个字符的位置
int end1 = num1.size() - 1, end2 = num2.size() - 1;
string retstr;
// 提前开好空间
retstr.reserve(num1.size() > num2.size() ? num1.size() + 1 : num2.size() + 1);
// 表示进位
int next = 0;
// 注意:长字符串应该最后才结束相加
while (end1 >= 0 || end2 >= 0)
{
int val1 = end1 >= 0 ? num1[end1--] - '0' : 0;
int val2 = end2 >= 0 ? num2[end2--] - '0' : 0;
int ret = val1 + val2 + next;
next = ret / 10; // 取进位
ret = ret % 10; // 取个位数
//头插,时间复杂度为n^2
//retstr.insert(0, 1, ret + '0');
//尾插
retstr += '0' + ret;
}
if (next == 1)
{
//retstr.insert(0, 1, '1');
retstr += '1';
}
//将字符串反转,时间复杂度提升到O(n)
reverse(retstr.begin(), retstr.end());
return retstr;
}
};
四、扩展阅读
🥤:面试中string的一种正确写法

https://coolshell.cn/articles/10478.html
🍺:STL中的string类怎么了

https://blog.csdn.net/haoel/article/details/1491219
声明
本文内容仅代表作者观点,或转载于其他网站,本站不以此文作为商业用途
如有涉及侵权,请联系本站进行删除
转载本站原创文章,请注明来源及作者。