人工智能课设——基于A*算法的五子棋博弈系统(Python实现)
汪汪小乌拉 2024-07-10 09:01:04 阅读 92
一、课设要求
基于A*算法的五子棋博弈系统
A)给出用 A*算法设计实现五子棋博弈的思想与方法。
B)设计实现五子棋博弈交互系统。
C)对不同的格局,以及不同的初始状态和目标状态,记录 A*算法的落棋求解结果。
分析A*算法设计实现五子棋博弈的有效性。
二、代码实现
注:该代码在码者编辑此文档时进行过微调,如有bug可评论或私信,感谢。
2.1 原代码
作者:罗WWEEII (luo_wweeii) - Gitee.com项目链接:gobang_AI: 基于博弈树α-β剪枝搜索的五子棋AI (gitee.com)
因为本人不擅长python,再加上从零开始也很浪费时间,所以直接去gitee上面找的现有代码进行修改。(原作者如有介意请联系删除)
2.2 核心代码
2.2.1 A*算法实现
open表:用于存储待评估的点;closed表:用于记录已经评估过的点;价值:价值越高,越容易获胜;代价:价值取反;
首先,将所有落子的邻接点放入open表中,放入的时候会进行落子评估,获取落子在一个点后的棋局价值;从open表中取出价值最高的点;落子判断,判断当前点是否合法、当前点是否在closed表中、当前搜索是否达到搜索深度(DEPTH);将当前落子的所有邻接点放入open表,放入前也会进行价值计算;循环第二步至第四步,直到到达循环出口(open表为空,达到递归深度);
代码:
<code>def a_star_search():
open_list = [] # 所有带搜索的点
closed_set = { } # 记录已经搜索过的点以及其价值评估分数
for point in list3:
neighbors = get_neighbors(point) # 取出所有落子的邻接点
for neighbor in neighbors:
if neighbor in list_all and neighbor not in list3 and neighbor not in closed_set.keys(): # 修改此处检查邻居是否在 closed_set 的键中
# 后续两个append()和remove()是为了评估落下评估点后的棋局状态(但实际还未落下),所以需要先添加进两个list中,之后再删除
list1.append(neighbor) # 将邻居加入AI列表
list2.append(neighbor) # 将邻居加入人类落子列表
if neighbor not in [node for (_, node) in open_list]: # 检查节点是否已经存在于open列表中
heapq.heappush(open_list, (-evaluation(True), neighbor)) # 将当前点加入open列表
# 从列表中删除刚刚加入的邻居
list1.remove(neighbor)
list2.remove(neighbor)
if not open_list:
return None
while open_list:
# 在a_star_search函数中修改取出具有最小代价的节点的行为
min_cost = min(open_list)[0] # 获取当前最小代价
min_cost_nodes = [node for cost, node in open_list if cost == min_cost] # 找到所有具有最小代价的节点列表
current_node = random.choice(min_cost_nodes) # 从具有相同最小代价的节点列表中随机选择一个节点
open_list.remove((min_cost, current_node)) # 从open_list中移除选择的节点
current_cost = min_cost
if current_node not in closed_set:
if current_node not in list3:
closed_set[current_node] = current_cost # 记录当前点和评估分数
if len(closed_set) >= DEPTH: # 到达搜索深度
max_score_node = min(closed_set, key=closed_set.get) # 找到评估分数最大的点(代价最小,即价值最大)
return max_score_node
neighbors = get_neighbors(current_node)
for neighbor in neighbors:
if neighbor in list_all and neighbor not in list3 and neighbor not in closed_set.keys(): # 修改此处检查邻居是否在 closed_set 的键中
list1.append(neighbor) # 将邻居加入AI列表
list2.append(neighbor) # 将邻居加入列表
if neighbor not in [node for (_, node) in open_list]: # 检查节点是否不在open列表中
heapq.heappush(open_list, (-evaluation(True), neighbor)) # 将节点推入open列表
# 从列表中删除刚刚加入的邻居
list1.remove(neighbor)
list2.remove(neighbor)
# 如果搜索完所有可搜索的点时仍未到达搜索深度,则返回评估分数最大的点
max_score_node = min(closed_set, key=closed_set.get)
return max_score_node
2.2.2 评估函数
1> 评估模型
当某一行/列构成评估模型中的状态时,便相应的累加记分。
# 棋型的评估分数,例:落子为* * 1 1 0 0 0 * * 时的棋型得10分 1为计算分数的对象的棋子,0为可落子的空位置
shape_score = [(10, (1, 1, 0, 0, 0)),
(10, (1, 0, 1, 0, 0)),
(10, (1, 0, 0, 1, 0)),
(50, (0, 1, 1, 0, 0)),
(50, (0, 1, 0, 1, 0)),
(100, (1, 1, 0, 1, 0)),
(100, (0, 0, 1, 1, 1)),
(100, (1, 1, 1, 0, 0)),
(500, (0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0)),
(500, (0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0)),
(2000, (0, 1, 1, 1, 0)),
(4000, (1, 1, 1, 0, 1)),
(4000, (1, 1, 0, 1, 1)),
(4000, (1, 0, 1, 1, 1)),
(5000, (1, 1, 1, 1, 0)),
(5000, (0, 1, 1, 1, 1)),
(100000, (0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0)),
(99999999, (1, 1, 1, 1, 1))]
2> 评估函数
在评估函数中,首先会根据传参,相应的进行待计算棋子列表的初始化,然后计算双方每个落子的每个方向上的得分情况(使用score_all_arr来保证不会对一种得分情况进行重复计算),最后带权相加当前的棋局得分情况。
ratio:进攻的系数;小于1:进攻型、大于1:防守型
# 一个点的价值评估函数
def evaluation(is_ai):
if is_ai:
my_list = list1
enemy_list = list2
else:
my_list = list2
enemy_list = list1
# 算自己的得分
score_all_arr = [] # 得分形状的位置,避免重复计算
my_score = 0
for pt in my_list:# 计算自己的所有点在四个方向上的得分情况
m = pt[0]
n = pt[1]
my_score += cal_score(m, n, 0, 1, enemy_list, my_list, score_all_arr)
my_score += cal_score(m, n, 1, 0, enemy_list, my_list, score_all_arr)
my_score += cal_score(m, n, 1, 1, enemy_list, my_list, score_all_arr)
my_score += cal_score(m, n, -1, 1, enemy_list, my_list, score_all_arr)
# 算敌人的得分
score_all_arr_enemy = []
enemy_score = 0
for pt in enemy_list:
m = pt[0]
n = pt[1]
enemy_score += cal_score(m, n, 0, 1, my_list, enemy_list, score_all_arr_enemy)
enemy_score += cal_score(m, n, 1, 0, my_list, enemy_list, score_all_arr_enemy)
enemy_score += cal_score(m, n, 1, 1, my_list, enemy_list, score_all_arr_enemy)
enemy_score += cal_score(m, n, -1, 1, my_list, enemy_list, score_all_arr_enemy)
total_score = my_score + enemy_score * ratio
return total_score
3> 得分计算
该函数会根据参数,相应的查找传入点的传入方向上的前后共十一个位置,优先记录该方向上得分最高的相应得分棋型。同时这里还增加了部分特判规则,当待查找的点落入棋盘外时,会调整直接进入下一次循环,避免无效查询。
# 一个方向上的分值计算
def cal_score(m, n, x_direct, y_direct, enemy_list, my_list, score_all_arr):
add_score = 0 # 加分项
# 在一个方向上, 只取最大的得分项
max_score_shape = (0, None)
# 如果此方向上,该点已经有得分形状,不重复计算
for item in score_all_arr:
for pt in item[1]:
if m == pt[0] and n == pt[1] and x_direct == item[2][0] and y_direct == item[2][1]:
return 0
# 在落子点 左右方向上循环查找得分形状
for offset in range(-5, 1):
# offset = -2
pos = []
found_valid_pos = False # 布尔变量用于记录是否找到有效位置
for i in range(0, 6):
next_pos = (m + (i + offset) * x_direct, n + (i + offset) * y_direct)
if not (0 <= next_pos[0] <= COLUMN and 0 <= next_pos[1] <= ROW) and i != 5:
found_valid_pos = True # 如果存在不满足条件的情况,设置布尔变量为 True
break
if next_pos in my_list:
pos.append(1)
elif next_pos in enemy_list:
pos.append(2)
else:
pos.append(0)
if found_valid_pos: # 检查布尔变量是否为真
continue # 如果找到无效位置,跳出内层循环
tmp_shap5 = (pos[0], pos[1], pos[2], pos[3], pos[4])
tmp_shap6 = (pos[0], pos[1], pos[2], pos[3], pos[4], pos[5])
for (score, shape) in shape_score:
if tmp_shap5 == shape or tmp_shap6 == shape:
if tmp_shap5 == (1, 1, 1, 1, 1):
print('到达赛点咯!')
if score > max_score_shape[0]: # 棋型记录
max_score_shape = (score, ((m + (0 + offset) * x_direct, n + (0 + offset) * y_direct),
(m + (1 + offset) * x_direct, n + (1 + offset) * y_direct),
(m + (2 + offset) * x_direct, n + (2 + offset) * y_direct),
(m + (3 + offset) * x_direct, n + (3 + offset) * y_direct),
(m + (4 + offset) * x_direct, n + (4 + offset) * y_direct)),
(x_direct, y_direct))
# 计算两个形状相交, 如两个3活 相交, 得分增加 一个子的除外(该代码为原作者代码,此处暂做保留,但码者并未详看,所以暂不做注解)
if max_score_shape[1] is not None:
for item in score_all_arr:
for pt1 in item[1]:
for pt2 in max_score_shape[1]:
if pt1 == pt2 and max_score_shape[0] > 10 and item[0] > 10:
add_score += item[0] + max_score_shape[0]
score_all_arr.append(max_score_shape)
return add_score + max_score_shape[0]
2.2.3 难度设置
通过难度设置,可以动态的调整A*算法的搜索深度,以达到更加的搜索结果。
这里通过添加了三个按钮,监听点击事件,当相应的点击到了按钮所在区域后,执行相应逻辑代码,否则保持监听
def set_difficulty(win):
global DEPTH # 搜索深度
button_width = 80
button_height = 20
button_spacing = 100
button_y = win.getHeight() / 2 - button_height / 2
buttons = []
button_labels = ["简单", "中等", "高级"]
depths = [1, (ROW + 1) * (COLUMN + 1) * 0.3, (ROW + 1) * (COLUMN + 1)]
button_x1 = (win.getWidth() - 3 * button_spacing) / 2
for label, depth in zip(button_labels, depths): # 显示按钮
button_x2 = button_x1 + button_width
button = Rectangle(Point(button_x1, button_y), Point(button_x2, button_y + button_height))
button.setFill('light gray')
button_text = Text(Point((button_x1 + button_x2) / 2, button_y + button_height / 2), label)
button.draw(win)
button_text.draw(win)
buttons.append((button, button_text, depth))
button_x1 += button_spacing
clicked = False
while not clicked:
click_point = win.getMouse()
x = click_point.getX()
y = click_point.getY()
for button, _, depth in buttons: # 遍历所有难度按钮
button_x1, button_x2 = button.getP1().getX(), button.getP2().getX()
button_y1, button_y2 = button.getP1().getY(), button.getP2().getY()
if button_x1 < x < button_x2 and button_y1 < y < button_y2: # 判断是否点击的当前按钮
DEPTH = depth
clicked = True
break
if 210 <= x <= 290 and 10 <= y <= EXTRA_HEIGHT - 10: # 玩家点击了退出按钮
win.close()
return True
for button, button_text, _ in buttons:
button.undraw() # 删除按钮
button_text.undraw() # 删除按钮文本
return False
2.2.4 重置游戏
重置游戏的逻辑就是清空所有数据,重新初始化相关图形化界面。
def reset_game(win):
# 清空棋盘列表和图形
list1.clear()
list2.clear()
list3.clear()
for item in win.items[:]:
item.undraw()
# 重新绘制额外部分
extra_part = Rectangle(Point(0, 0), Point(COLUMN * GRID_WIDTH, EXTRA_HEIGHT))
extra_part.setFill('light blue')
extra_part.draw(win)
# 重新绘制按钮
reset_button = Rectangle(Point(10, 10), Point(90, EXTRA_HEIGHT - 10))
reset_button.setFill('light gray')
reset_button.draw(win)
reset_text = Text(Point(50, EXTRA_HEIGHT / 2), "重置游戏")
reset_text.draw(win)
undo_button = Rectangle(Point(110, 10), Point(190, EXTRA_HEIGHT - 10))
undo_button.setFill('light gray')
undo_button.draw(win)
undo_text = Text(Point(150, EXTRA_HEIGHT / 2), "悔棋")
undo_text.draw(win)
quit_button = Rectangle(Point(210, 10), Point(290, EXTRA_HEIGHT - 10))
quit_button.setFill('light gray')
quit_button.draw(win)
quit_text = Text(Point(250, EXTRA_HEIGHT / 2), "退出游戏")
quit_text.draw(win)
# 重新绘制棋盘的水平线条
for j in range(ROW + 1):
line_horizontal = Line(Point(0, j * GRID_WIDTH + EXTRA_HEIGHT),
Point(COLUMN * GRID_WIDTH, j * GRID_WIDTH + EXTRA_HEIGHT))
line_horizontal.draw(win)
# 重新绘制棋盘的垂直线条
for i in range(COLUMN + 1):
line_vertical = Line(Point(i * GRID_WIDTH, EXTRA_HEIGHT),
Point(i * GRID_WIDTH, ROW * GRID_WIDTH + EXTRA_HEIGHT))
line_vertical.draw(win)
return set_difficulty(win)
2.2.5 悔棋
悔棋通过动态的删除AI和人类相关list最顶上的元素,从而实现悔棋的效果。
def undo_move(win):
global move_hint
global player_wins
# 移除当前的红色圆圈(如果存在)
if move_hint:
move_hint.undraw()
if list1 and not player_wins:
last_ai_move = list1.pop()
list3.remove(last_ai_move)
x, y = last_ai_move
for item in win.items[:]:
if isinstance(item, Circle):
if item.getCenter().getX() == x * GRID_WIDTH and item.getCenter().getY() == y * GRID_WIDTH + EXTRA_HEIGHT:
item.undraw()
break
if list2:
last_human_move = list2.pop()
list3.remove(last_human_move)
x, y = last_human_move
for item in win.items[:]:
if isinstance(item, Circle):
if item.getCenter().getX() == x * GRID_WIDTH and item.getCenter().getY() == y * GRID_WIDTH + EXTRA_HEIGHT:
item.undraw()
break
# 如果还有AI的落子记录,更新红色圆圈的位置
if list1:
last_ai_move = list1[-1]
x, y = last_ai_move
move_hint = Circle(Point(GRID_WIDTH * x, GRID_WIDTH * y + EXTRA_HEIGHT), 16)
move_hint.setOutline('red')
move_hint.setWidth(3)
move_hint.draw(win)
player_wins = False
2.2.6 落子提示
落子提示通过记录一个全局变量,动态记录当前需要进行提示的棋子,主要的提示显示与提示撤销逻辑在主函数中。但是需要注意,在悔棋的函数中也需要动态的对该全局变量进行修改。
# 移除上一个玩家的落子提示圆圈(如果有的话)
if move_hint:
move_hint.undraw()
# 创建新的落子并设置为落子提示
piece = Circle(Point(GRID_WIDTH * pos[0], GRID_WIDTH * pos[1] + EXTRA_HEIGHT), 16)
piece.setFill('white')
piece.draw(win)
move_hint = Circle(Point(GRID_WIDTH * pos[0], GRID_WIDTH * pos[1] + EXTRA_HEIGHT), 16) # 创建落子提示圆圈
move_hint.setOutline('red') # 设置提示圆圈颜色为红色
move_hint.setWidth(3) # 设置提示圆圈的线宽
move_hint.draw(win) # 绘制落子提示圆圈
def undo_move(win):
global move_hint
global player_wins
# 移除当前的红色圆圈(如果存在)
if move_hint:
move_hint.undraw()
# 如果还有AI的落子记录,更新红色圆圈的位置
if list1:
last_ai_move = list1[-1]
x, y = last_ai_move
move_hint = Circle(Point(GRID_WIDTH * x, GRID_WIDTH * y + EXTRA_HEIGHT), 16)
move_hint.setOutline('red')
move_hint.setWidth(3)
move_hint.draw(win)
2.3 总体流程
首先创建一个游戏对象,该对象用于后续的相关函数传参,然后进行相应变量的初始化。随后进入main中的主要循环,该循环使用变量change来记录当前应该哪一方进行落子,在相应的落子逻辑中会先进行游戏胜利的判断:若游戏胜利则弹出弹框,反之进行落子显示。其中还包含了不少的逻辑分支,在此不进行一一列举,详见注解。
def main():
win = gomokuwin() # 游戏对象
for i in range(COLUMN + 1):
for j in range(ROW + 1):
list_all.append((i, j)) # list_all表示所有可进行落子的点
if set_difficulty(win): # 初始时先进行难度设置,返回值为真时表示点击了退出游戏
return
change = 0 # 表示当前的落子方
global move_hint # 落子提示
while 1:
if change % 2 == 1:
# 如果玩家或AI已经获胜,则跳过当前回合
if game_win(list1) or game_win(list2):
change += 1
continue
# 调用AI算法找到下一步落子位置
pos = a_star_search()
# 如果落子位置为 None,表示没有可落子的位置,游戏平局(该分支未测试)
if pos is None:
messagebox.showinfo("游戏结束", "平局!")
change += 1
break
# 移除上一个玩家的落子提示圆圈(如果存在的话)
if move_hint:
move_hint.undraw()
# 将AI的落子位置加入列表中
list1.append(pos)
list3.append(pos)
# 创建新的落子并设置为落子提示
piece = Circle(Point(GRID_WIDTH * pos[0], GRID_WIDTH * pos[1] + EXTRA_HEIGHT), 16)
piece.setFill('white')
piece.draw(win)
move_hint = Circle(Point(GRID_WIDTH * pos[0], GRID_WIDTH * pos[1] + EXTRA_HEIGHT), 16) # 创建落子提示圆圈
move_hint.setOutline('red') # 设置提示圆圈颜色为红色
move_hint.setWidth(3) # 设置提示圆圈的线宽
move_hint.draw(win) # 绘制落子提示圆圈
# 如果AI获胜,则显示游戏结束信息
if game_win(list1):
messagebox.showinfo("游戏结束", "你输了!")
change += 1
else:
click_point = win.getMouse() # 获得当前鼠标点击的点坐标
x = click_point.getX()
y = click_point.getY()
# 检查点击位置是否在按钮区域内
if 10 <= x <= 90 and 10 <= y <= EXTRA_HEIGHT - 10:
# 重置游戏
if reset_game(win):
return
continue
elif 110 <= x <= 190 and 10 <= y <= EXTRA_HEIGHT - 10:
# 悔棋
undo_move(win)
continue
elif 210 <= x <= 290 and 10 <= y <= EXTRA_HEIGHT - 10:
# 退出游戏
win.close()
return
# 如果点击事件在棋盘区域内且位置合法(落子点未存在棋子)
elif y > EXTRA_HEIGHT and not (
(round(x / GRID_WIDTH), round((y - EXTRA_HEIGHT) / GRID_WIDTH)) in list3) and not game_win(
list1) and not game_win(list2):
# 记录棋子
a2 = round(x / GRID_WIDTH)
b2 = round((y - EXTRA_HEIGHT) / GRID_WIDTH)
list2.append((a2, b2))
list3.append((a2, b2))
# 移除上一个玩家的落子提示圆圈(如果有的话)
if move_hint:
move_hint.undraw()
# # 创建新的落子并设置为落子提示
piece = Circle(Point(GRID_WIDTH * a2, GRID_WIDTH * b2 + EXTRA_HEIGHT), 16)
piece.setFill('black')
piece.draw(win)
move_hint = Circle(Point(GRID_WIDTH * a2, GRID_WIDTH * b2 + EXTRA_HEIGHT), 16) # 创建落子提示圆圈
move_hint.setOutline('red') # 设置提示圆圈颜色为红色
move_hint.setWidth(3) # 设置提示圆圈的线宽
move_hint.draw(win) # 绘制落子提示圆圈
# 如果玩家获胜,则显示游戏结束信息
if game_win(list2):
messagebox.showinfo("游戏结束", "你赢了!")
global player_wins
player_wins = True
change += 1
win.close()
2.4 效果实现
这里附上部分游戏运行截图:
开始游戏:
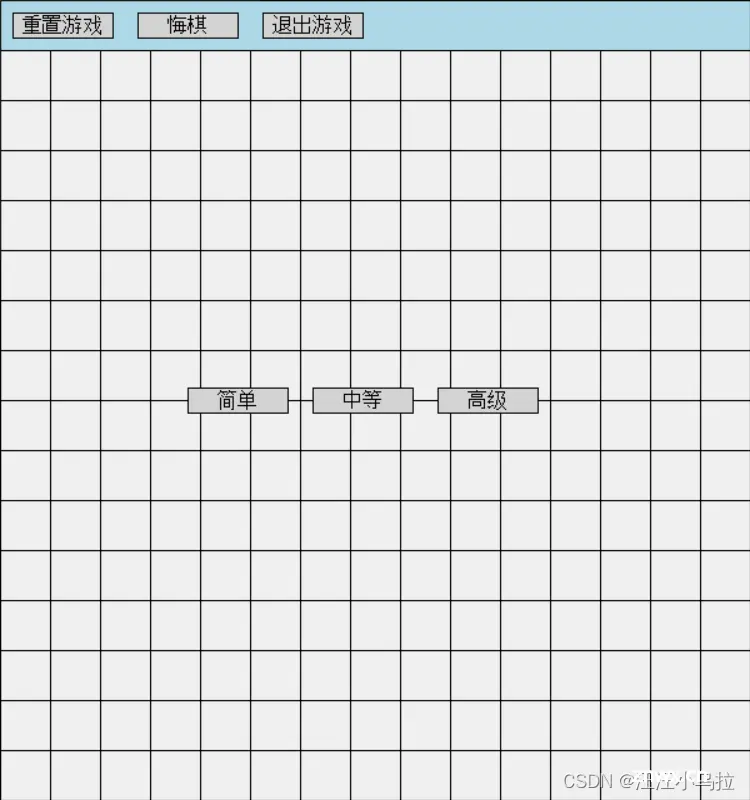
落子:
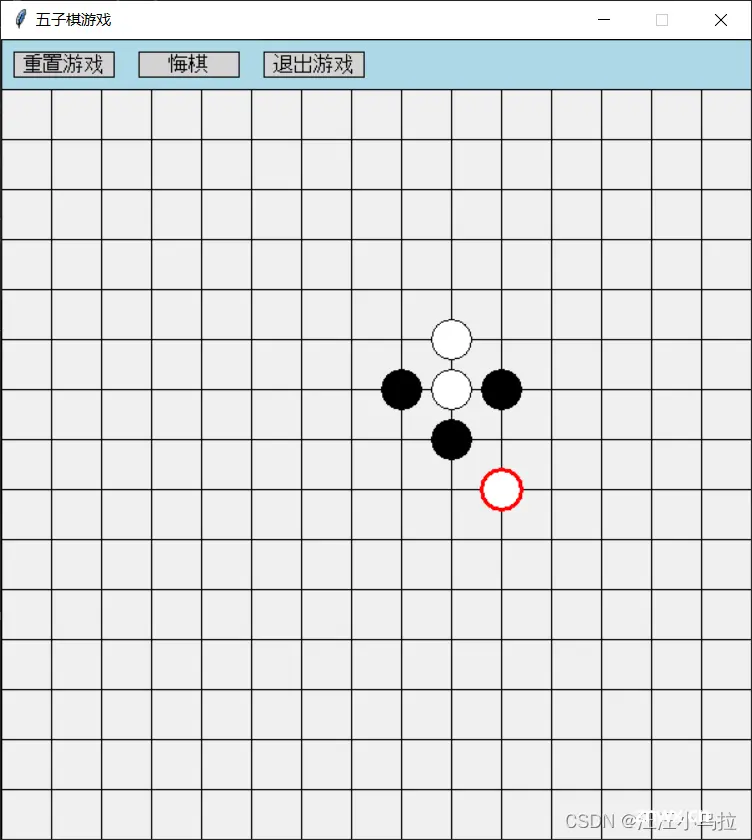
游戏结束:
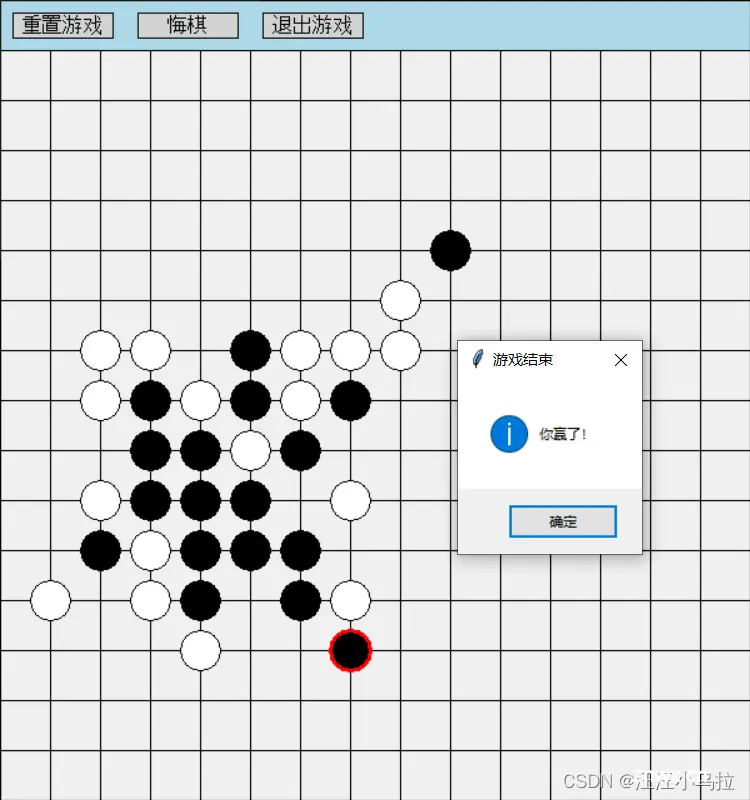
游戏结束后仅支持点击上方的三个按钮,直接关闭窗口会报错,因为没有按照正常流程进行操作,后台线程还在运行。游戏结束后还可以直接悔棋重寻神之一手。
三、源码链接
代码地址:人工智能课设——基于A*算法的五子棋博弈系统(Python实现) (gitee.com)
直接拉取下来大概率跑不了(环境问题),建议自己本地创建python环境,然后将两个主要的文件( gomoku.py、graphics.py)拷贝到自己的项目中运行
不熟悉gitee的可按如下操作:
点击链接进入gitee相关页面点击“克隆/下载”

点击下载ZIP
声明
本文内容仅代表作者观点,或转载于其他网站,本站不以此文作为商业用途
如有涉及侵权,请联系本站进行删除
转载本站原创文章,请注明来源及作者。